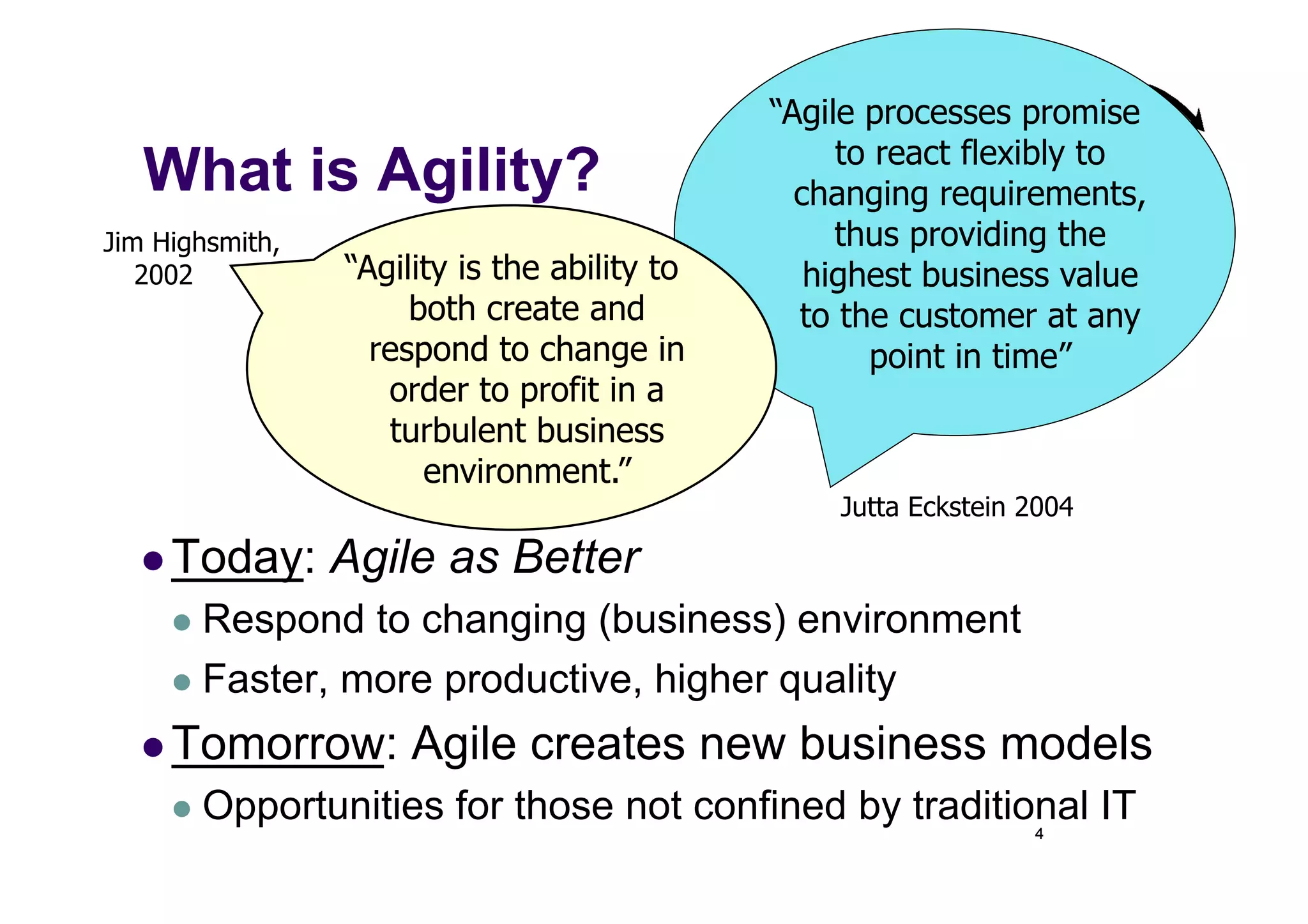
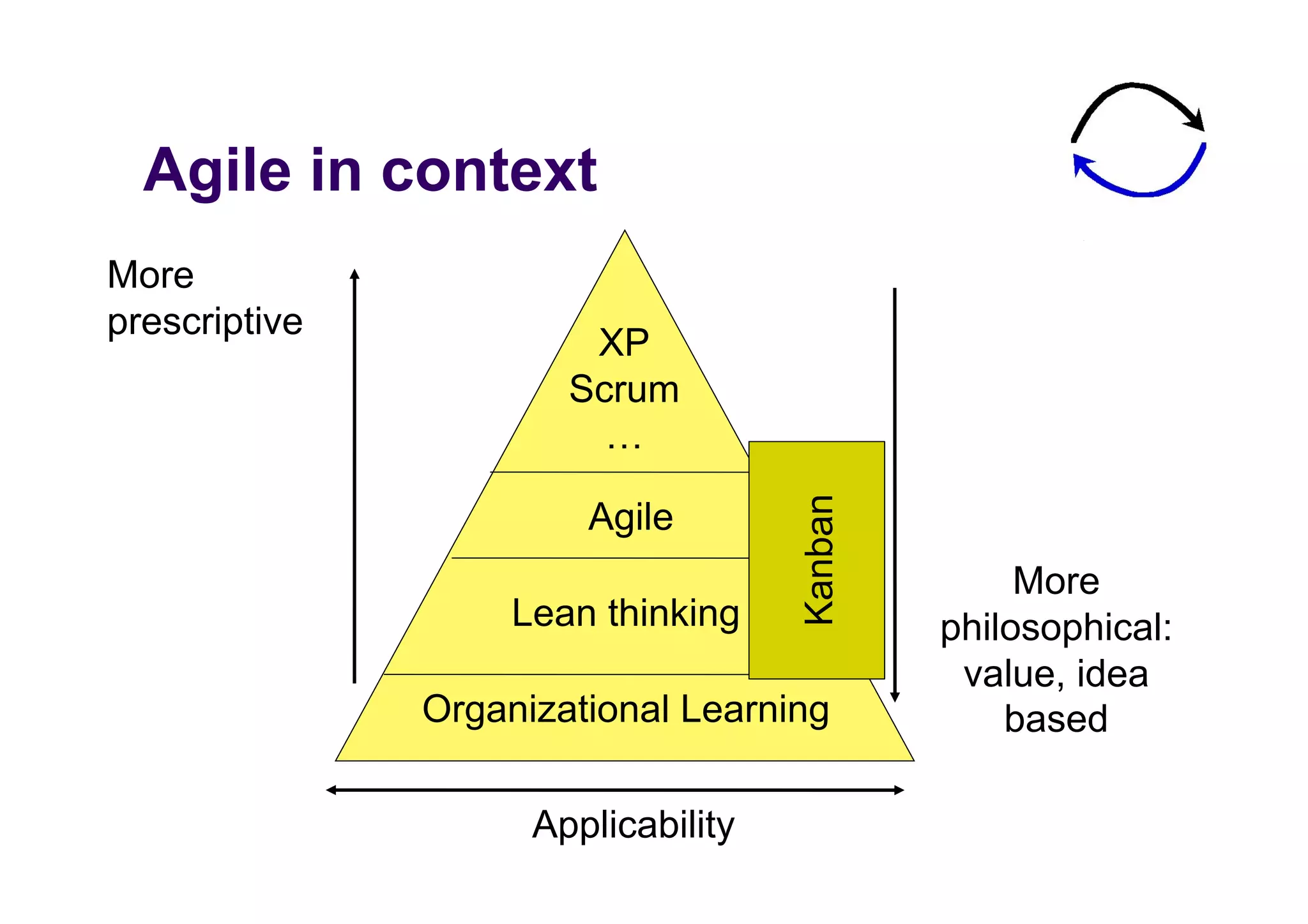
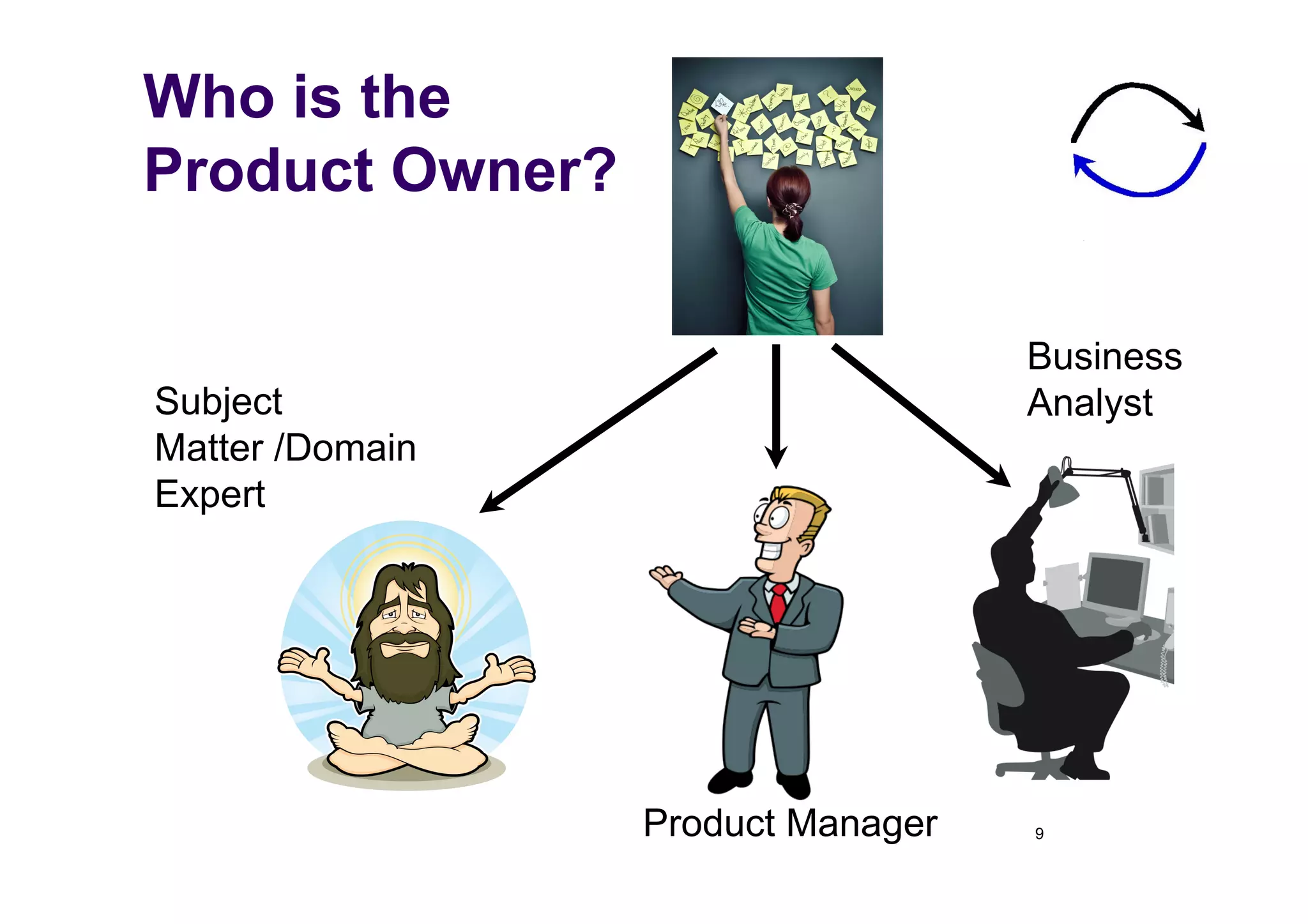
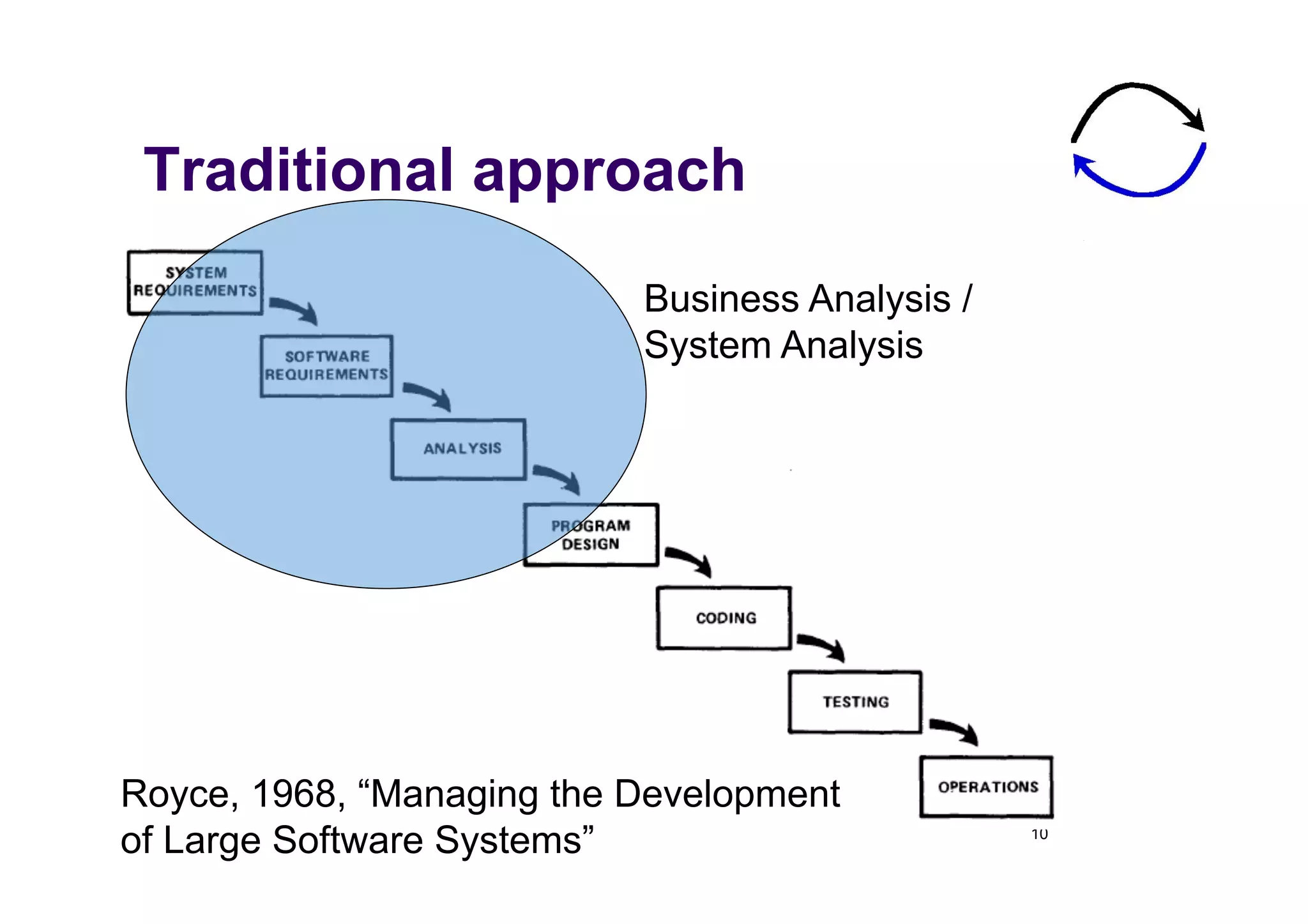
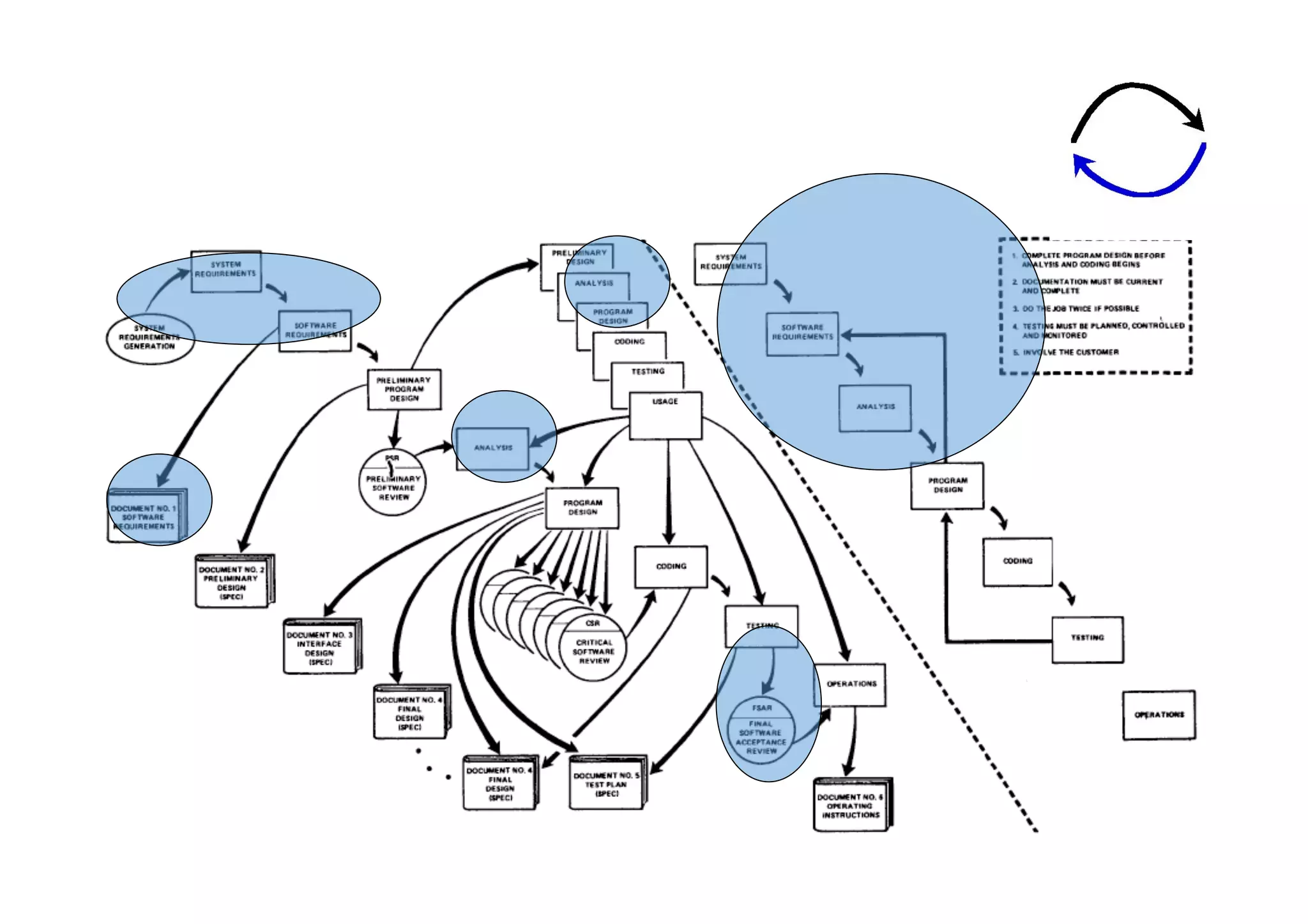
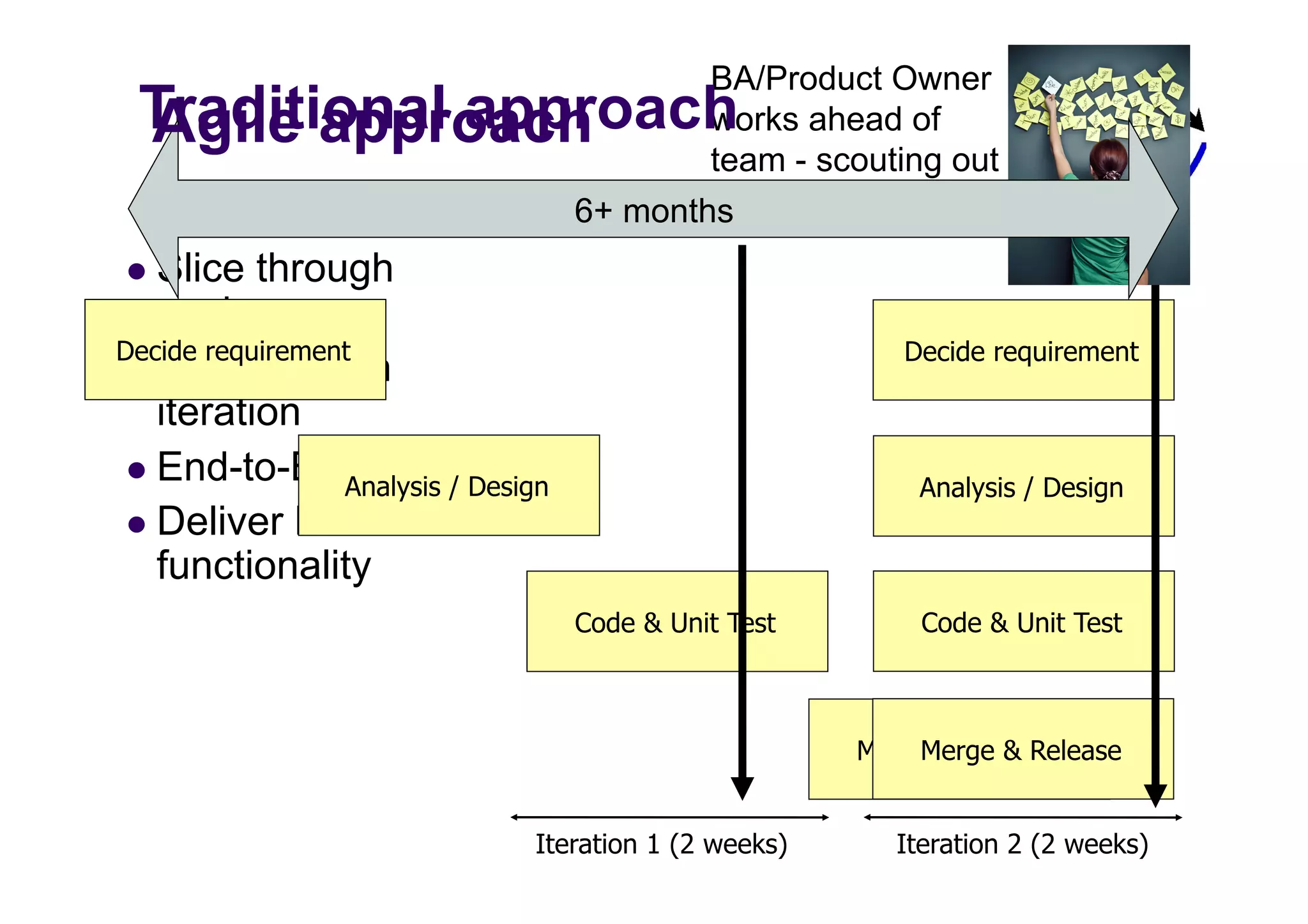
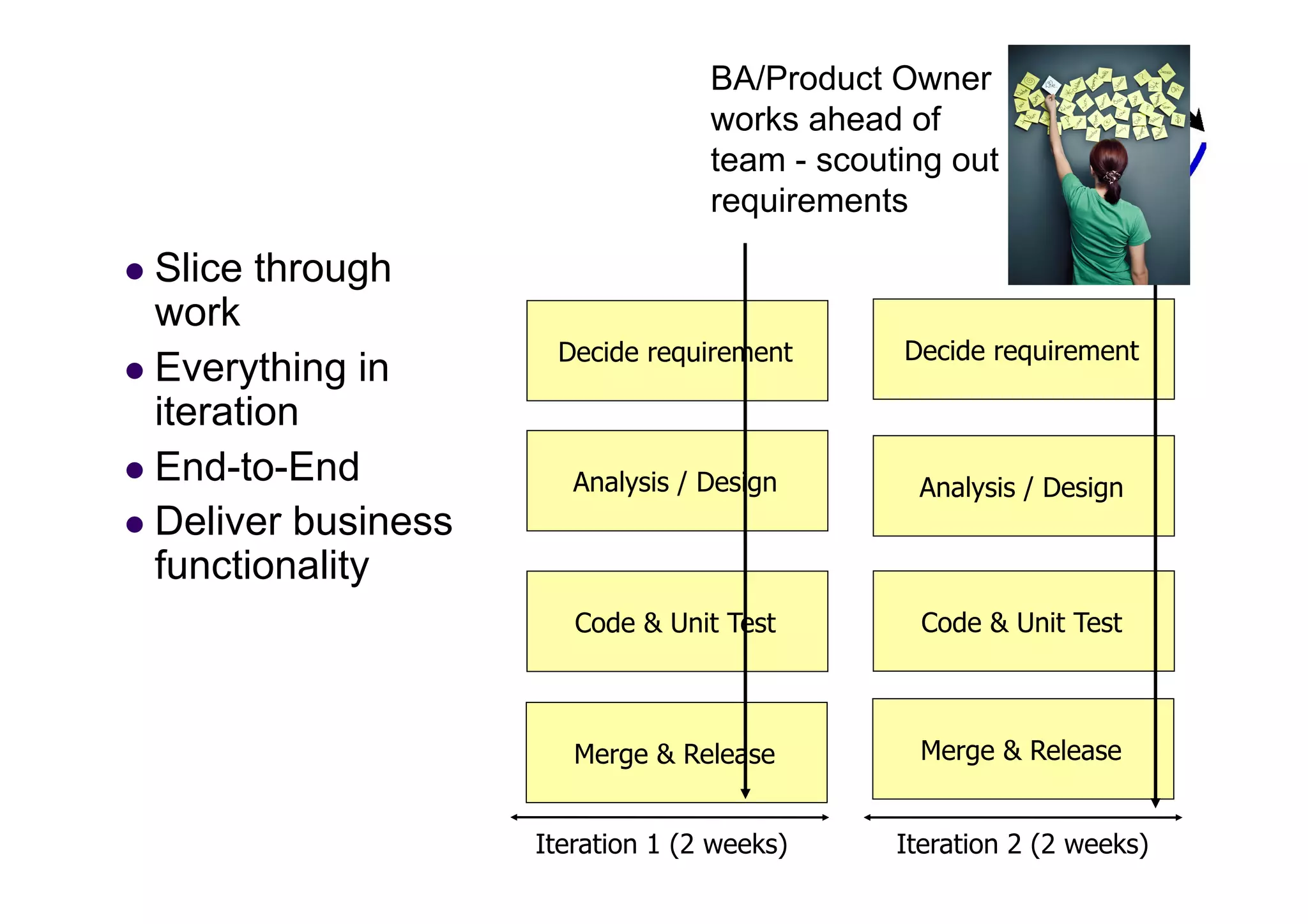
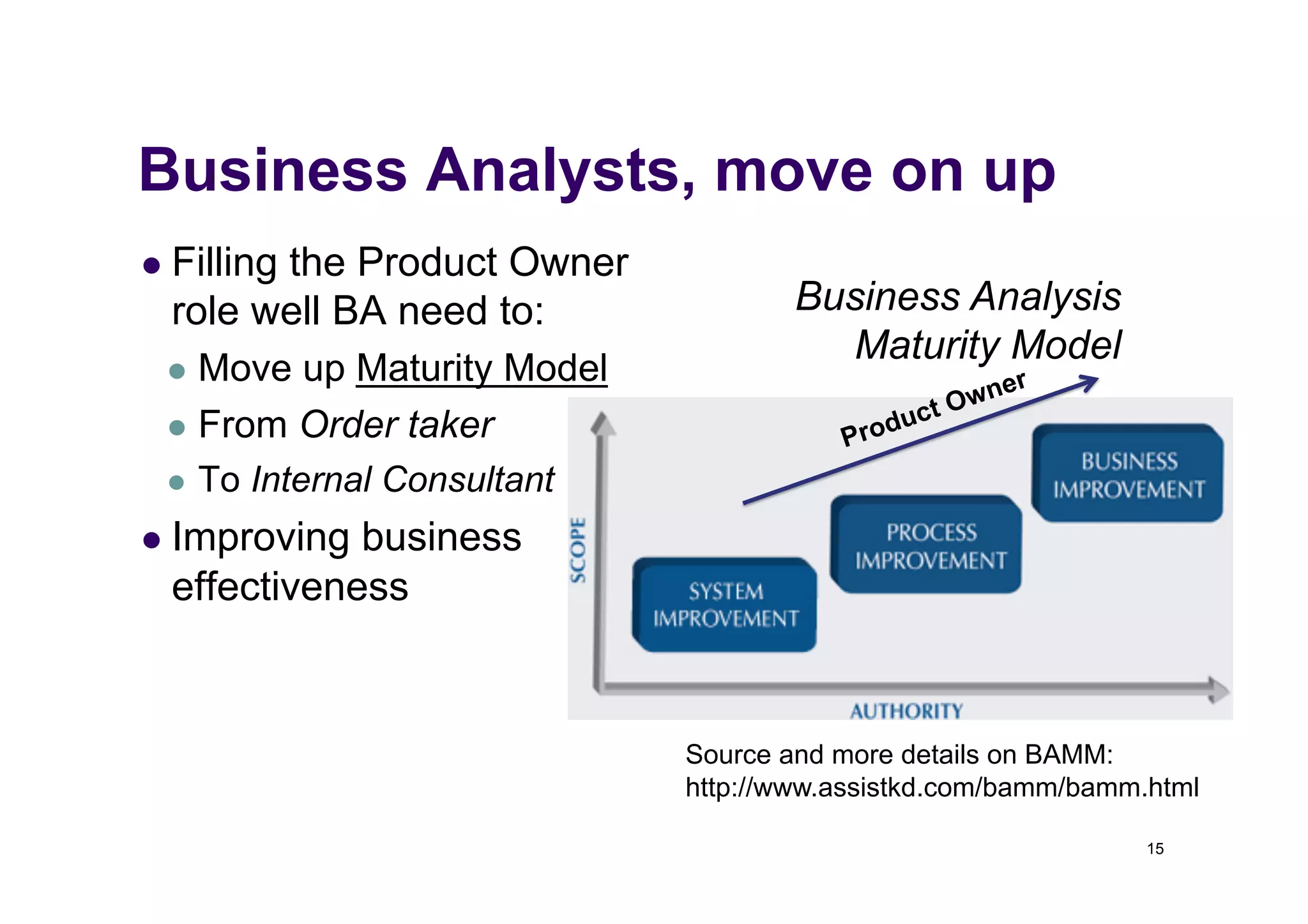
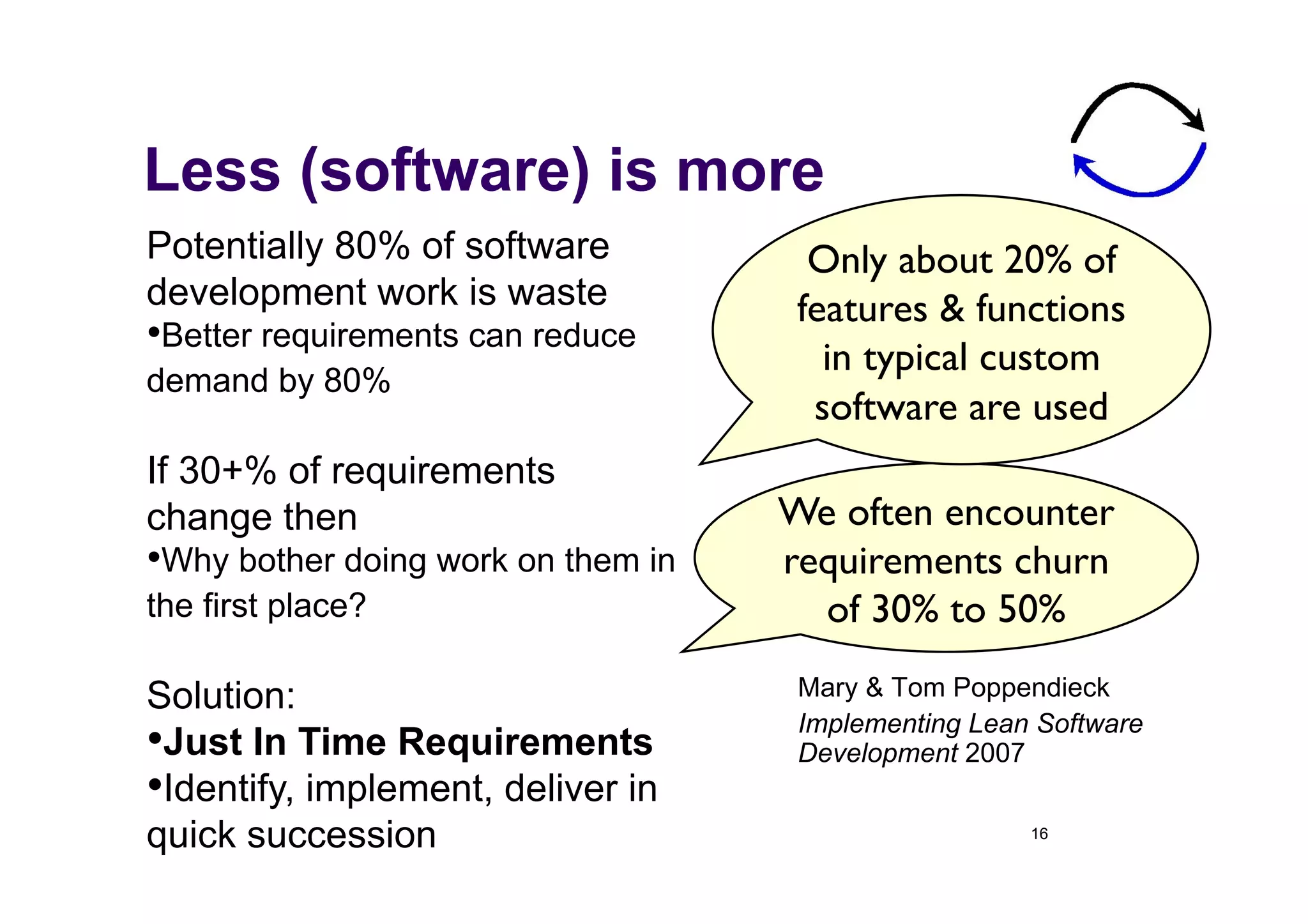
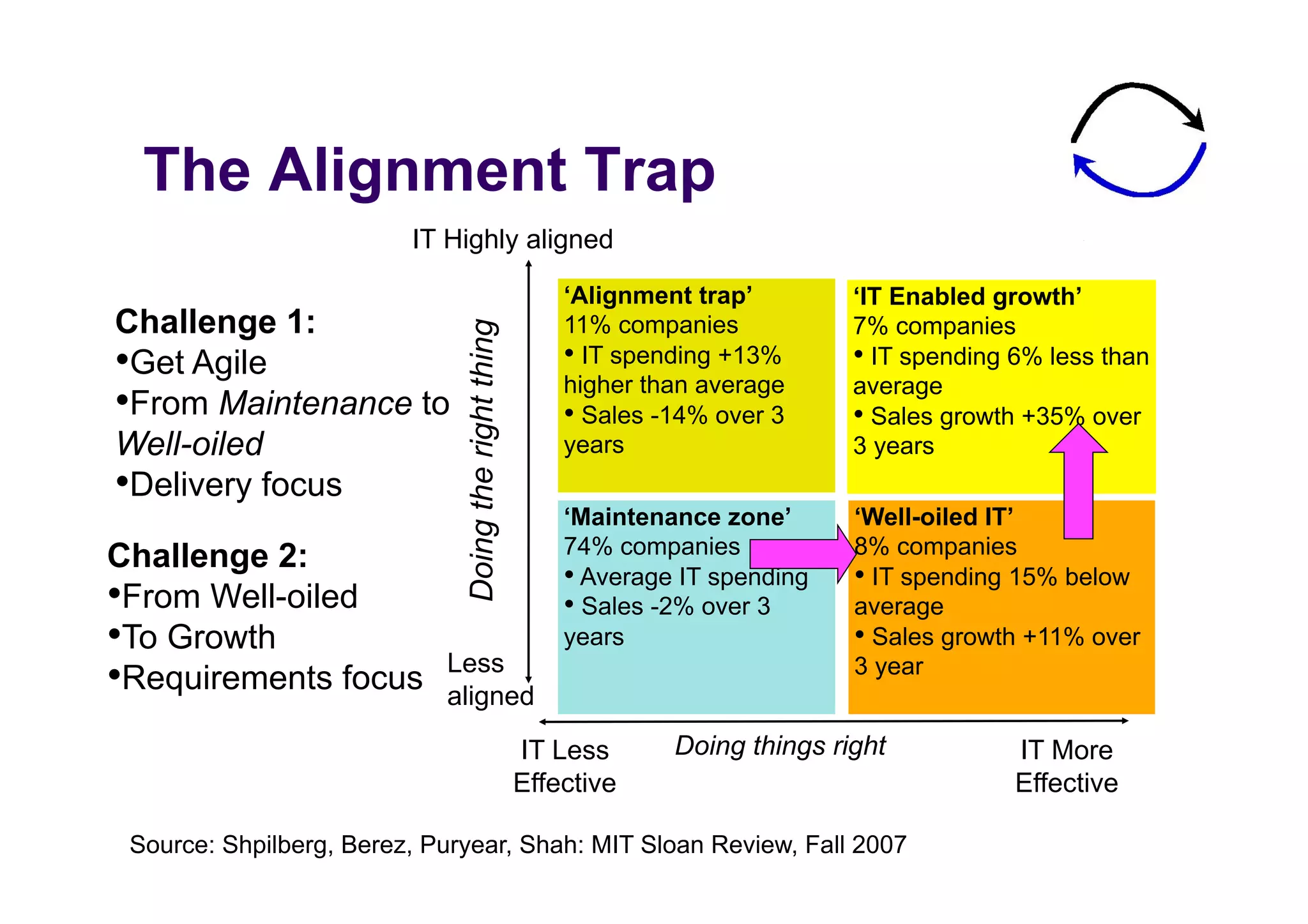
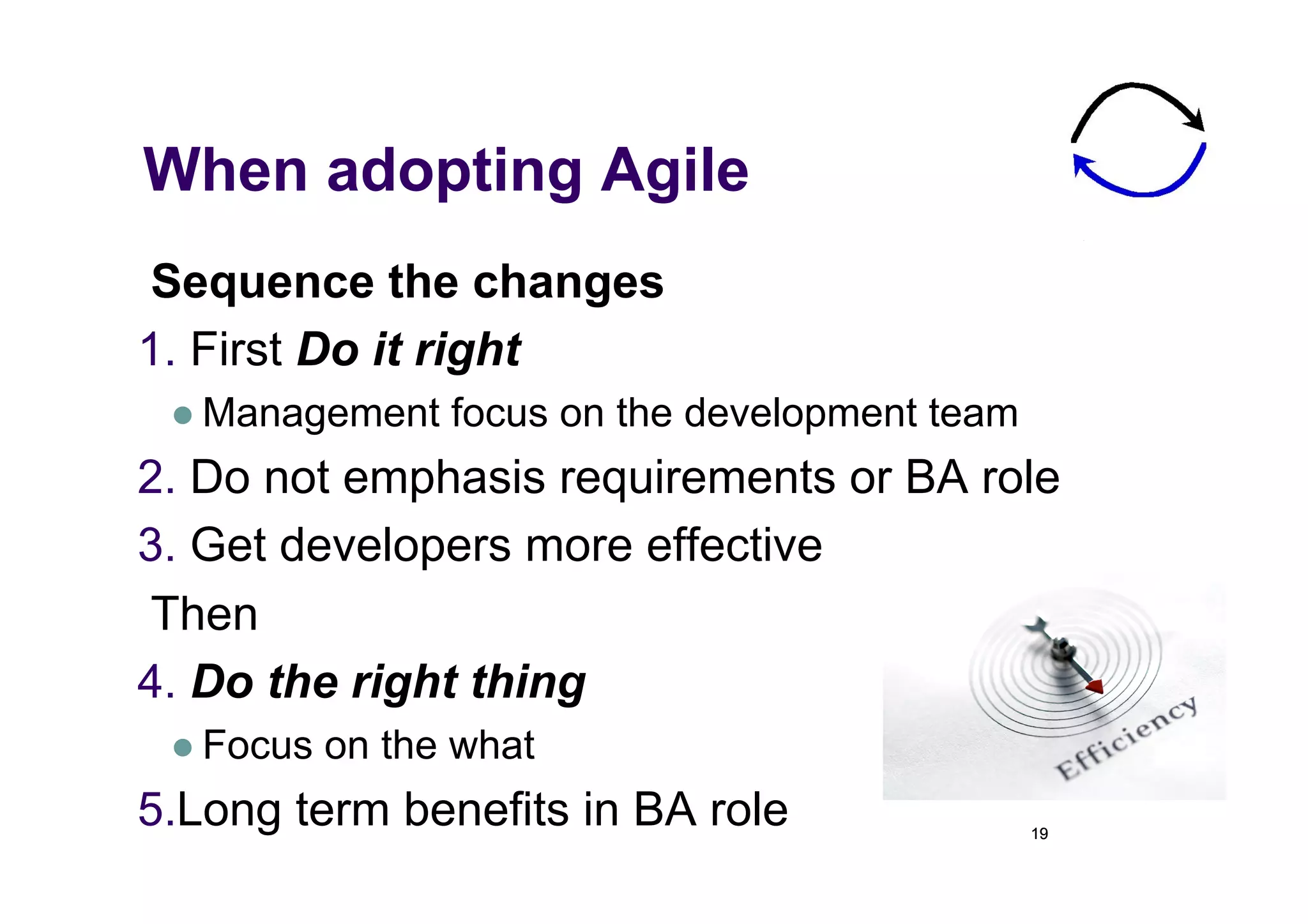
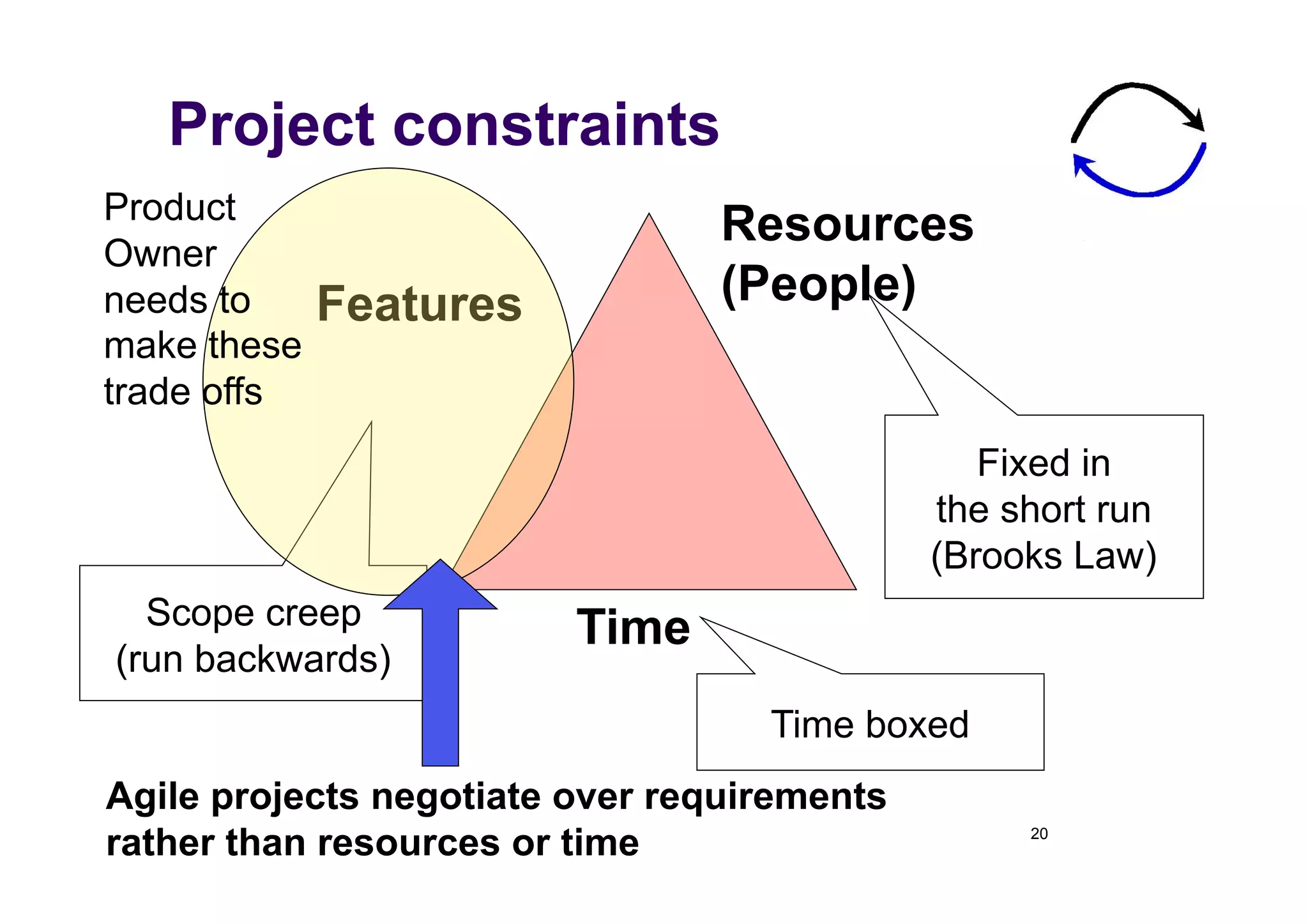
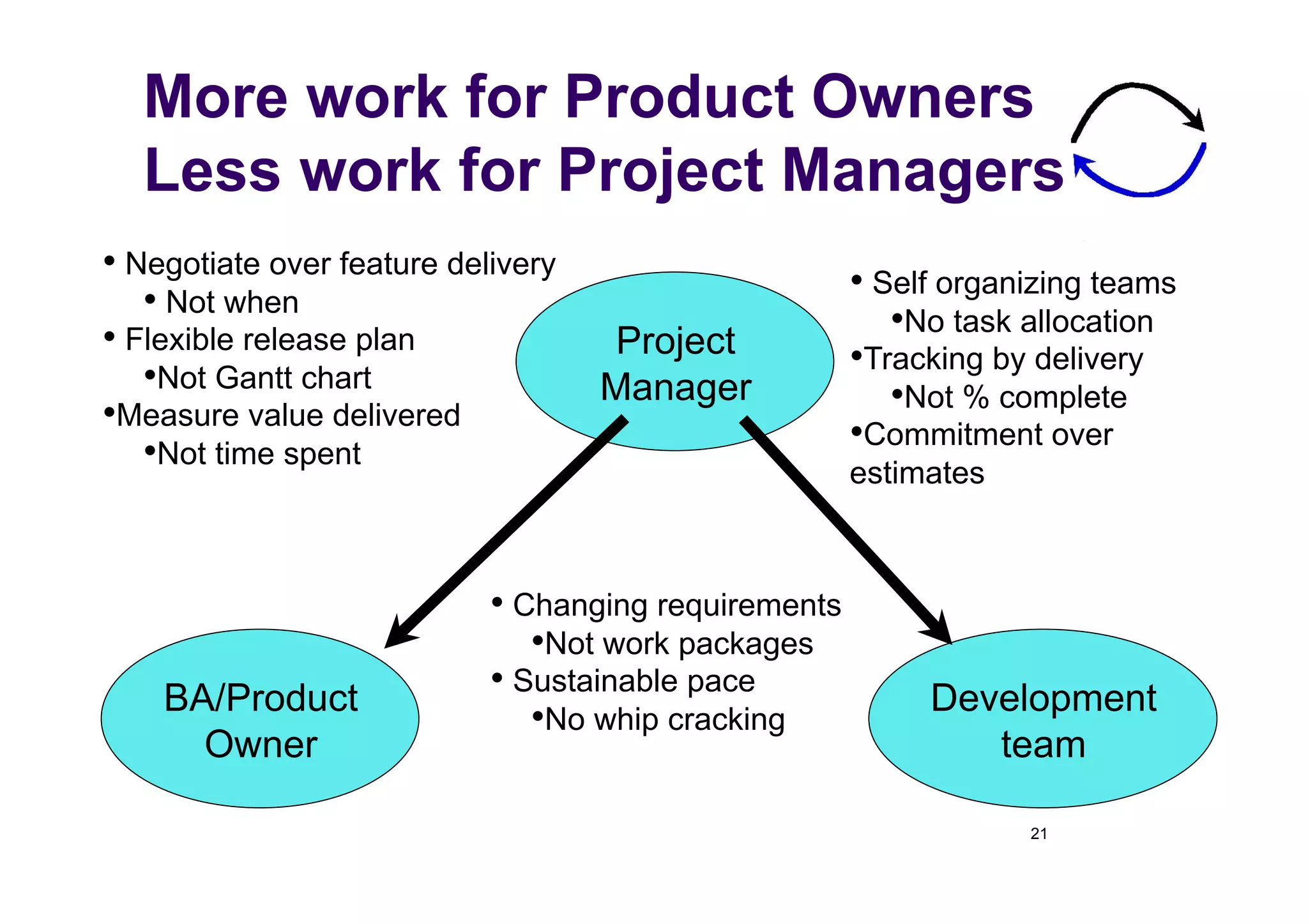
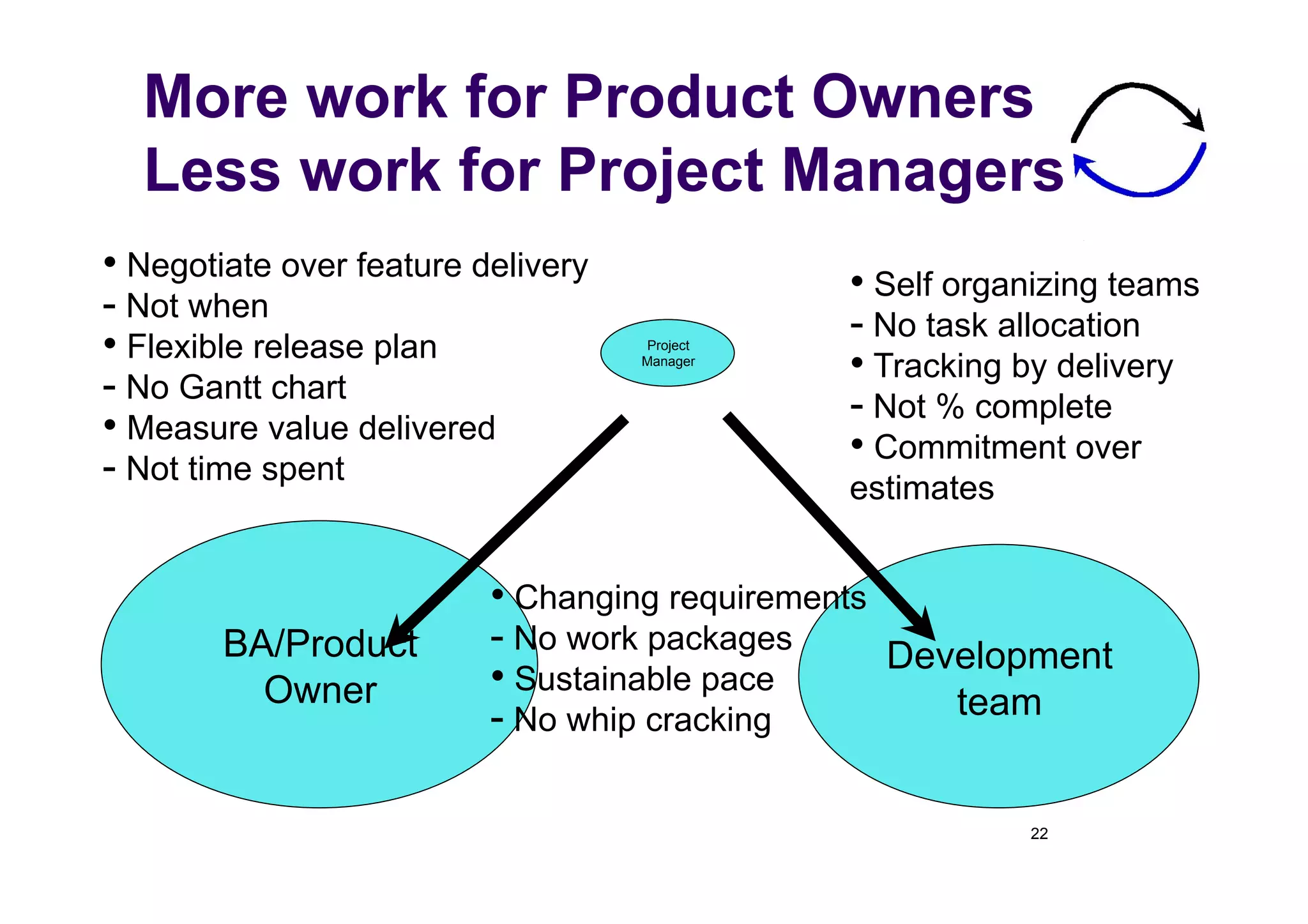
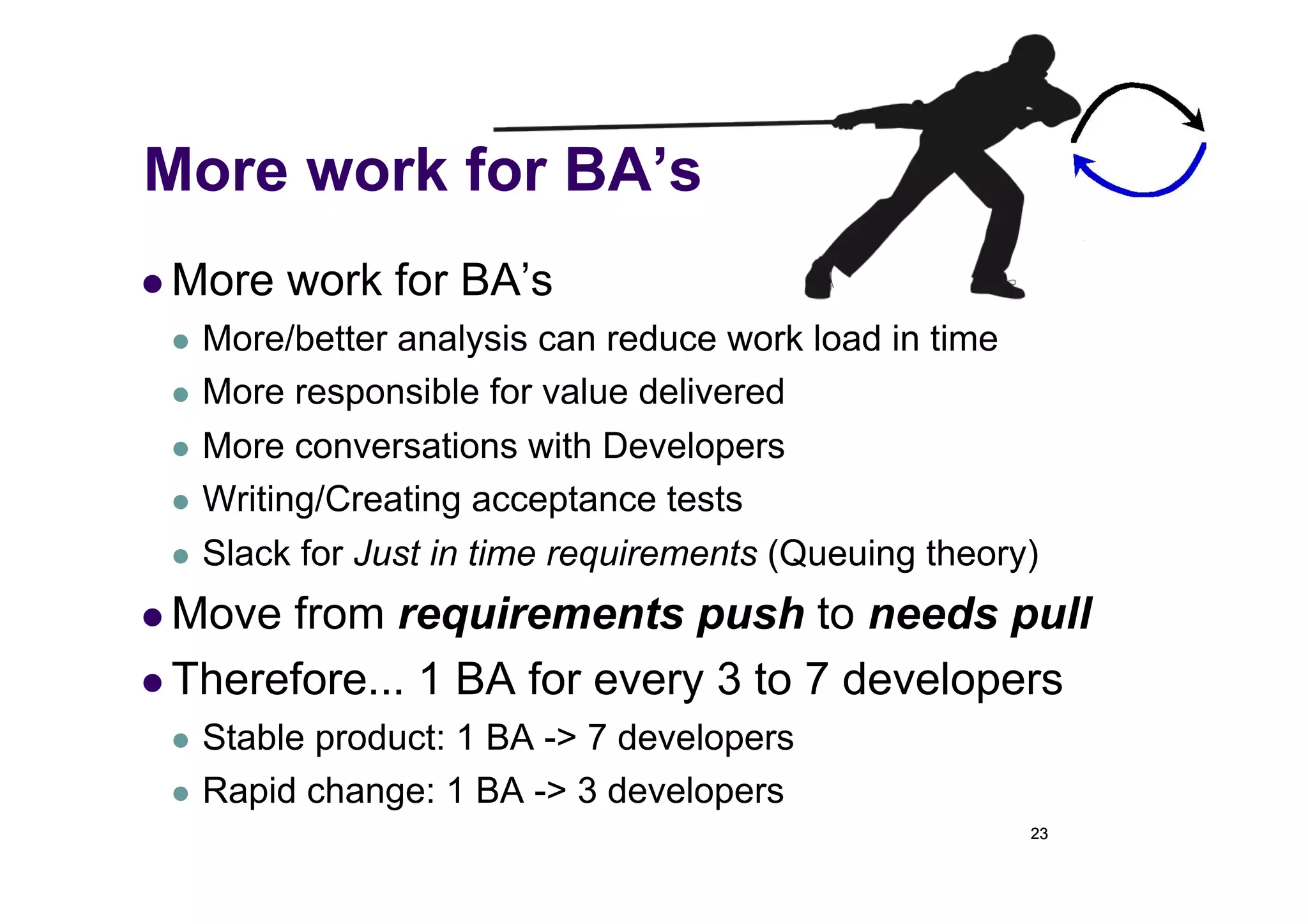
The document discusses the role of business analysts in agile software development. It argues that in traditional approaches, requirements are gathered at the start of a project by business analysts who then leave the project. However, in agile approaches, requirements gathering is an ongoing process and business analysts need to stay involved throughout to have a dialogue rather than just produce documents. The business analyst role evolves from an "order taker" to an internal consultant, facilitating discussions between business and development teams.