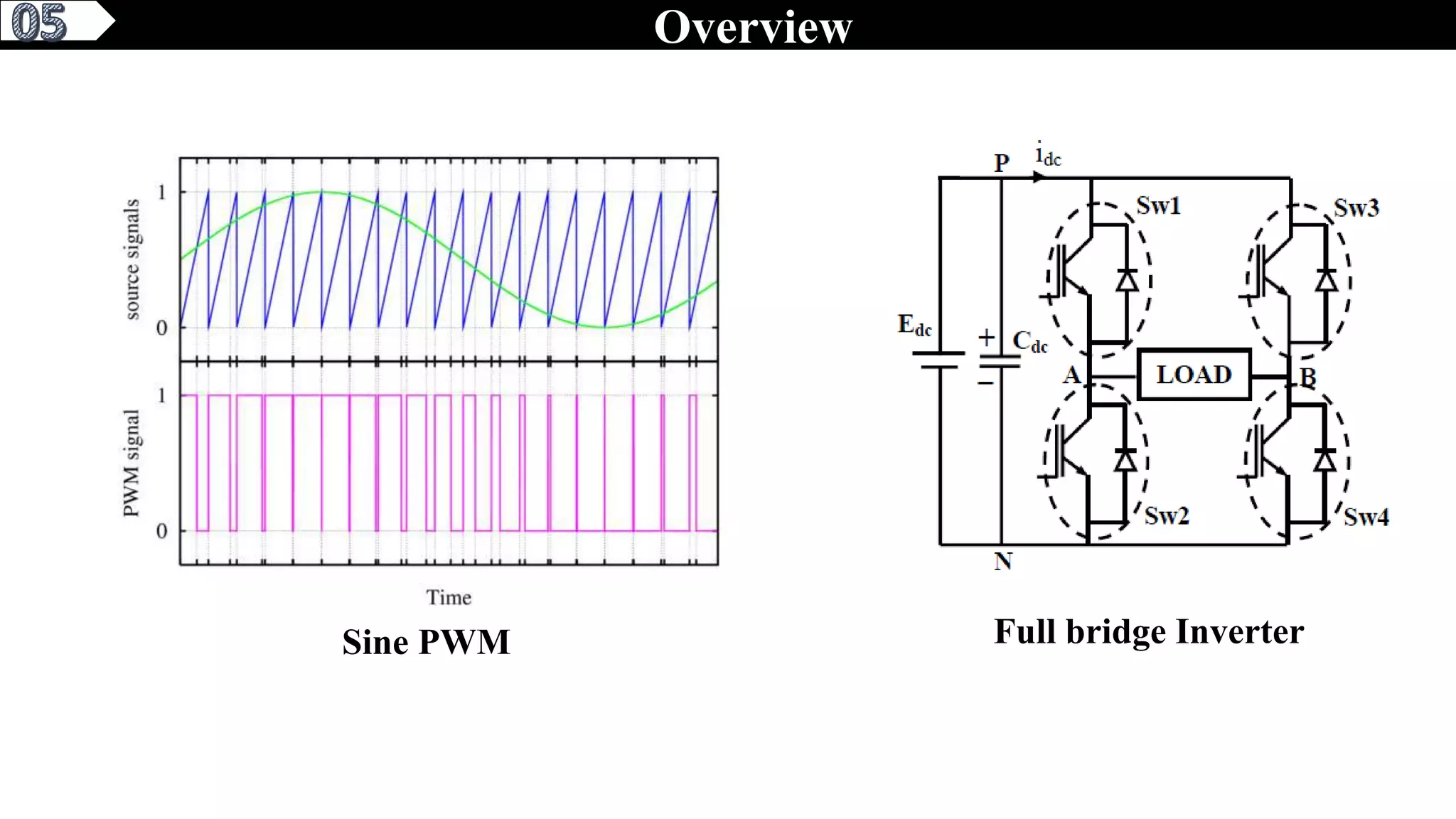
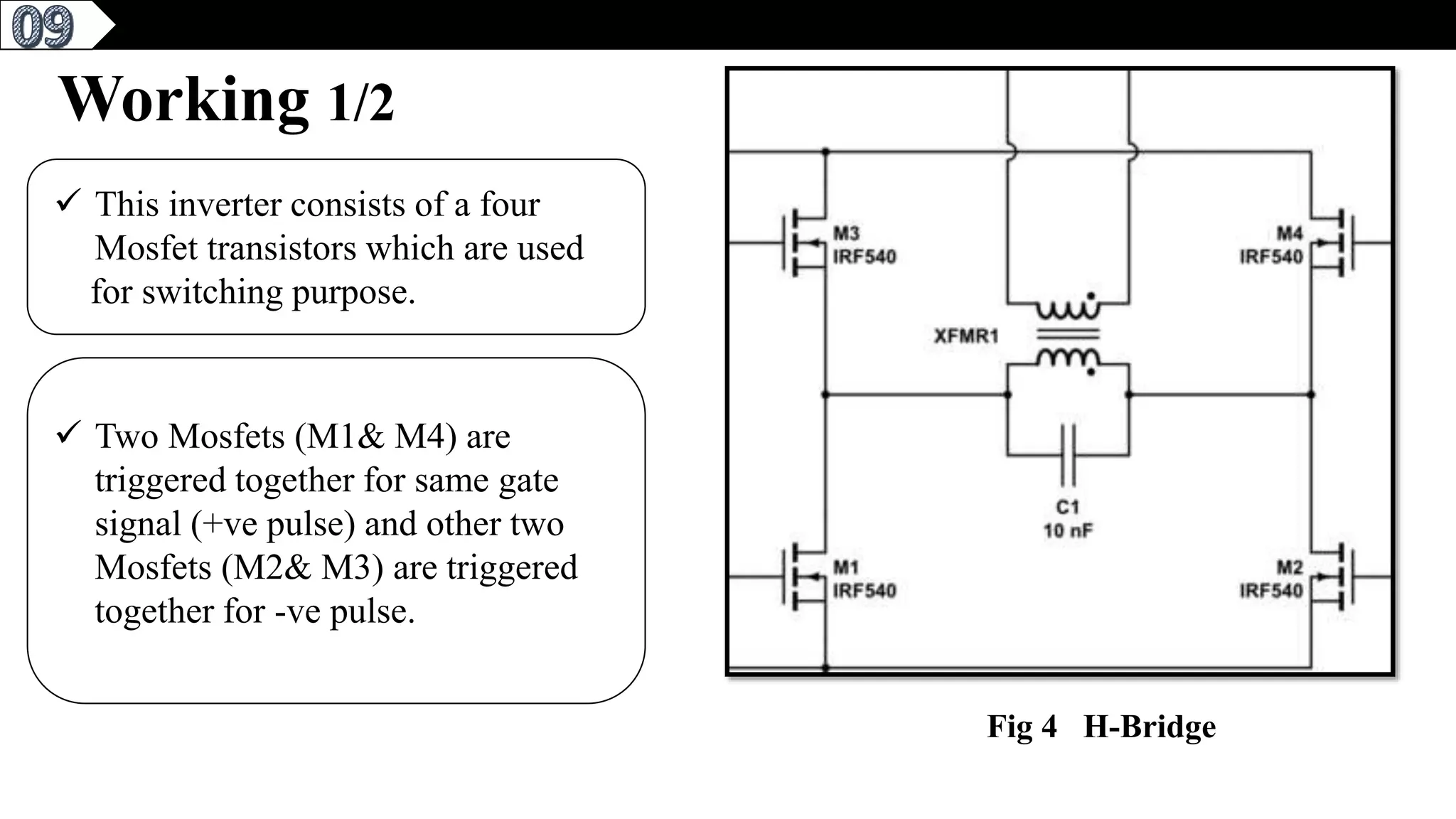
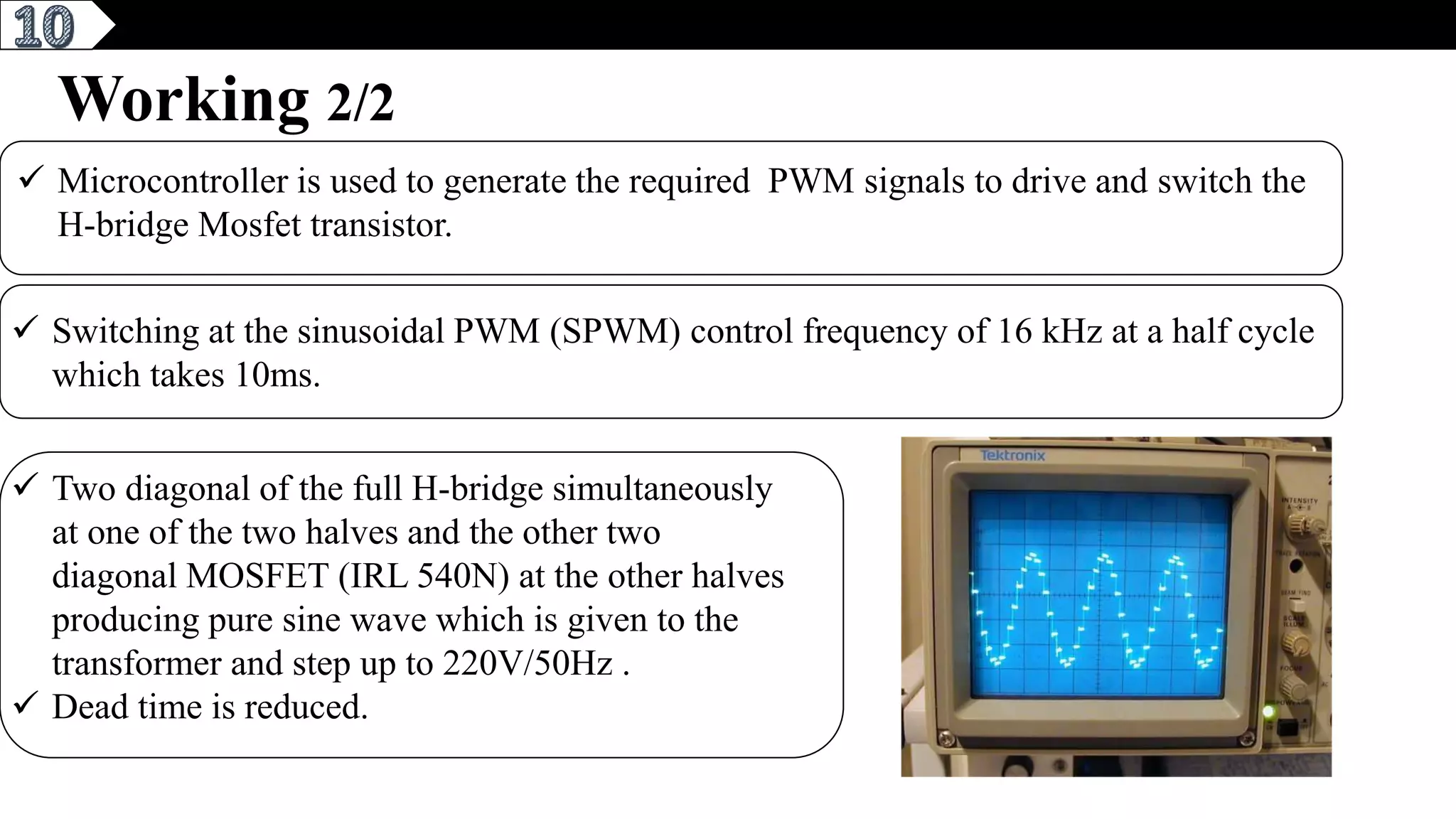
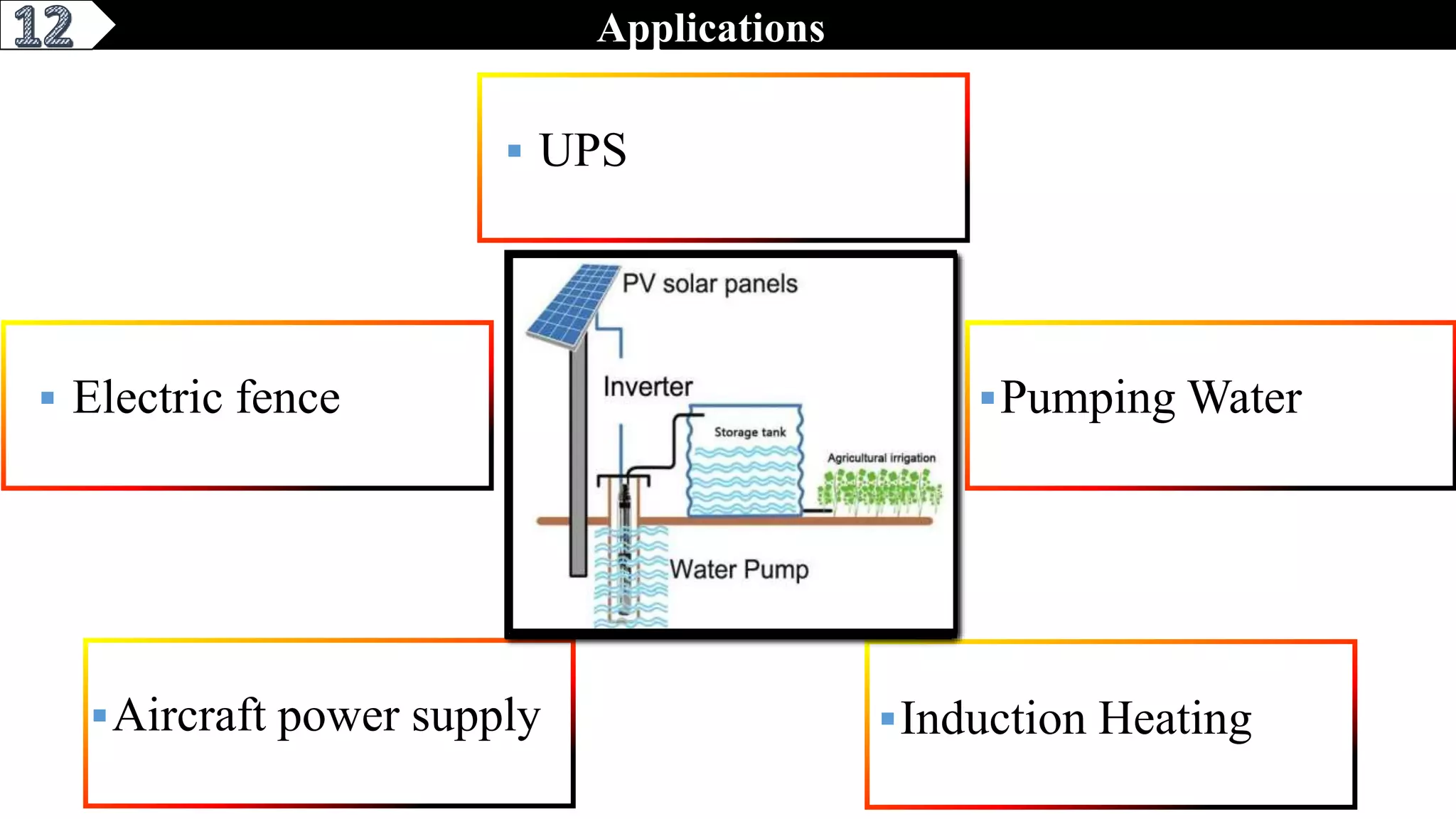
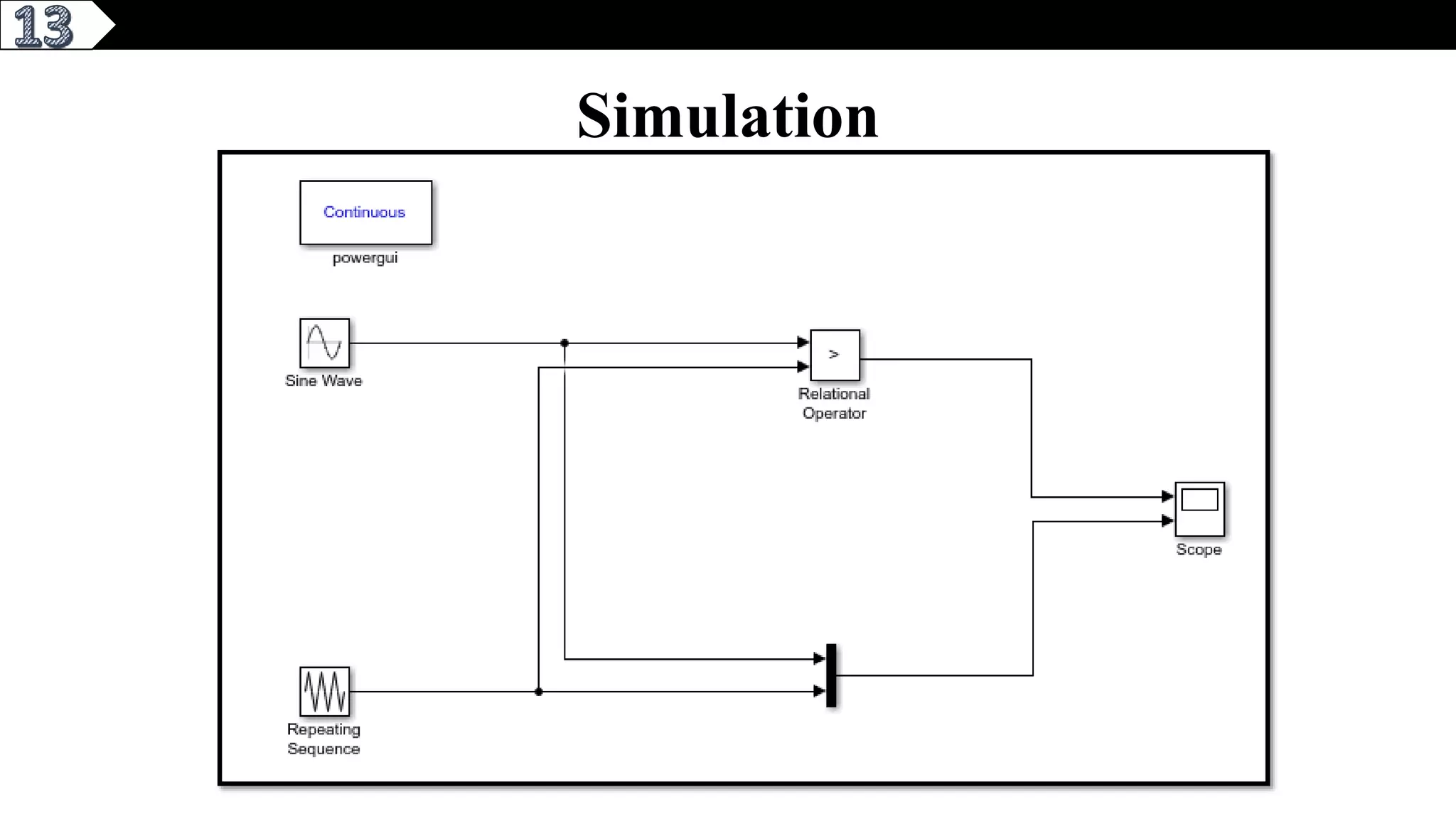
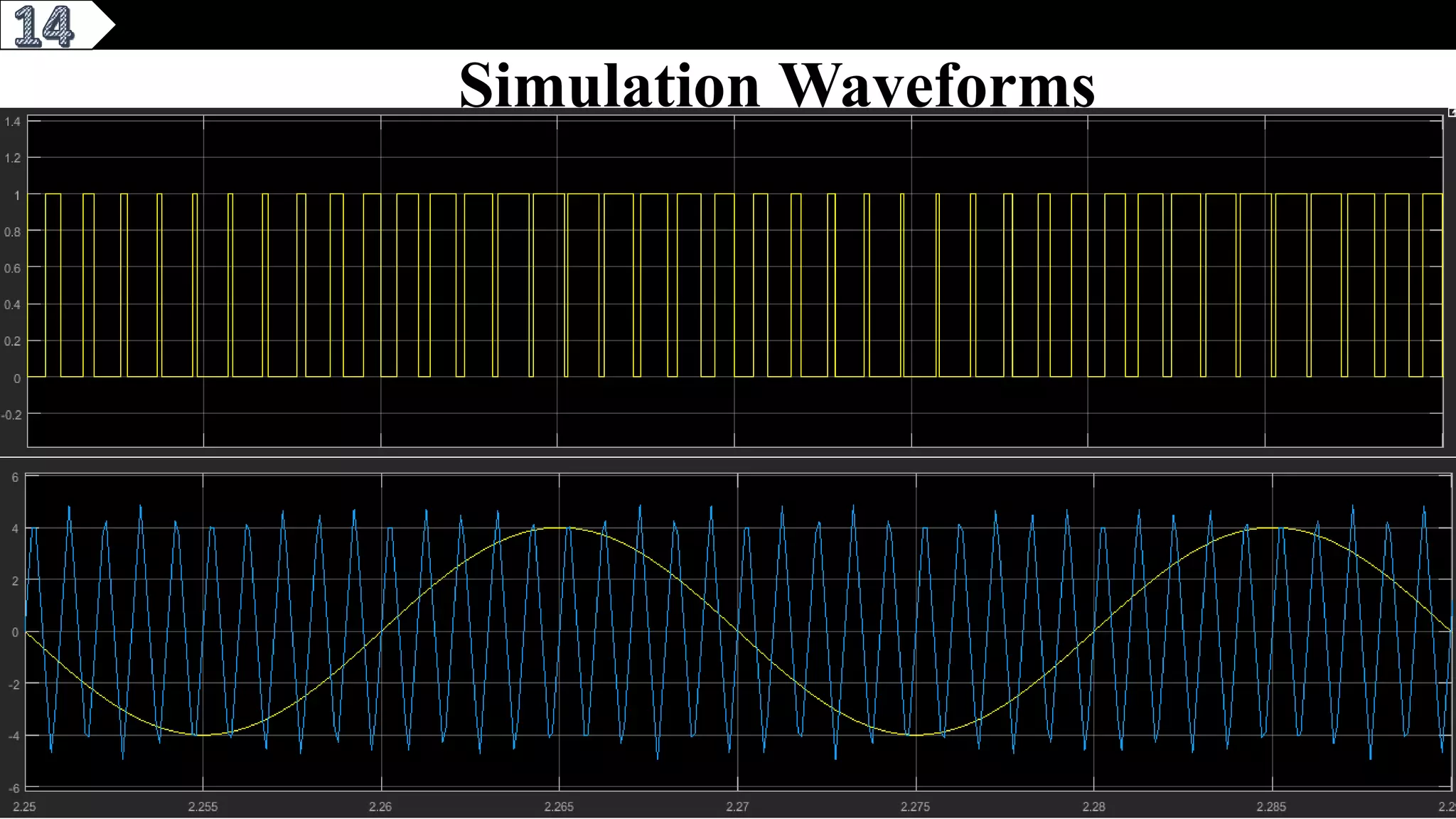
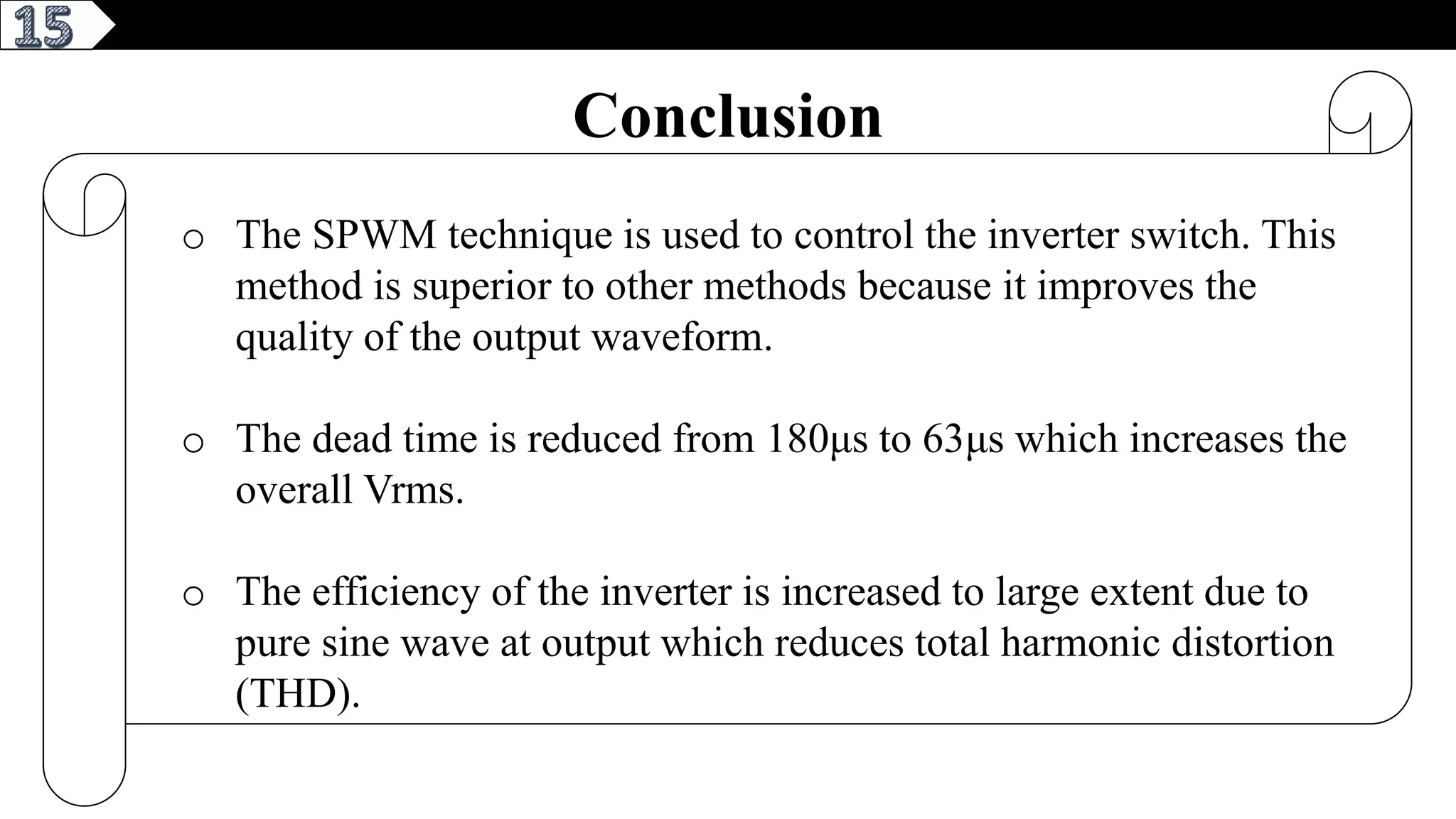
This document describes a pure sine wave single phase inverter. It uses SPWM (sine pulse width modulation) switching technique to convert DC to AC and produce a pure sine wave output. The inverter consists of an H-bridge of MOSFET transistors controlled by a microcontroller to generate PWM signals. It provides advantages like reducing harmonics, increasing efficiency, and producing a pure sinusoidal waveform compared to a square wave inverter. Applications include electric fences, aircraft power supplies, UPS systems, and induction heating.