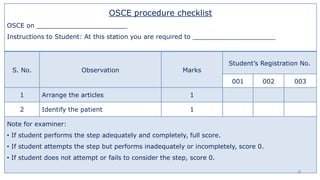
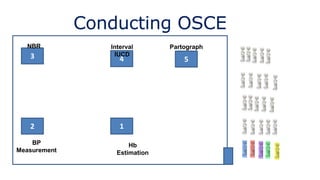
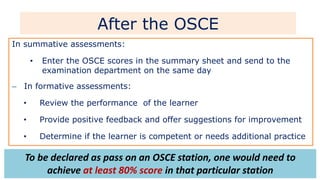
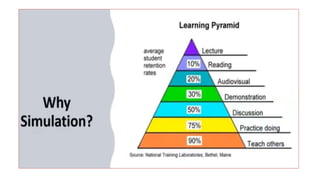
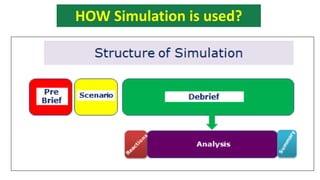
The document discusses the structure and evaluation processes of Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs) and Structured Bedside Examinations (SBE), highlighting their role in assessing clinical skills and competencies. It outlines the necessary components for OSCE preparation, including assessment tools and checklist usage to ensure consistent evaluation. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of simulation in medical education, including strategies for effective teaching and the necessity of reflective practices post-simulation.