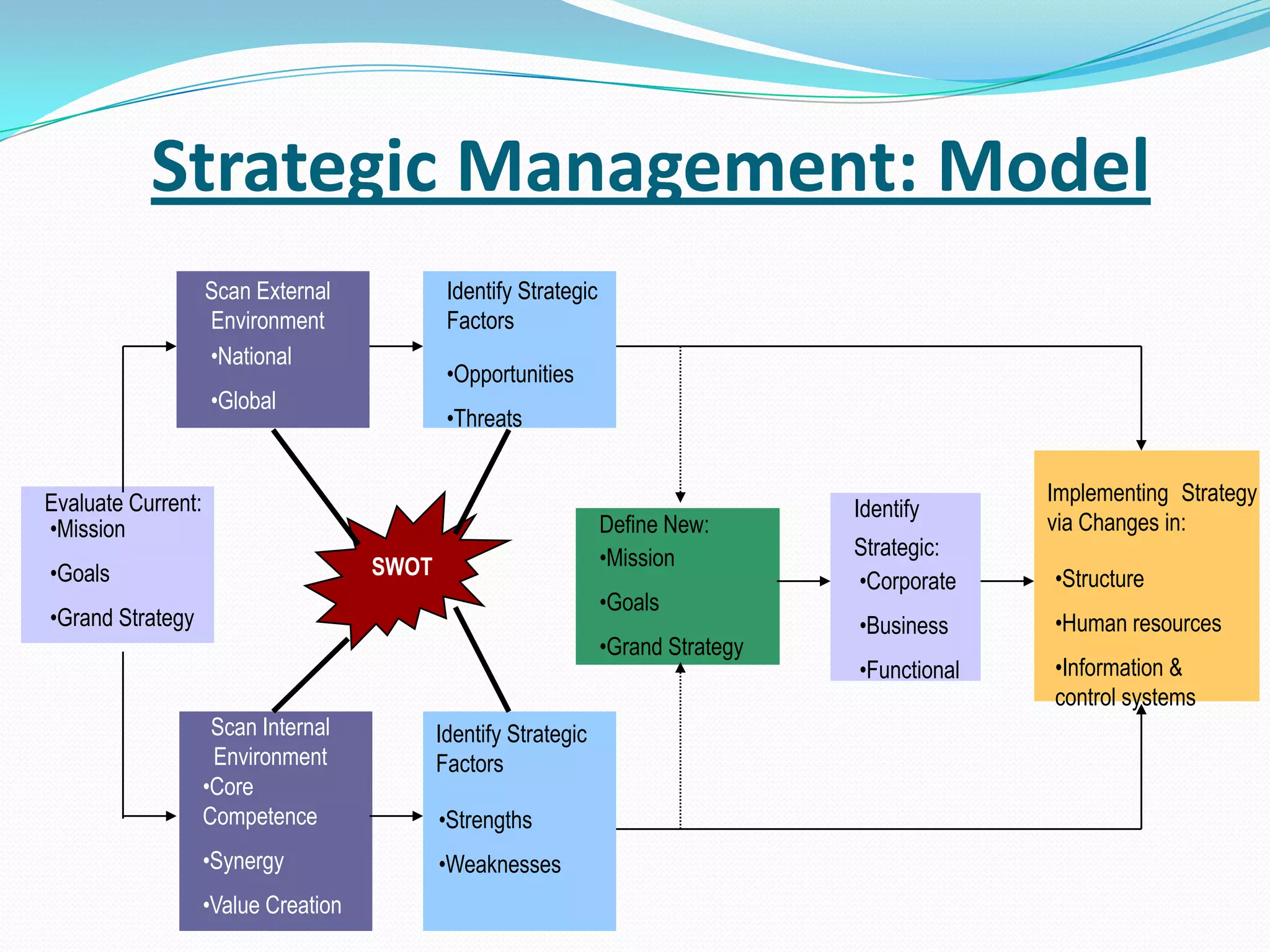
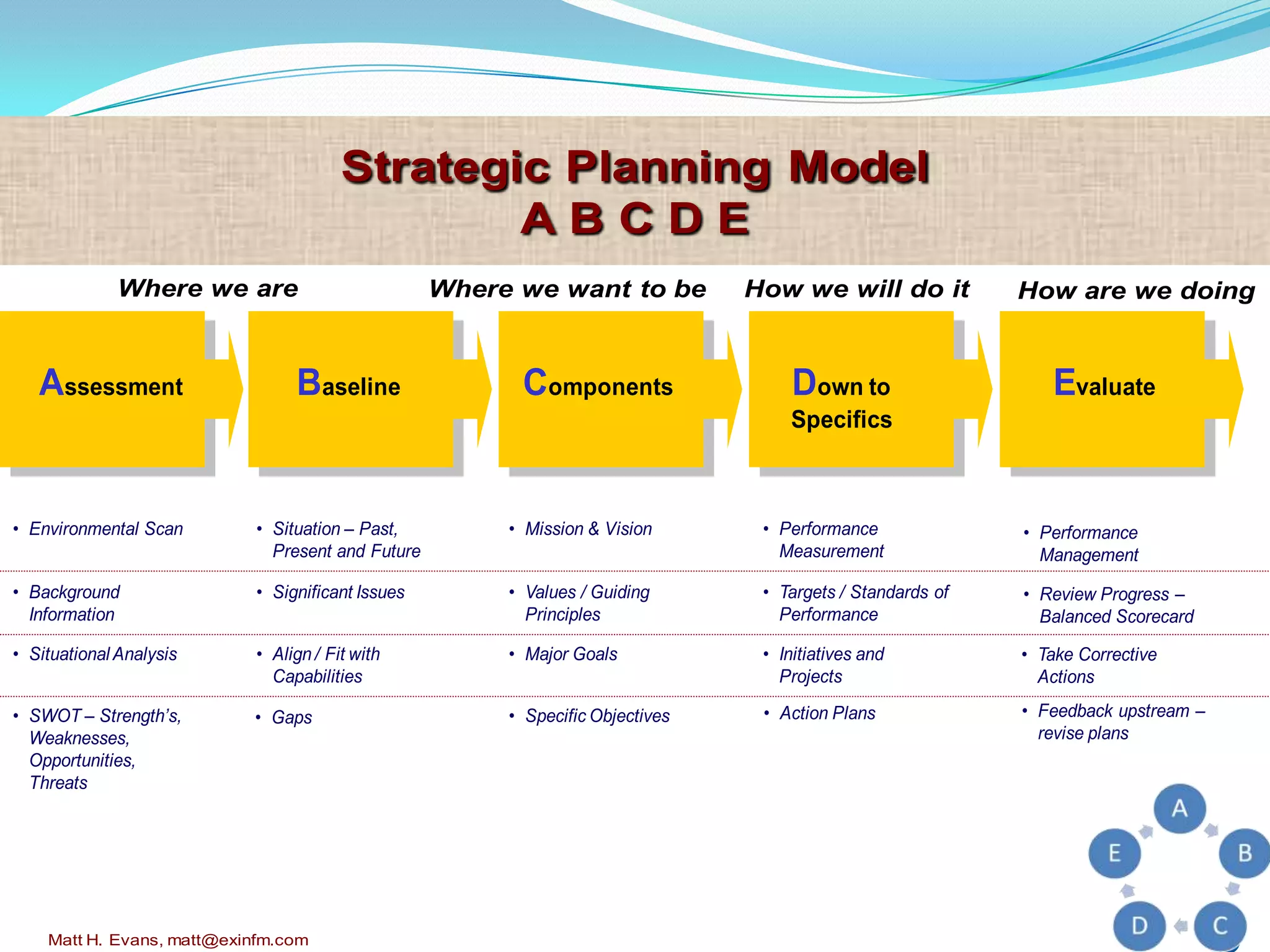
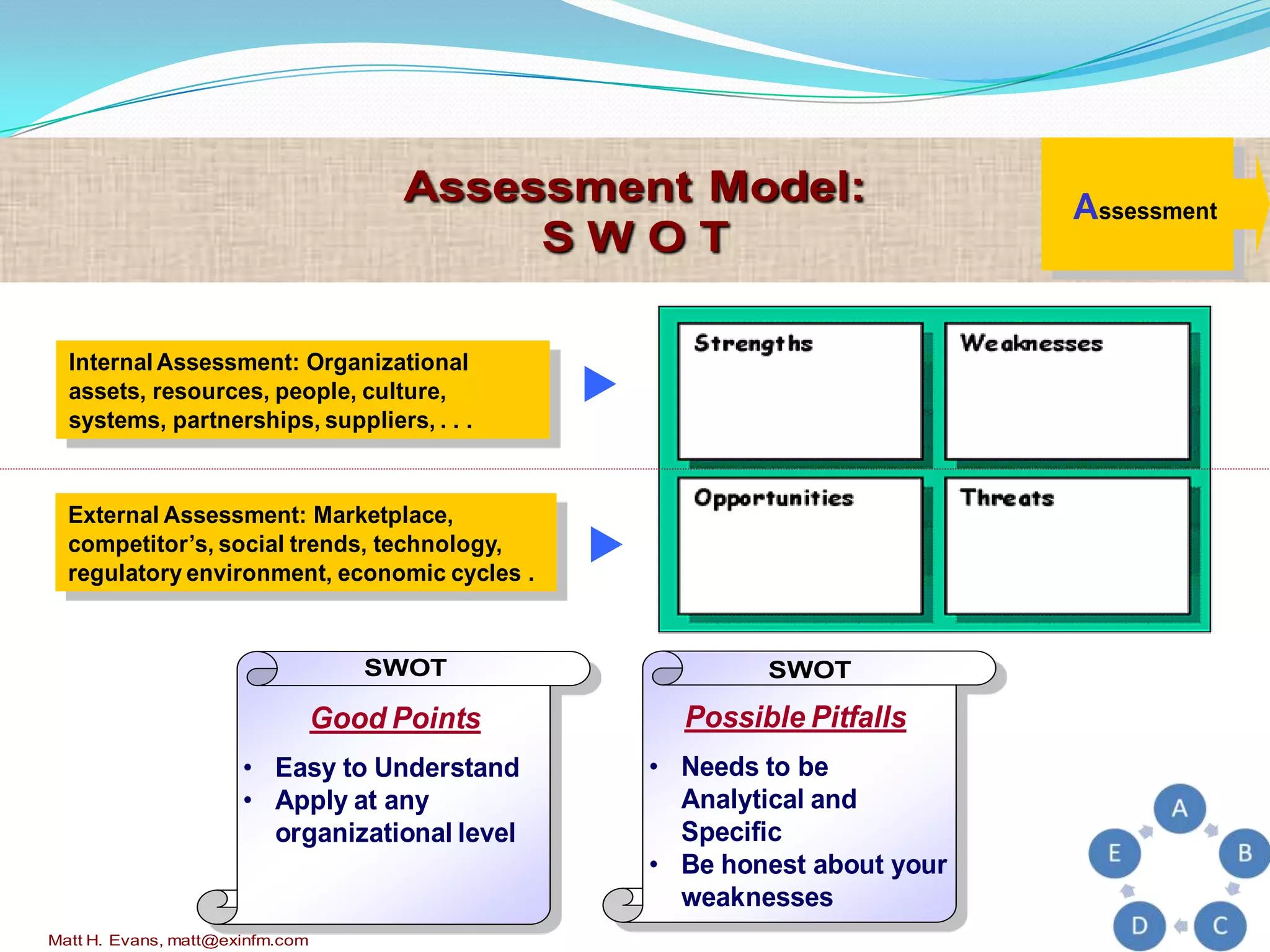
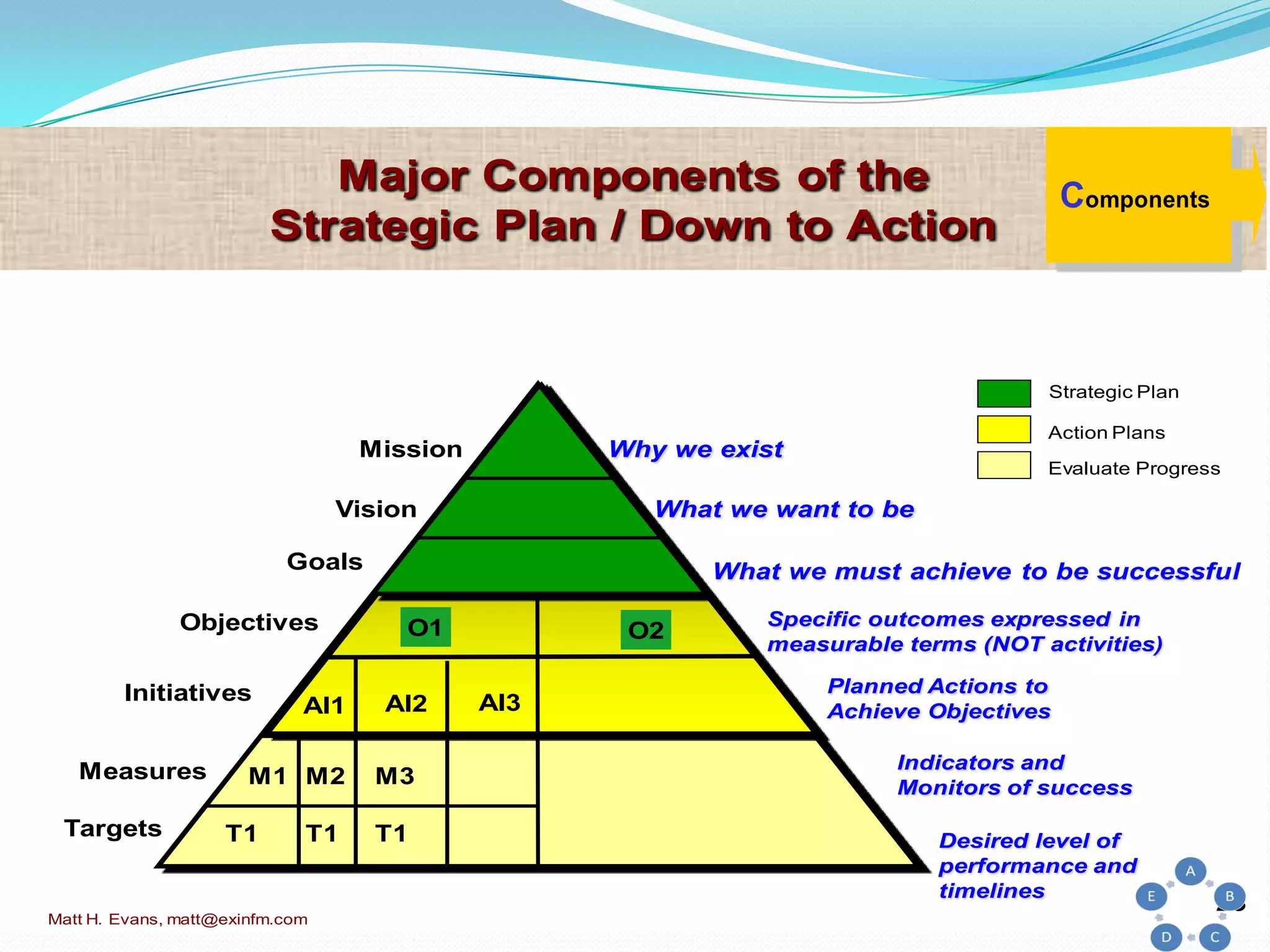
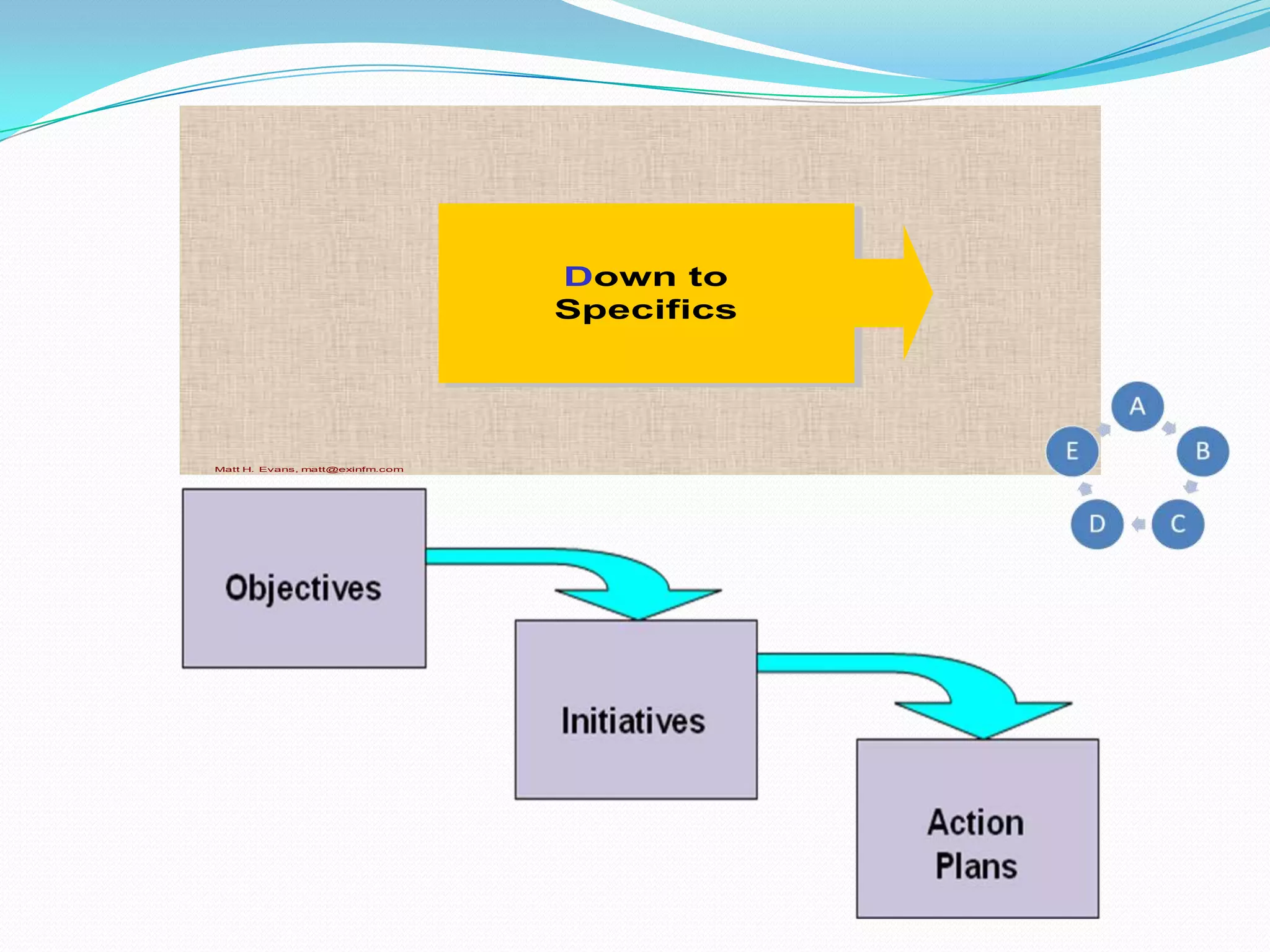
The document discusses strategic planning for medical practices. It defines strategic planning as a formal process that helps organizations maintain optimal alignment with their environment through goal setting and performance measurement. The strategic planning process involves conducting an environmental scan, developing a mission and vision, setting goals and objectives, creating action plans, and evaluating performance. It provides frameworks for conducting a SWOT analysis and developing a strategic plan with all necessary components.