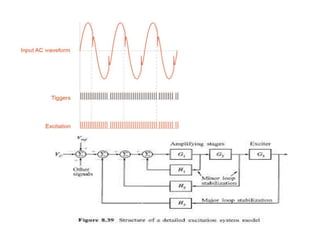
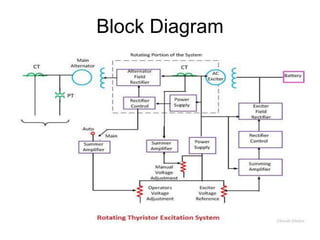
This document discusses power system modeling and excitation systems for alternators, detailing their function, types, and characteristics. It explains the process of strengthening the magnetic field of alternators through direct current supplied by exciters and compares various excitation systems, including DC and AC types. The conclusion highlights that the choice of excitation system is influenced by factors such as power, size, speed, and maintenance costs.