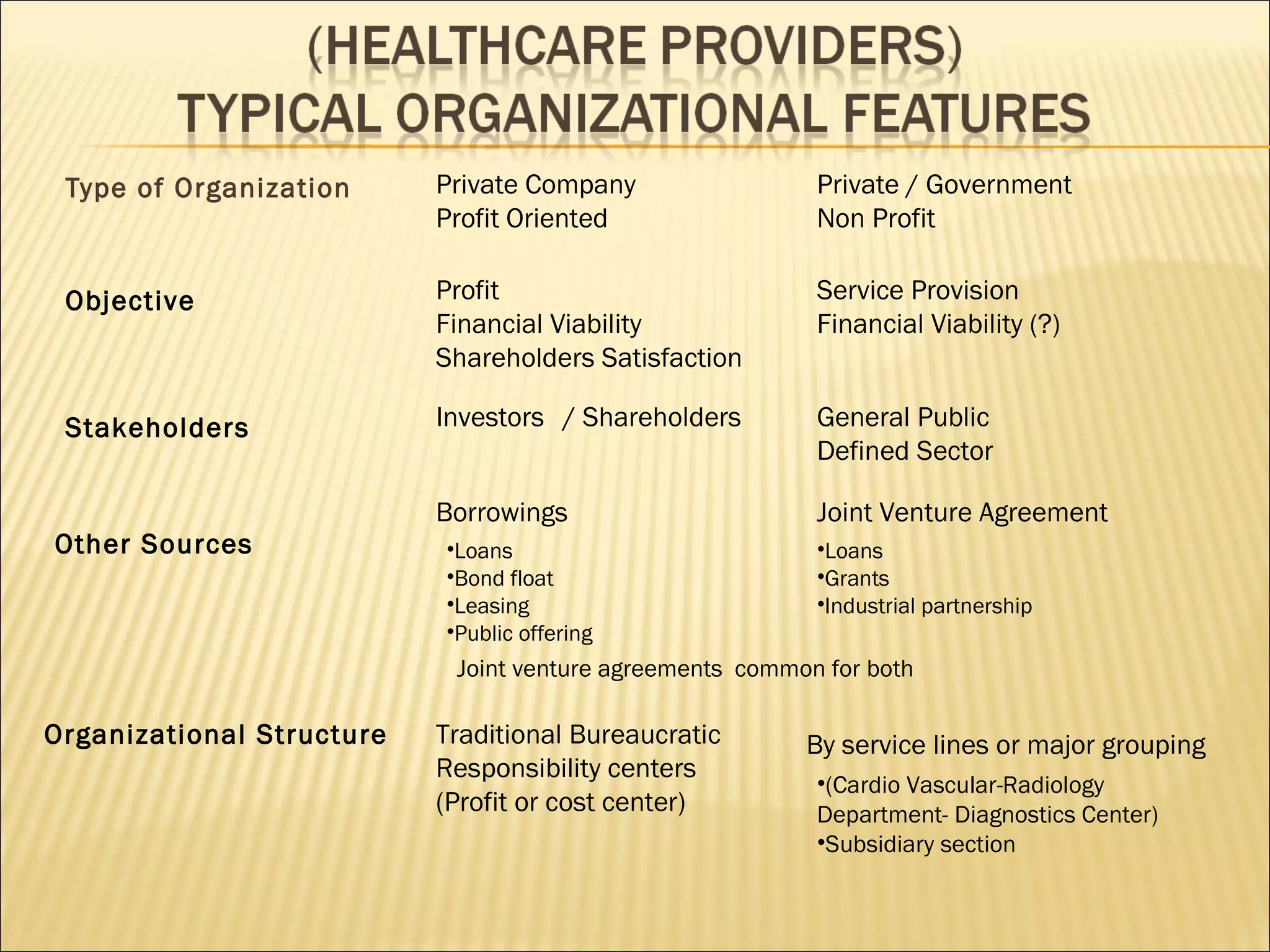
This document outlines the topics that will be covered in a financial management course for hospital executives. The course will cover fundamental financial management concepts like risks and rates of return, time value of money, and financial assets. It will also cover topics like capital budgeting, capital structure, working capital management, and financial planning. The document notes that financial management involves planning, directing, monitoring, organizing and controlling an organization's monetary resources. It aims to help organizations achieve financial objectives like profitability, risk control, and meeting stakeholder expectations.