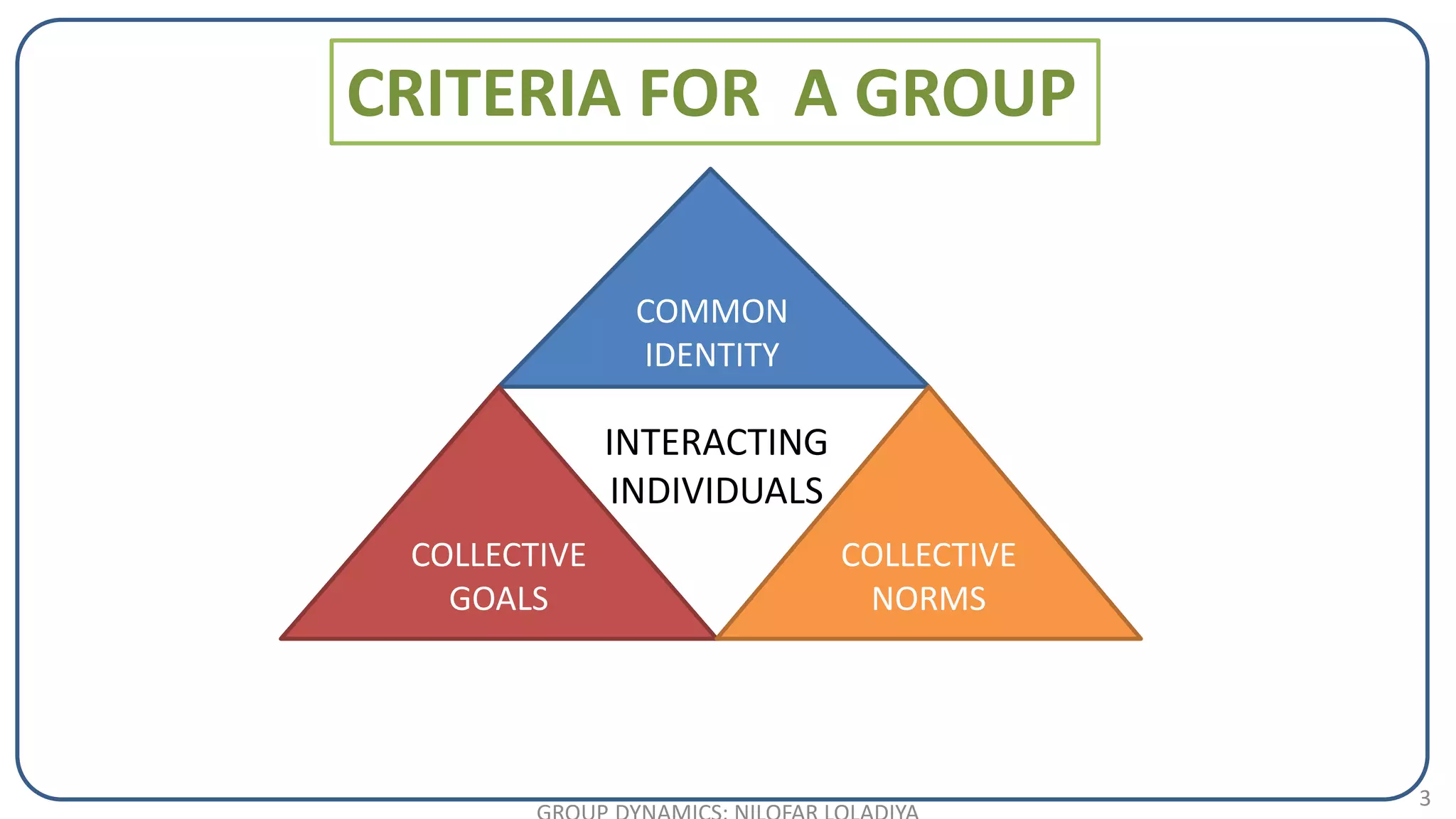
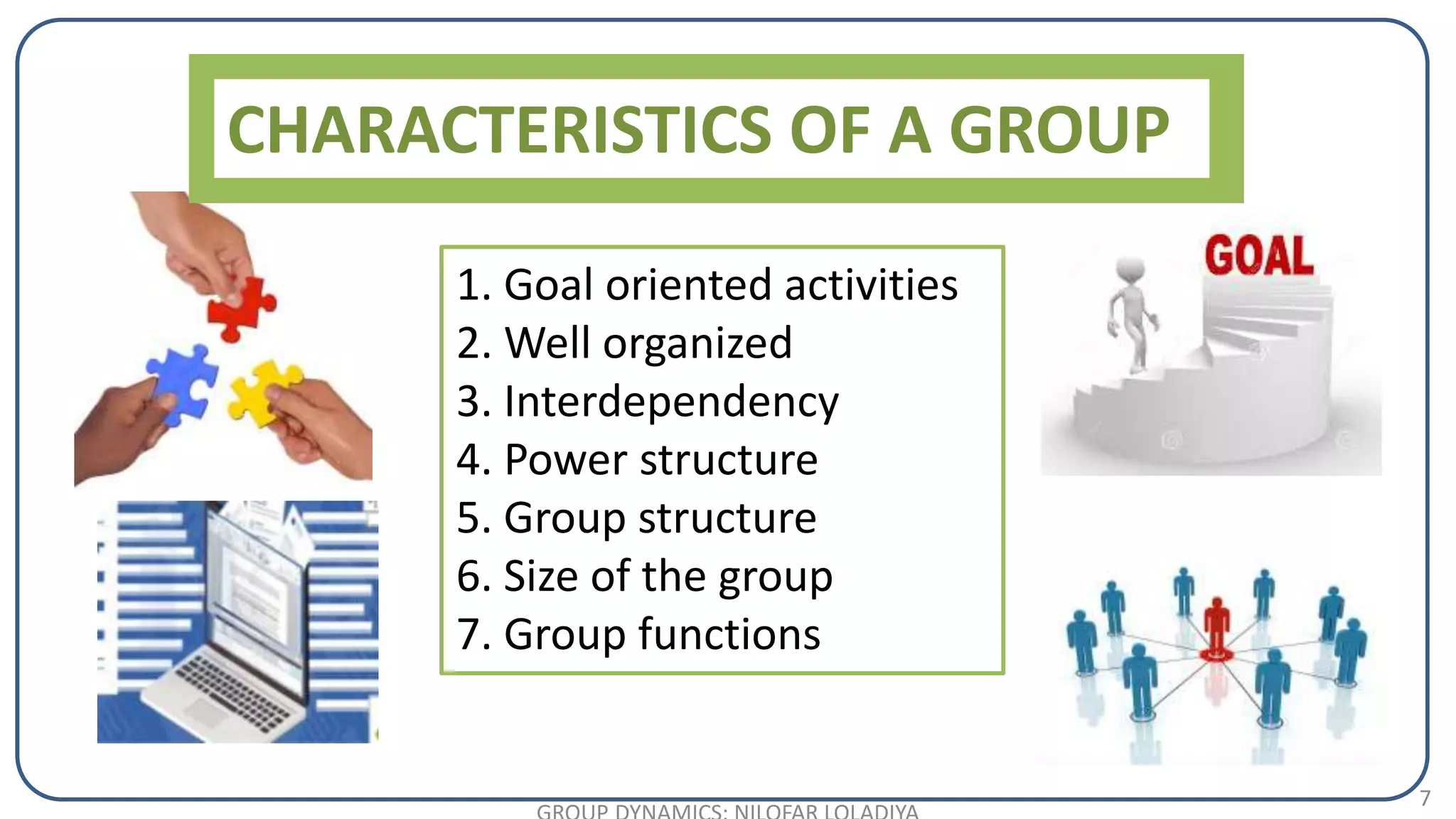
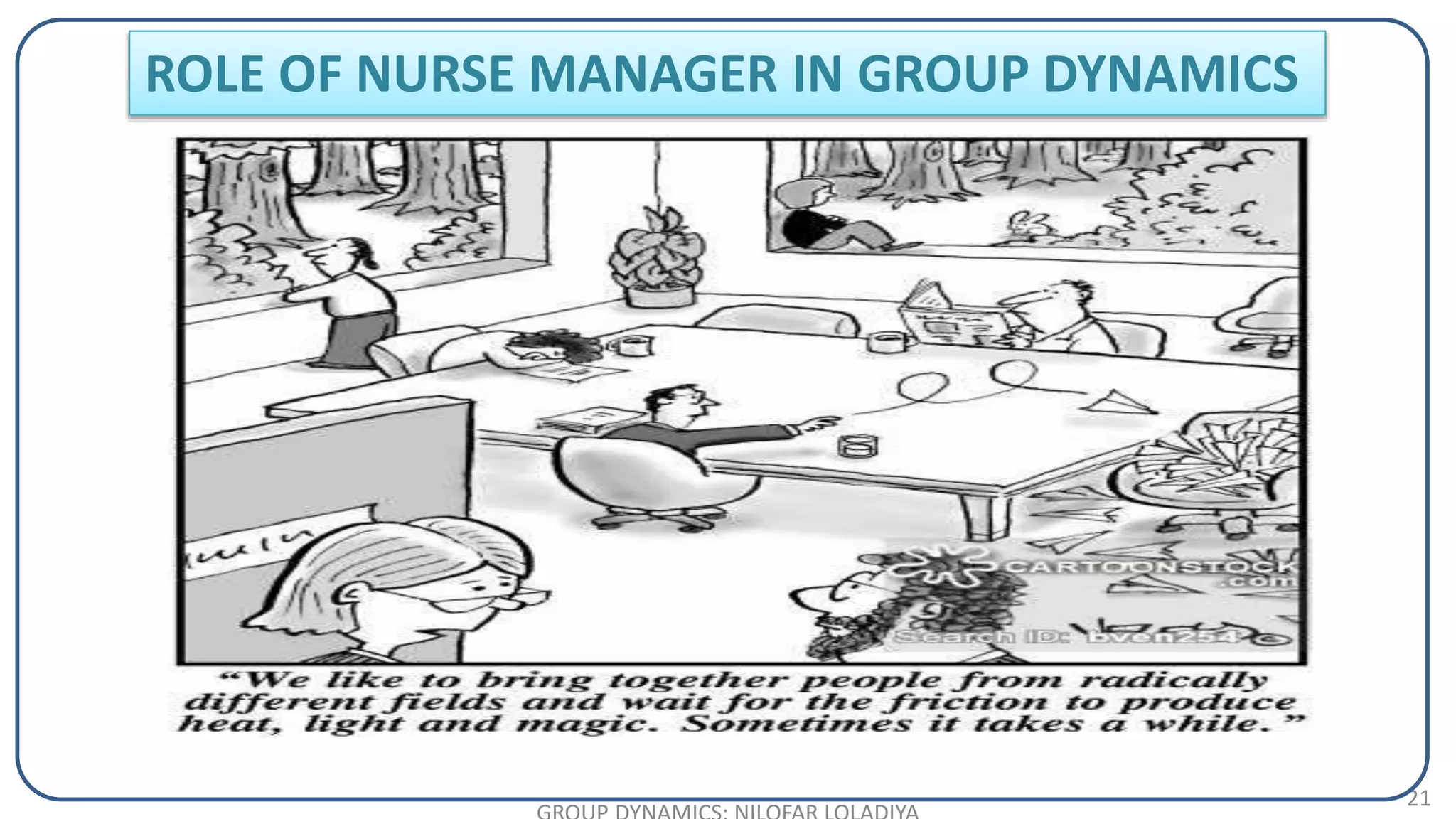
The document discusses the concept of groups and group dynamics, defining a group as individuals working towards a common goal and exploring the characteristics and types of groups. It highlights the importance of group interactions, communication, decision-making, and the roles of leaders within groups. Additionally, it addresses the impact of group dynamics on organizational performance and the role of nurse managers in facilitating effective group functioning.