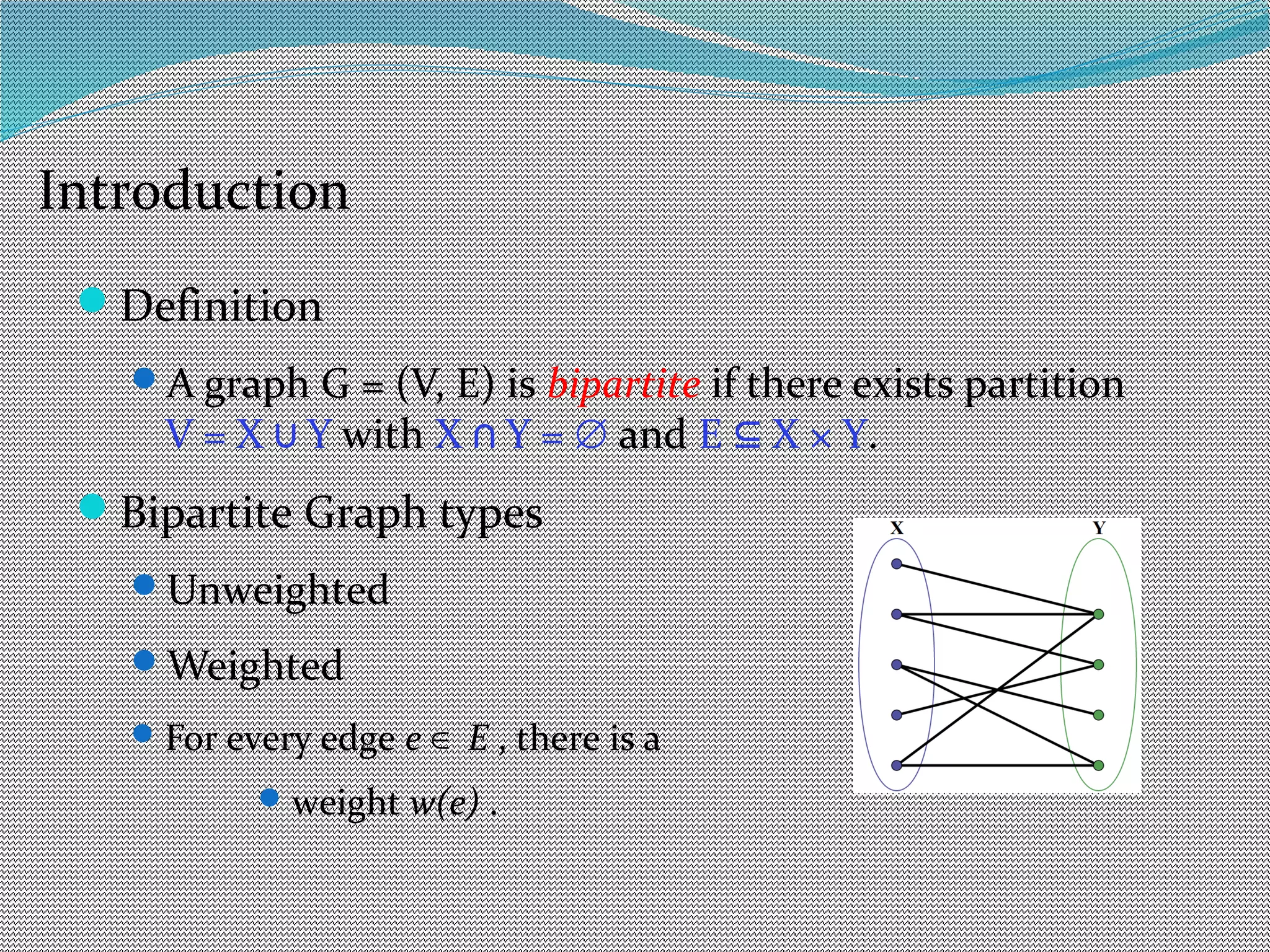
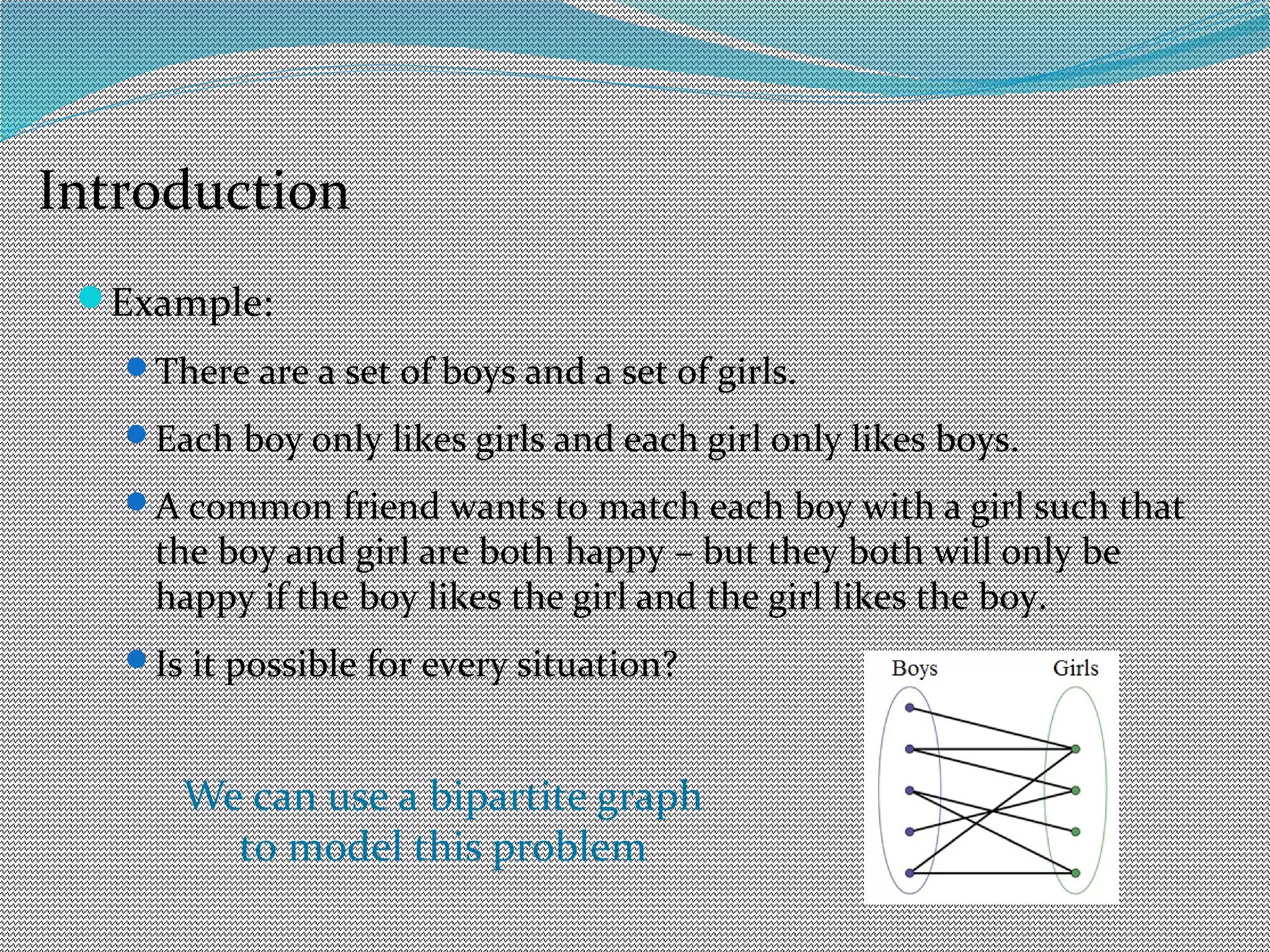
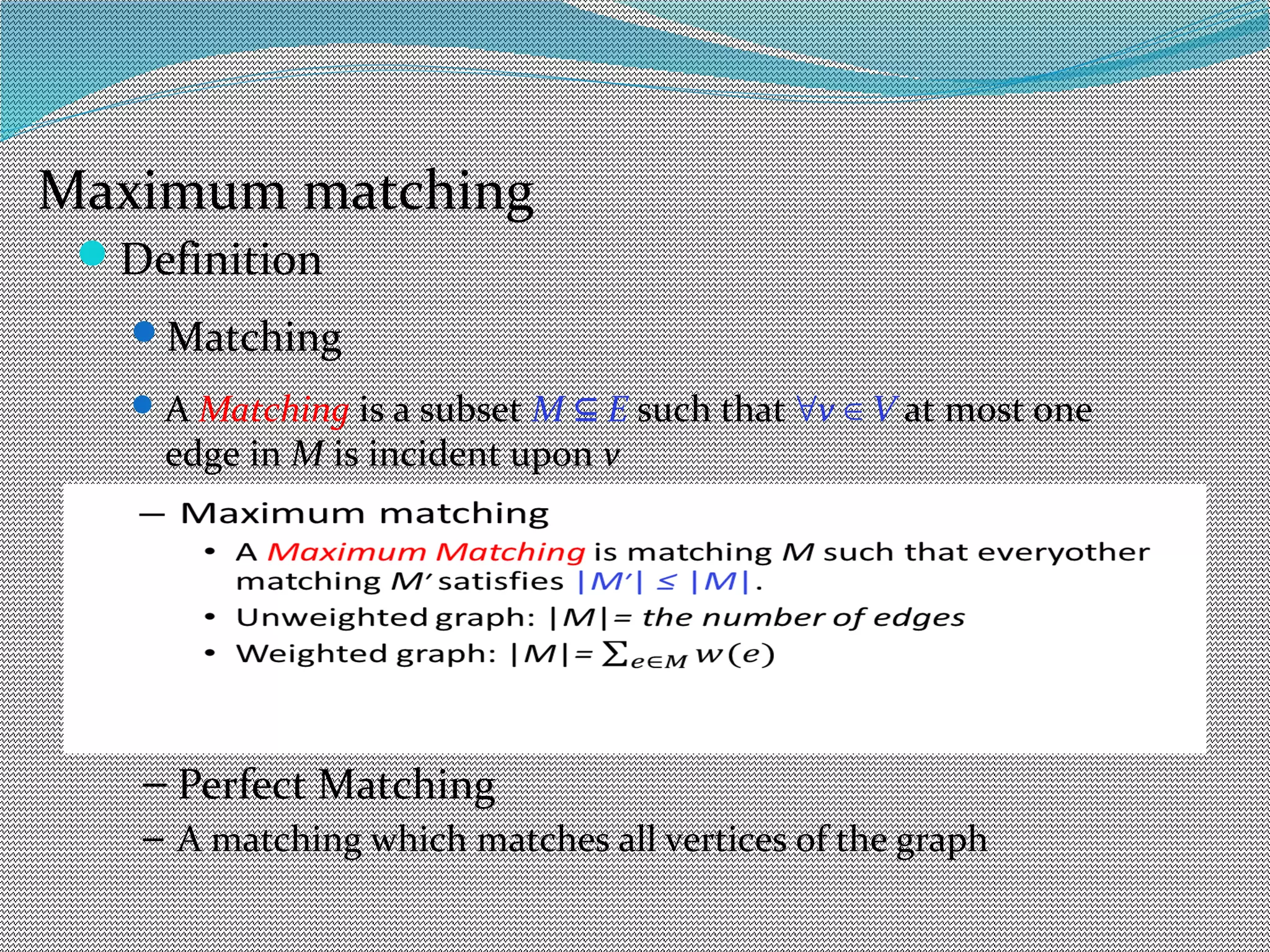
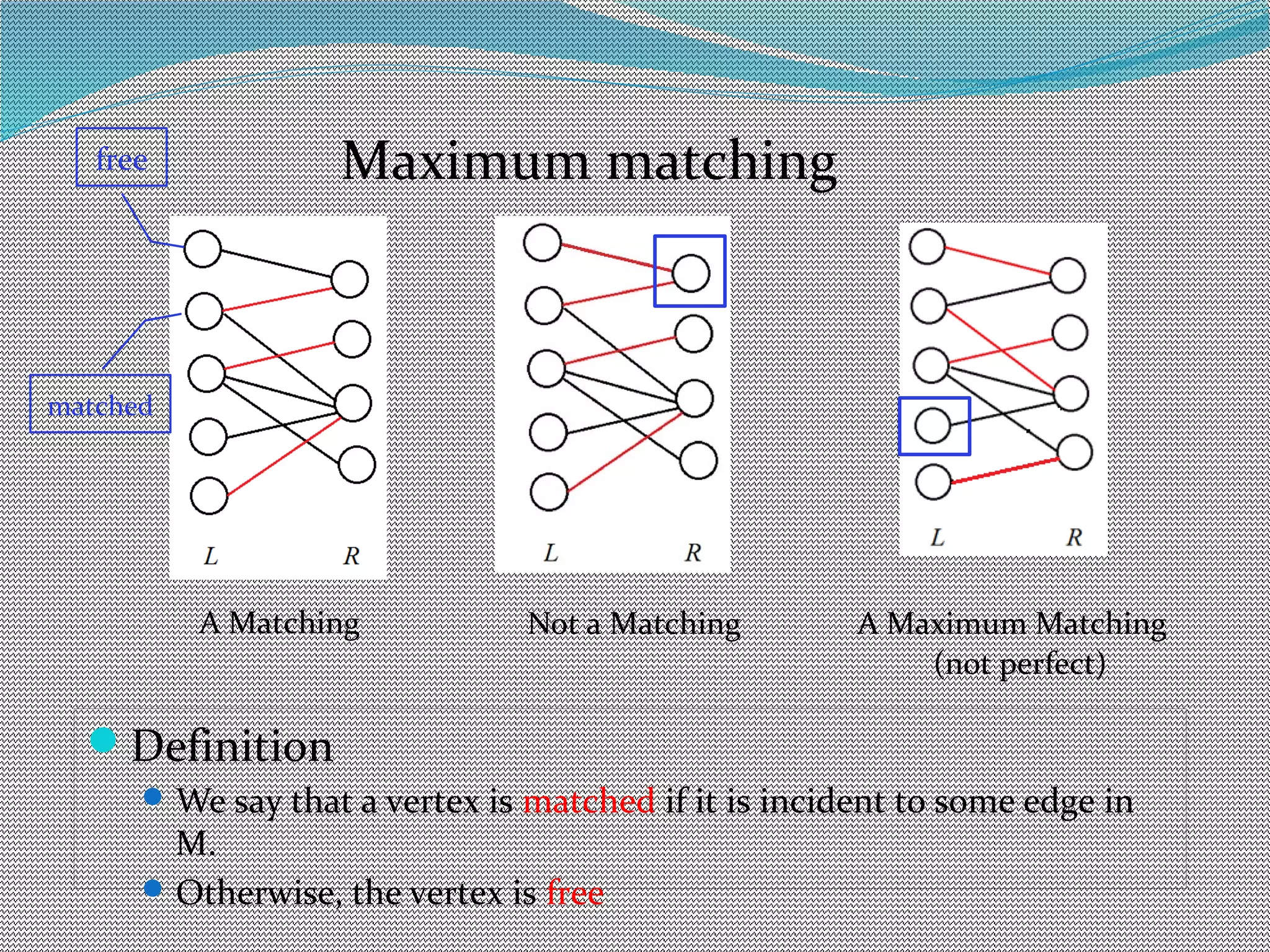
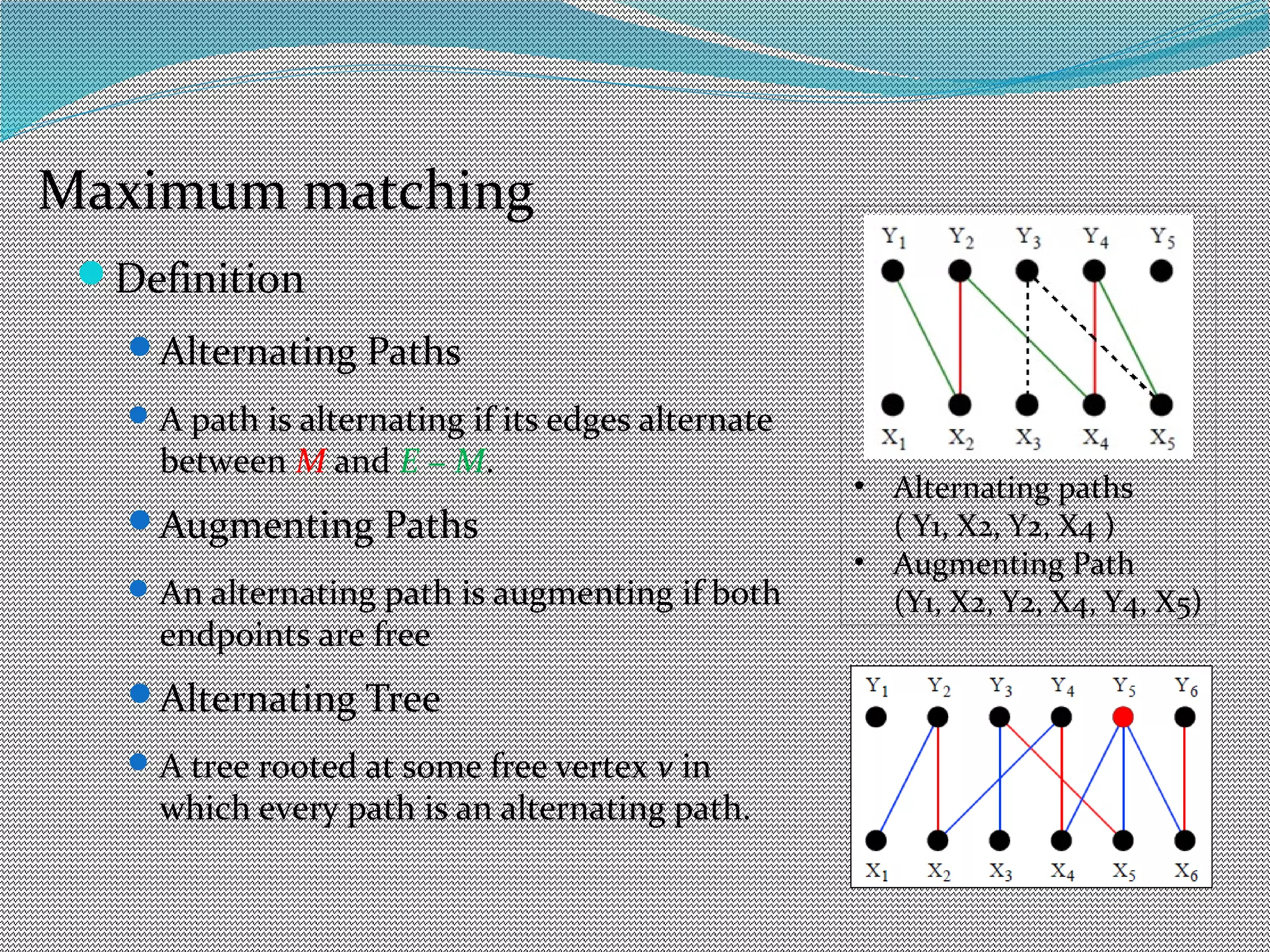
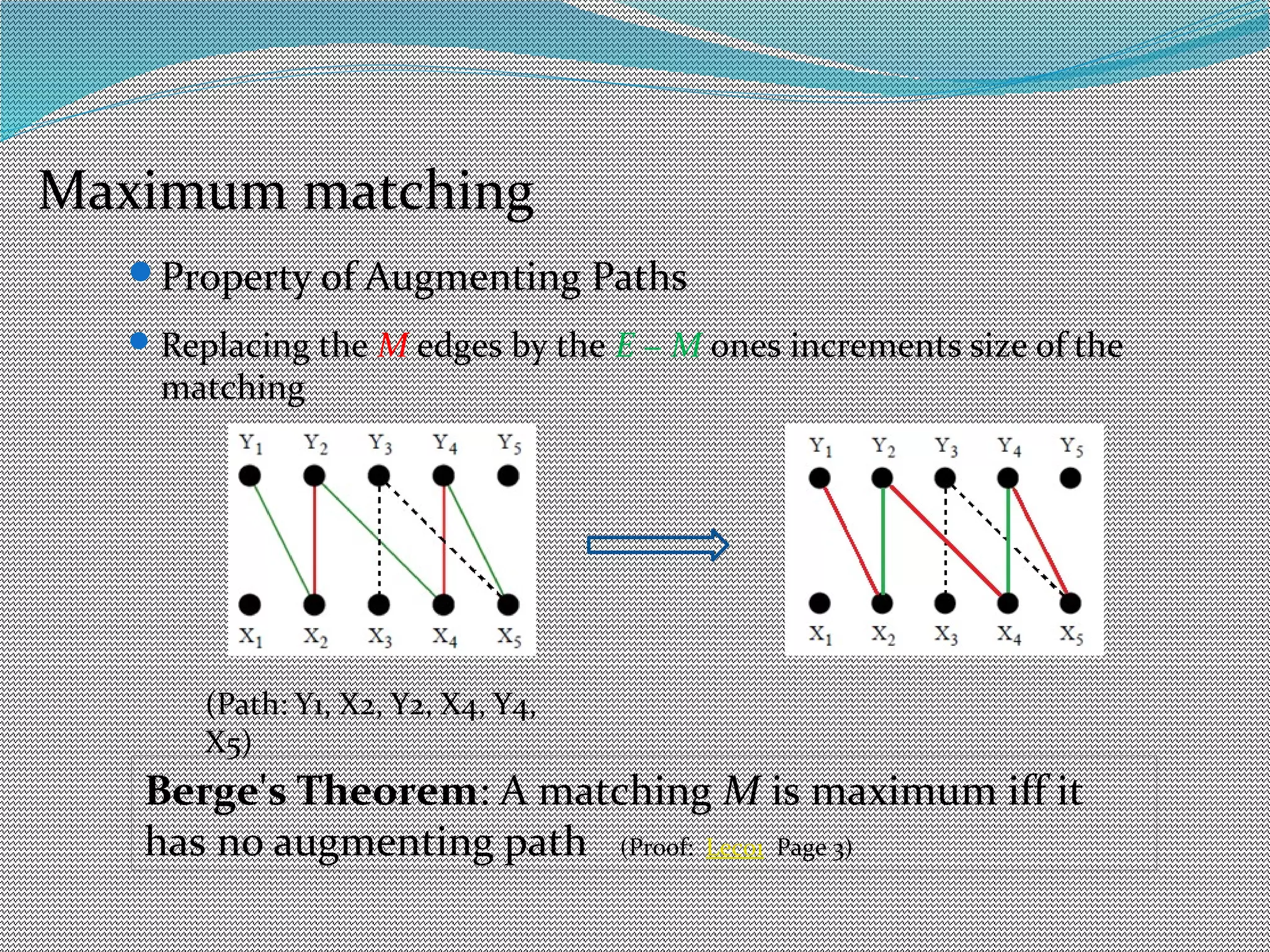
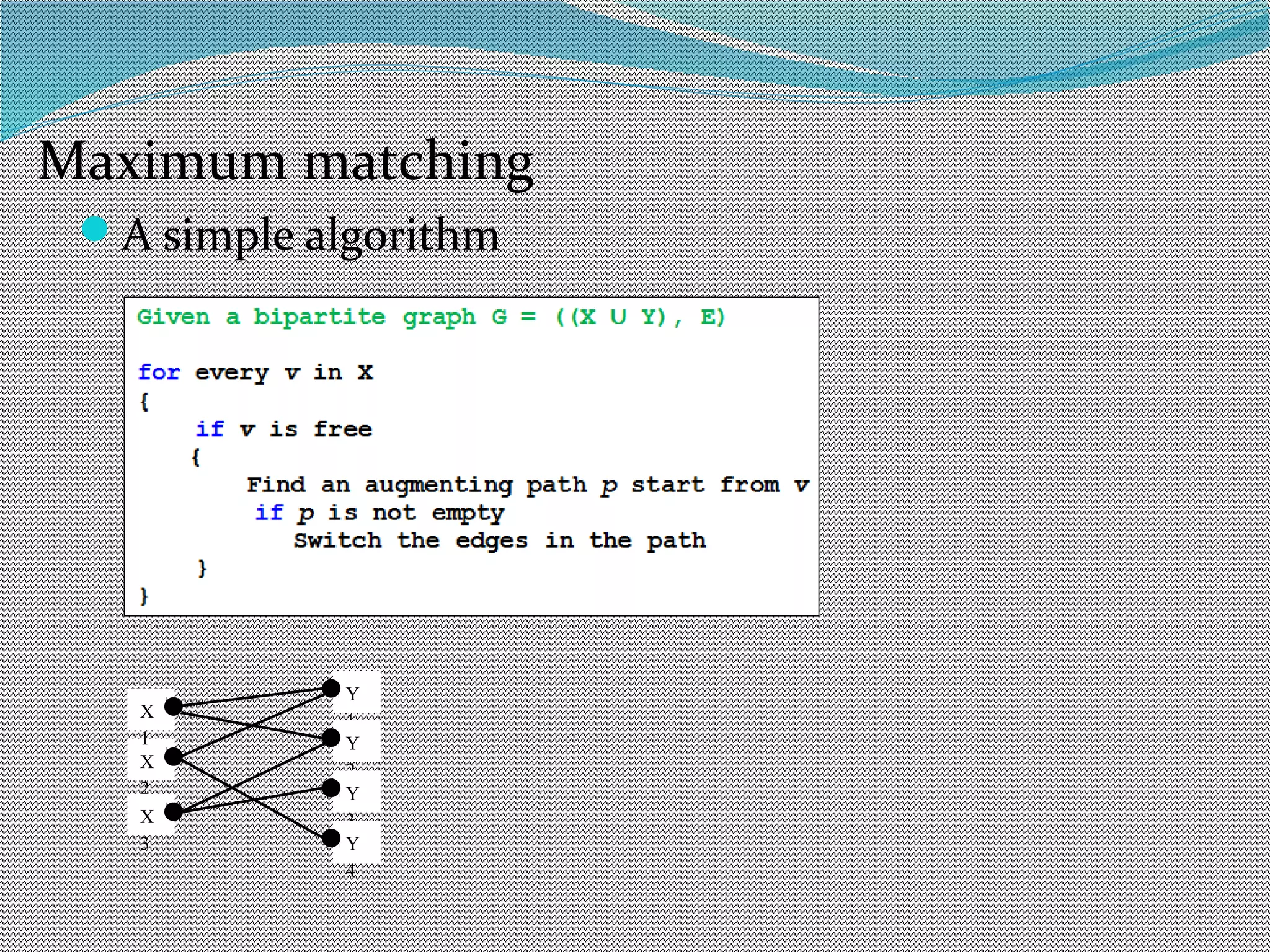
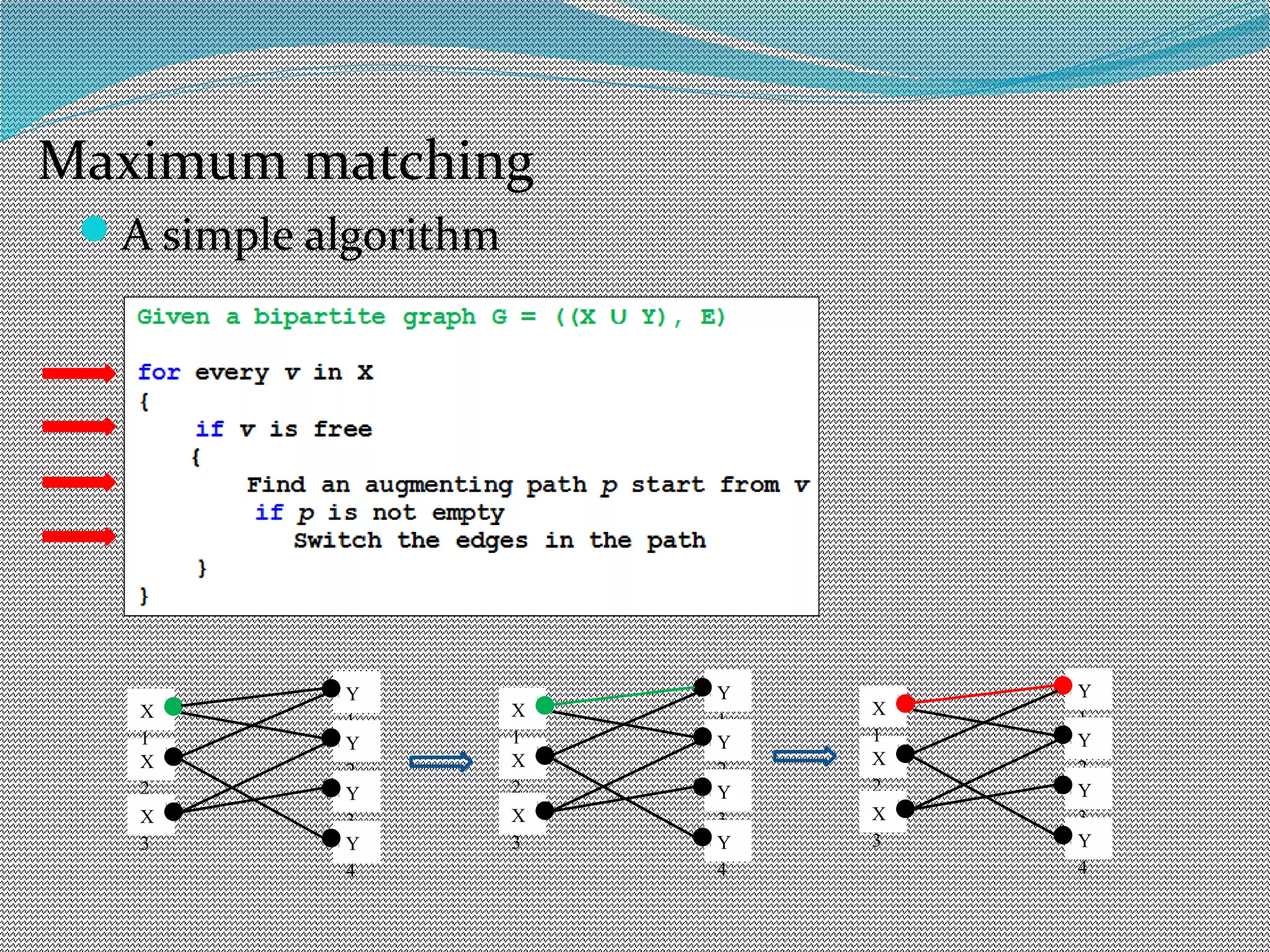
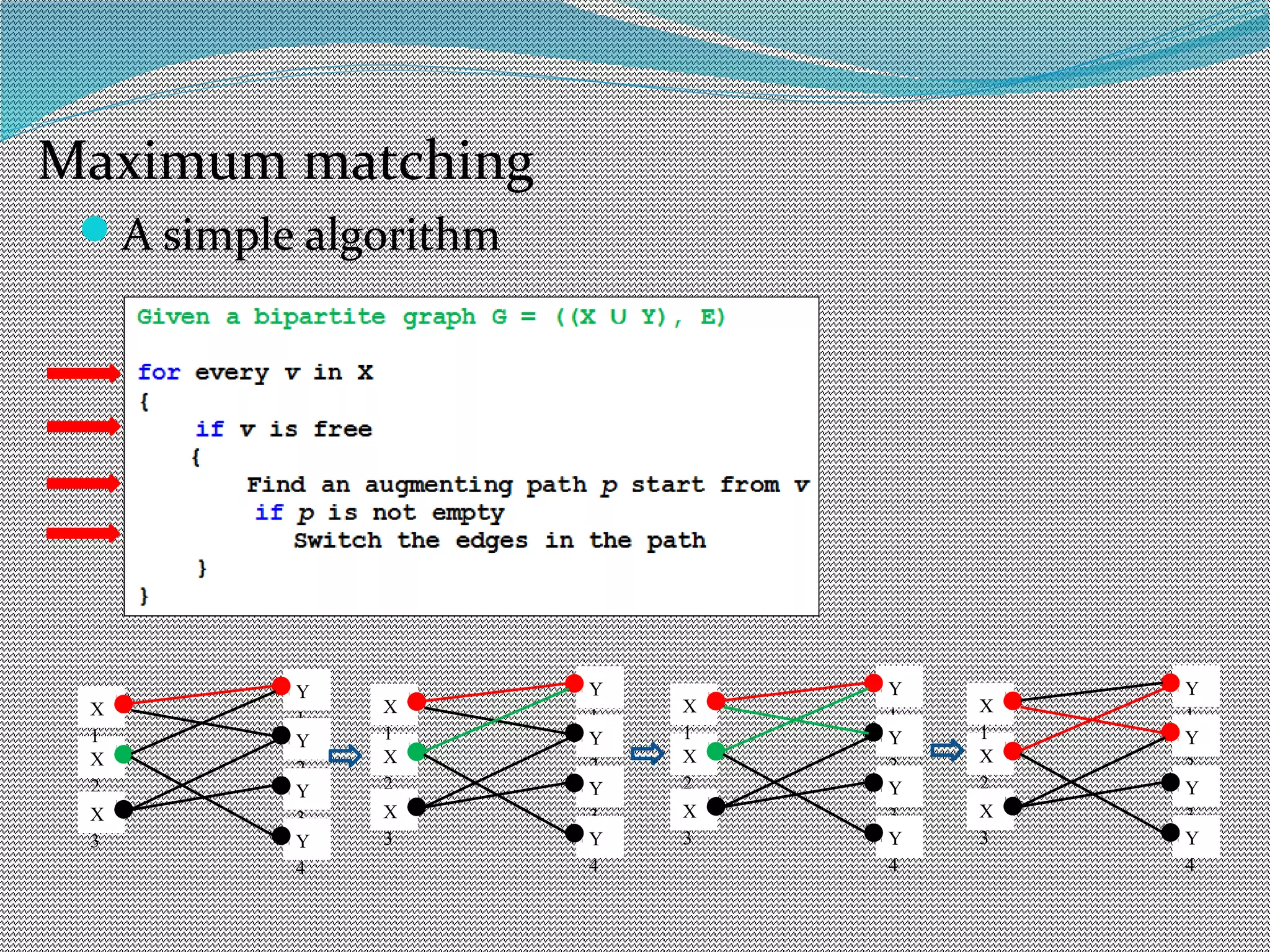
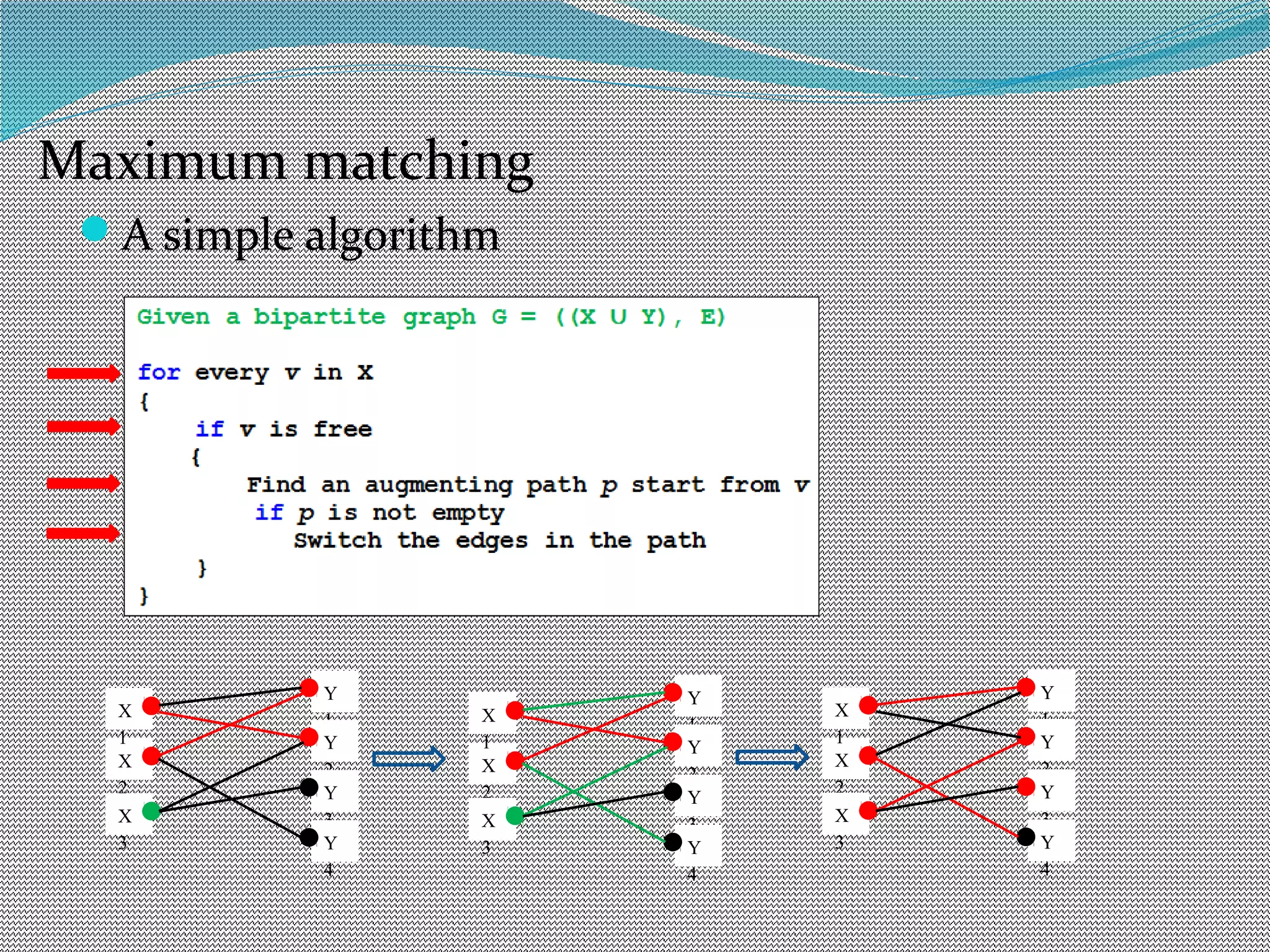
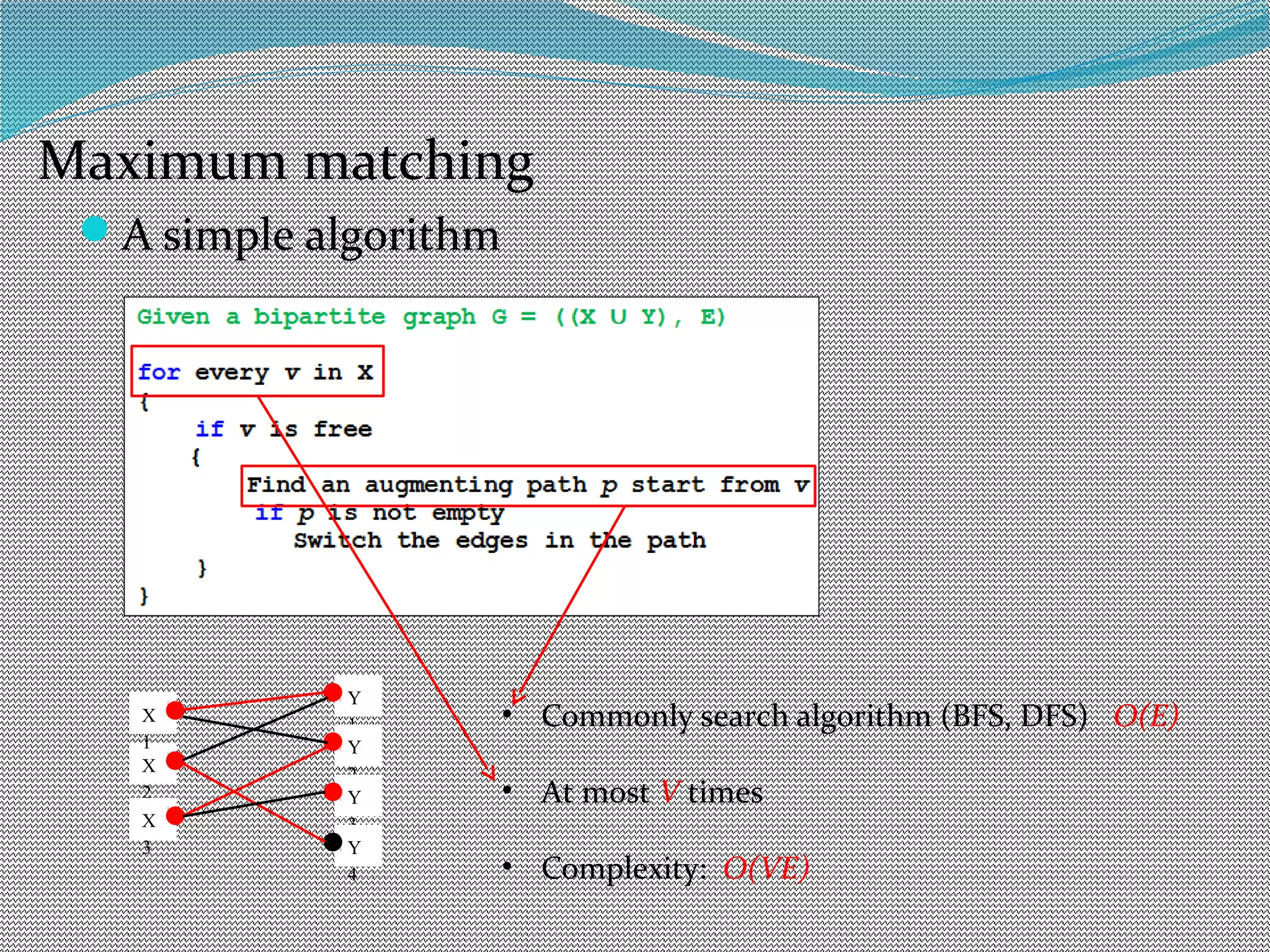
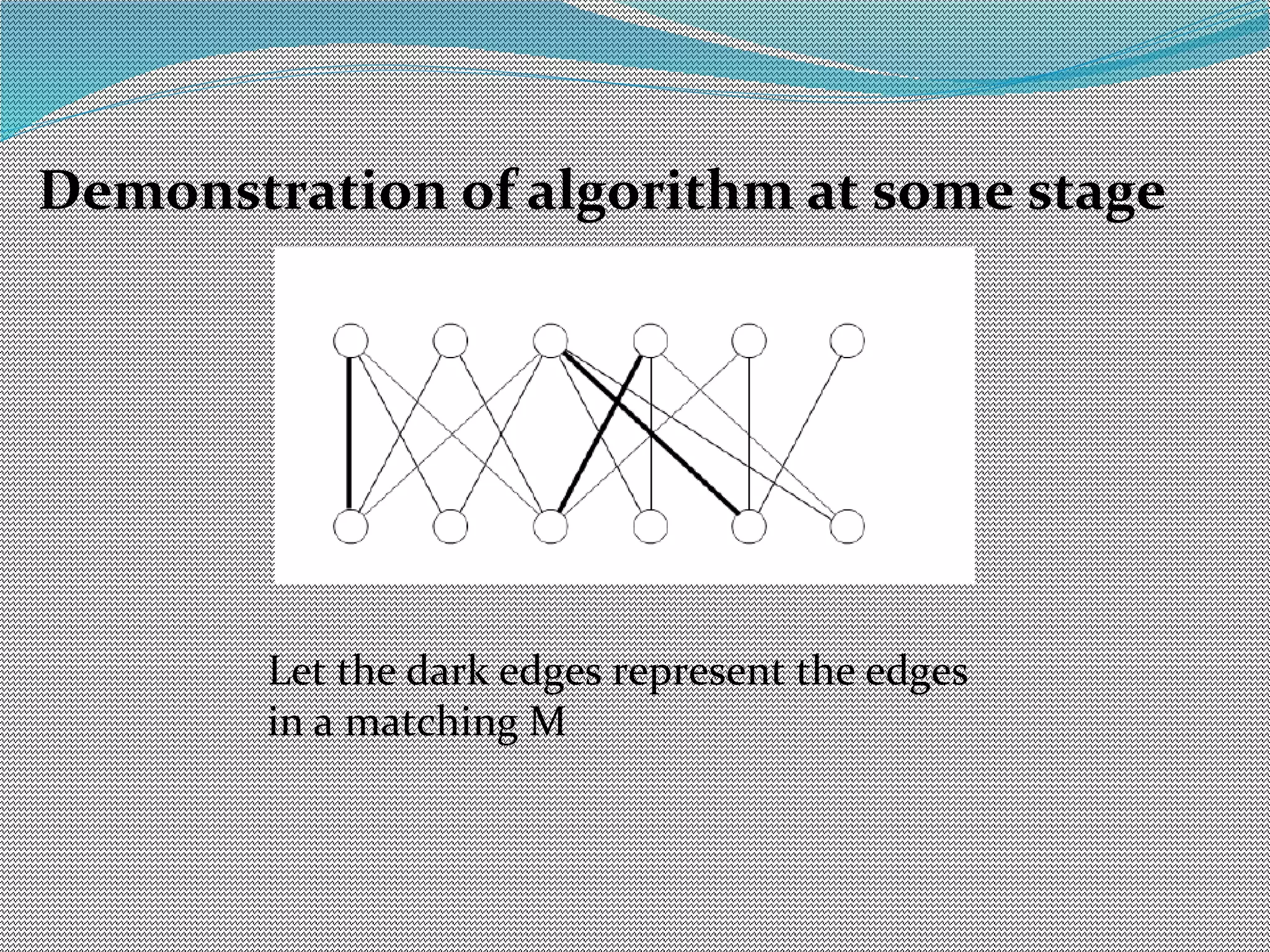
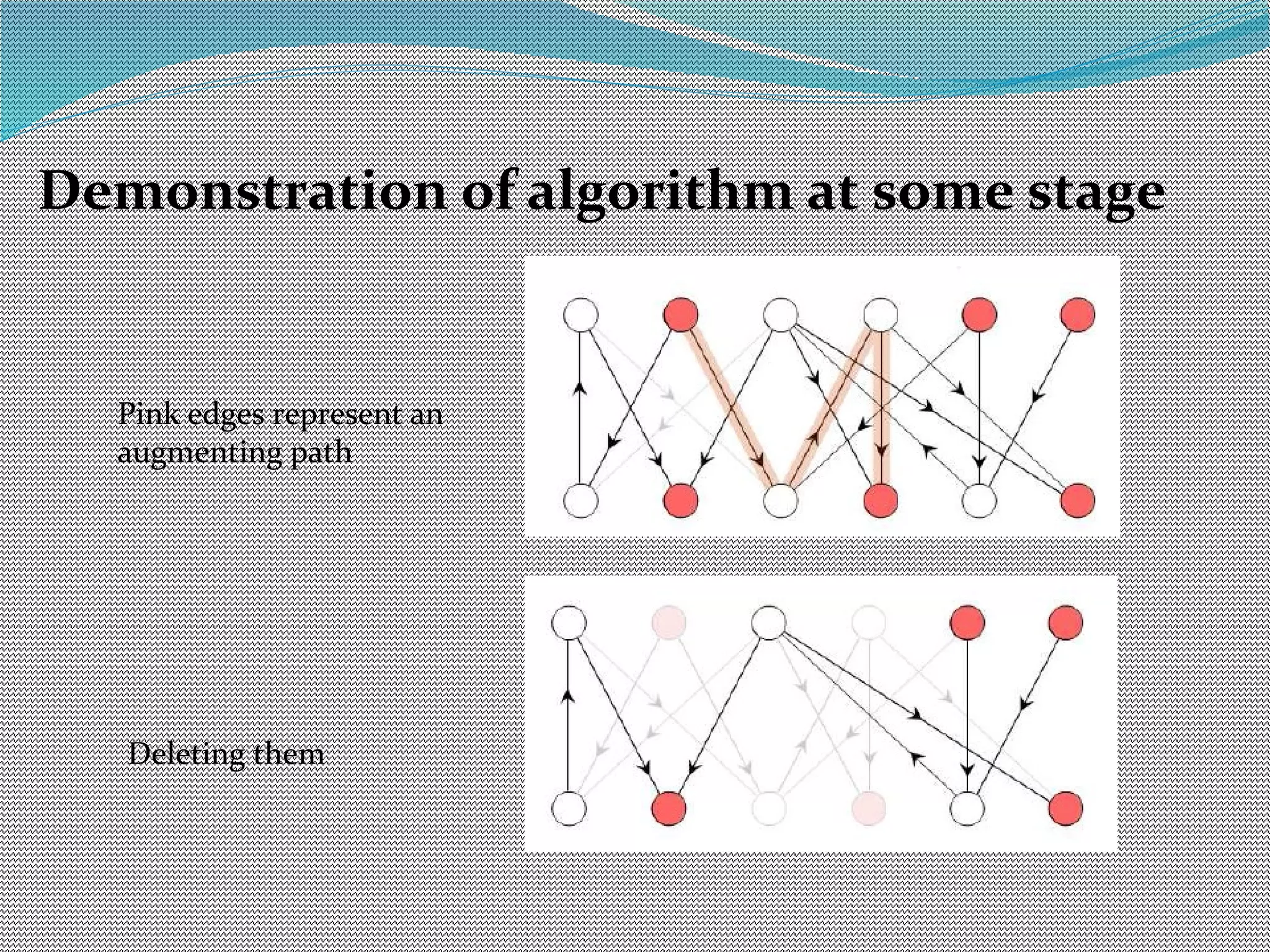
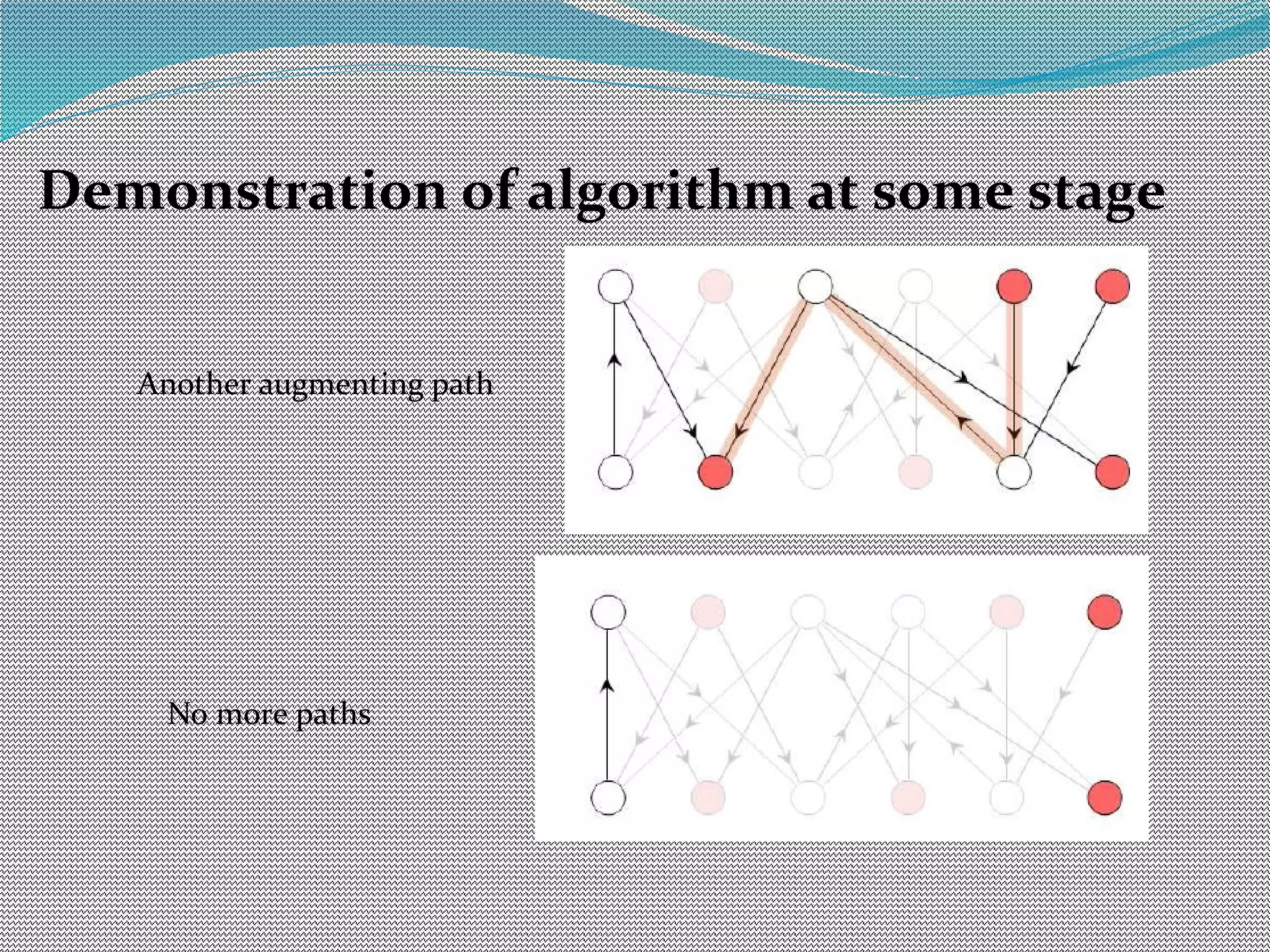
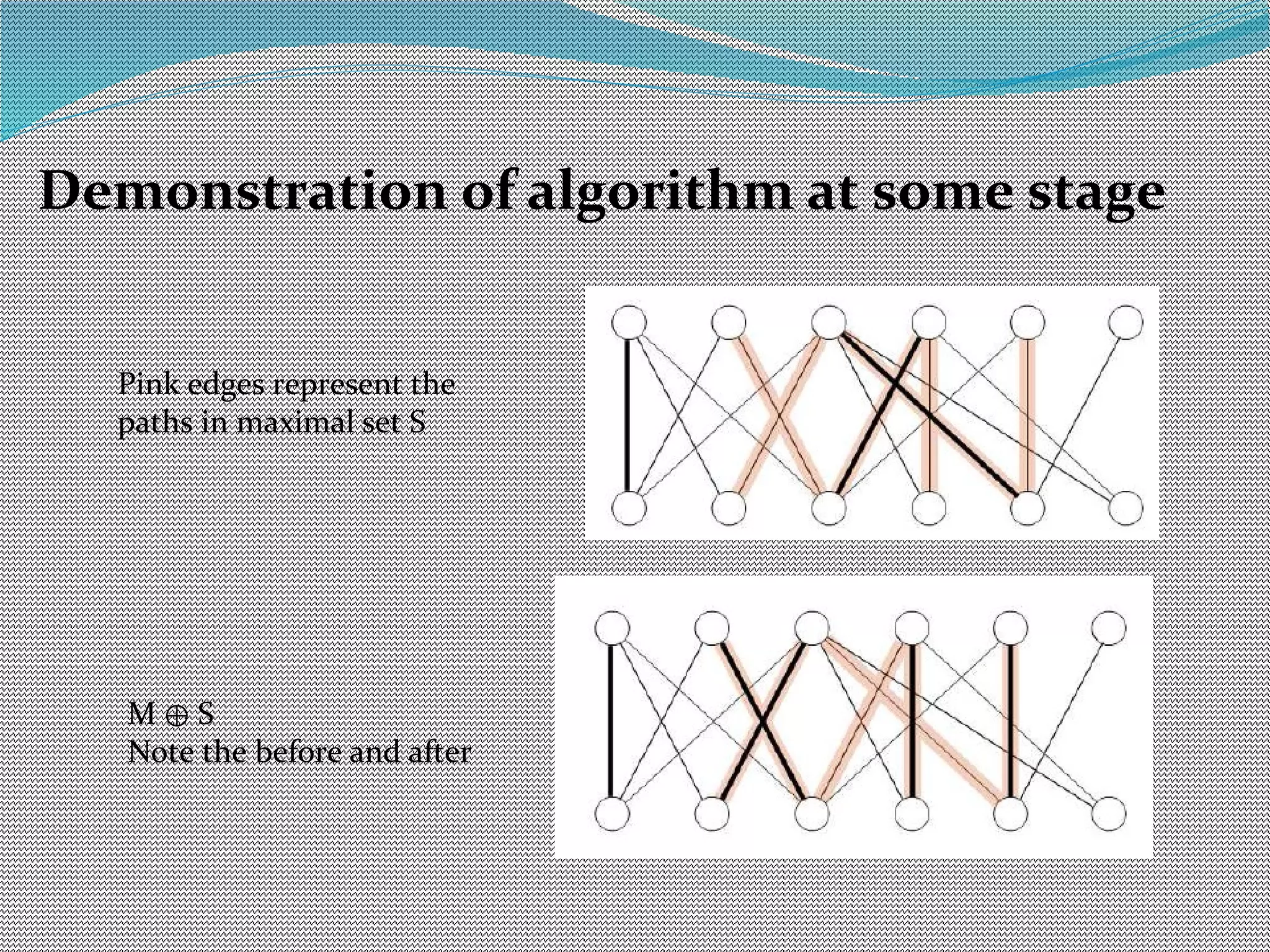
The document discusses algorithms for maximum matchings in bipartite graphs. It defines bipartite graphs and matchings. A simple algorithm finds augmenting paths and increments the matching size in each iteration, having complexity O(VE). The more efficient Hopcroft-Karp algorithm finds a maximal set of shortest augmenting paths and augments along all paths simultaneously in each iteration, achieving complexity O(√V√E). It demonstrates the algorithm augmenting the matching by alternating along paths in the maximal set.