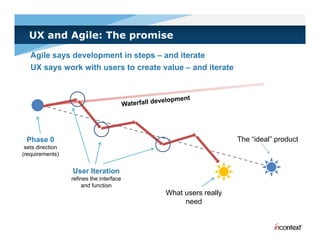
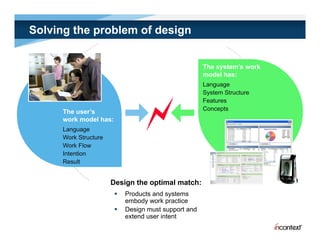
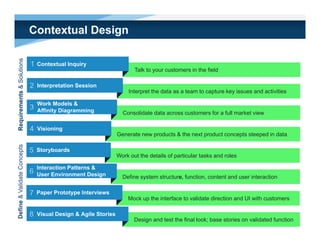
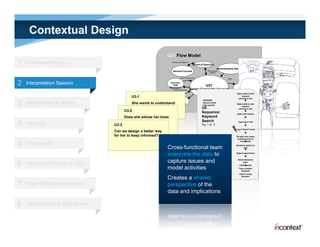
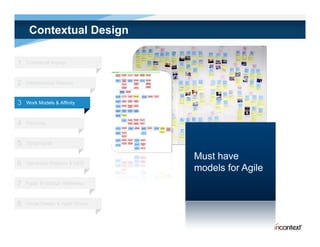
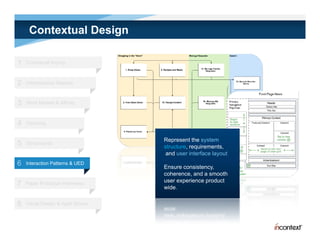
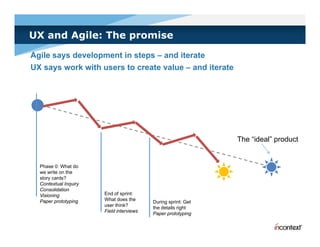
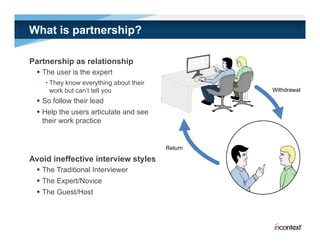
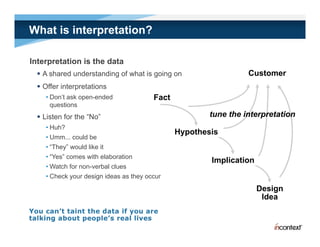
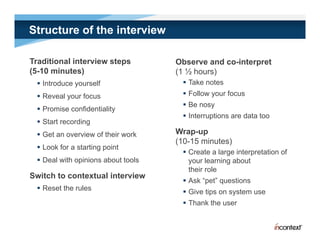
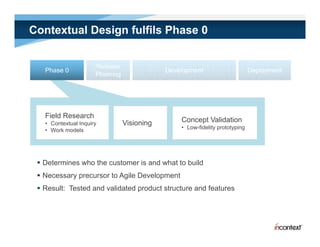
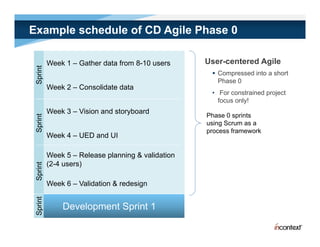
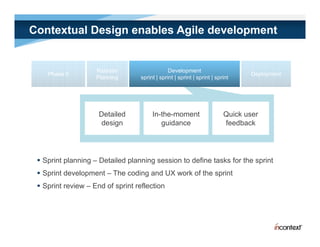
The document discusses simple methods for involving real users in product design and development through contextual design. It recommends conducting field studies to understand what users actually do and care about. Contextual design involves contextual inquiry, interpretation sessions, work models, affinity diagramming, visioning, storyboards, interaction patterns, paper prototyping, and agile development. The goal is to design products that support and extend user intentions by embodying users' work practices discovered through contextual inquiry in the field.