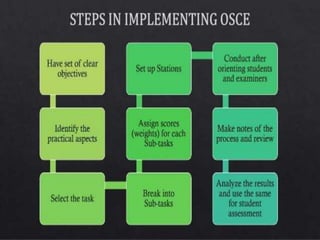
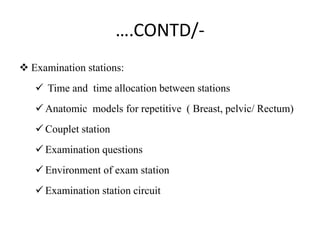
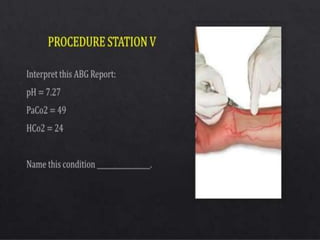
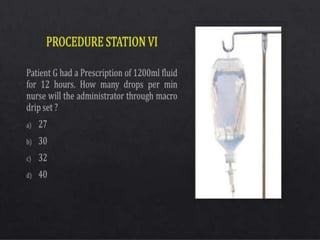
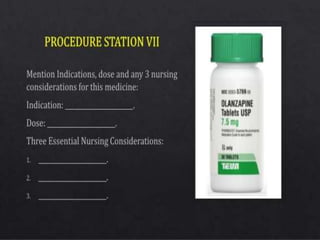
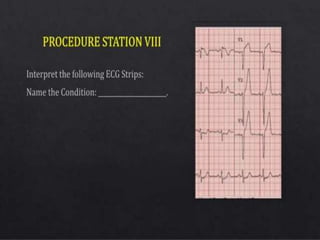
The document presents an overview of the Objective Structured Clinical Examination (OSCE), highlighting its role in assessing clinical skills in health sciences like nursing and medicine. Developed in the 1970s, OSCE evaluates candidates through a series of structured stations where they interact with standardized patients and perform clinical tasks. It emphasizes objective assessment, though it faces challenges such as time constraints and a need for trained observers, while offering advantages like increased reliability and a broader assessment of skills.