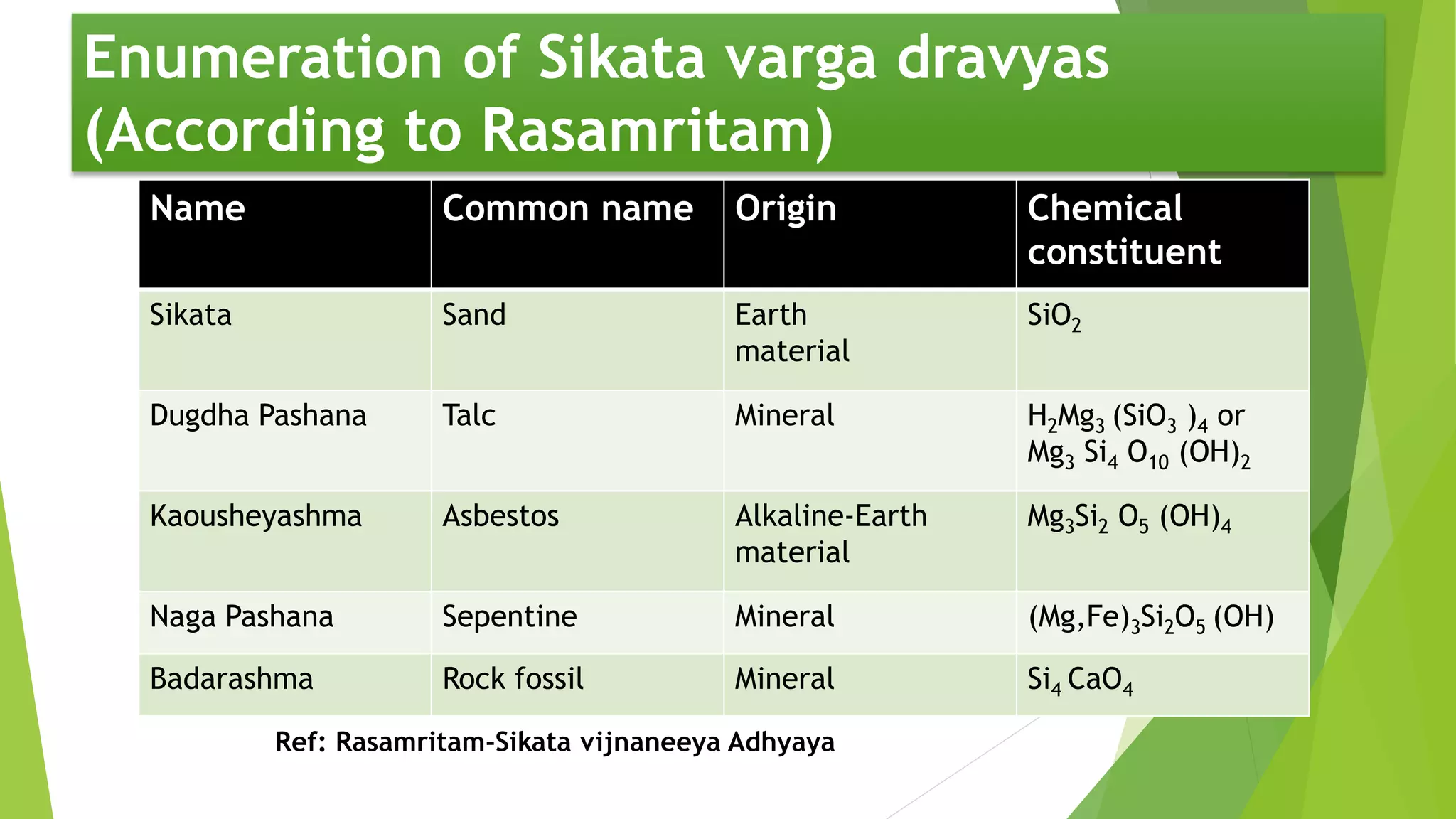
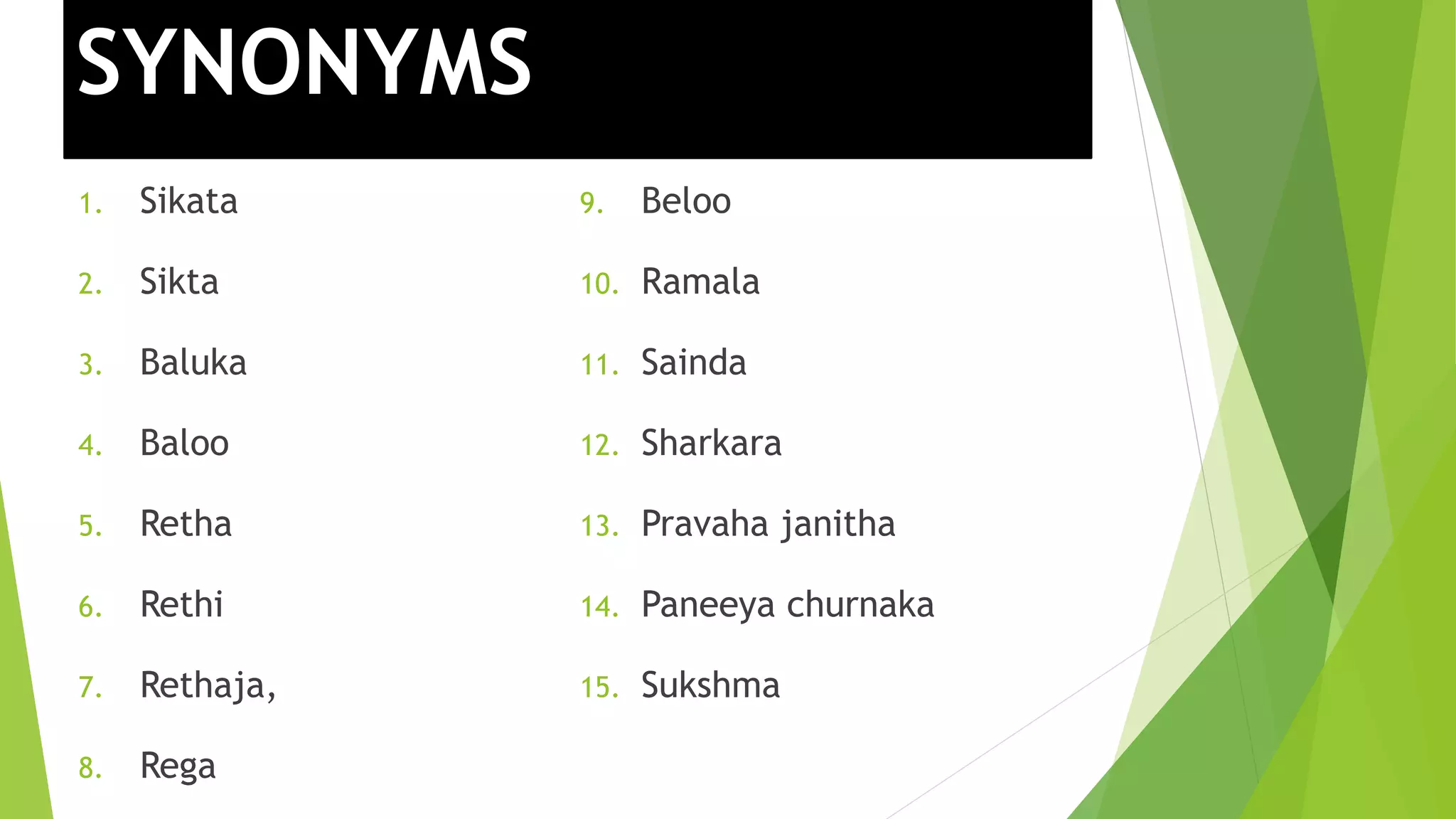
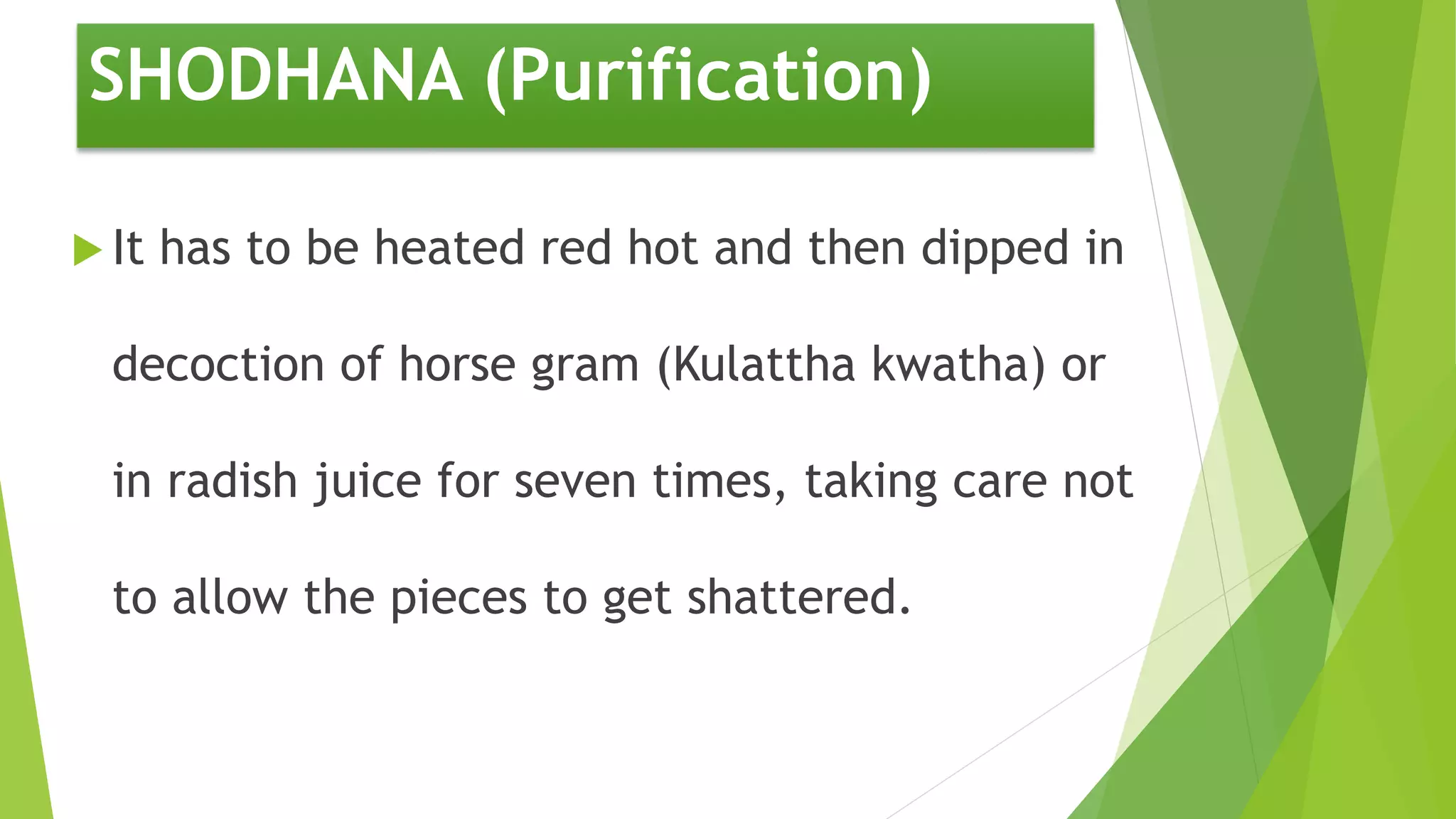
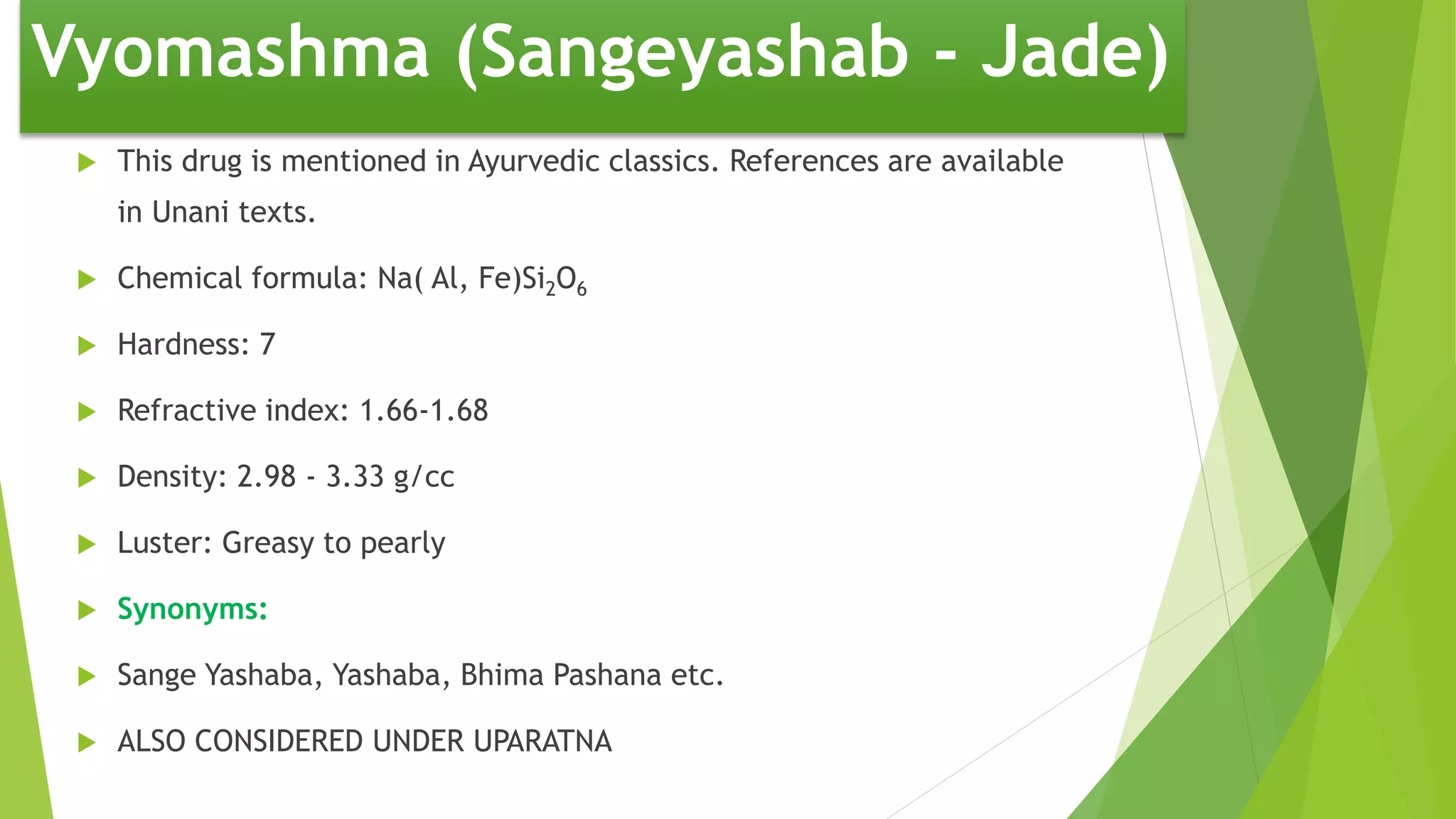
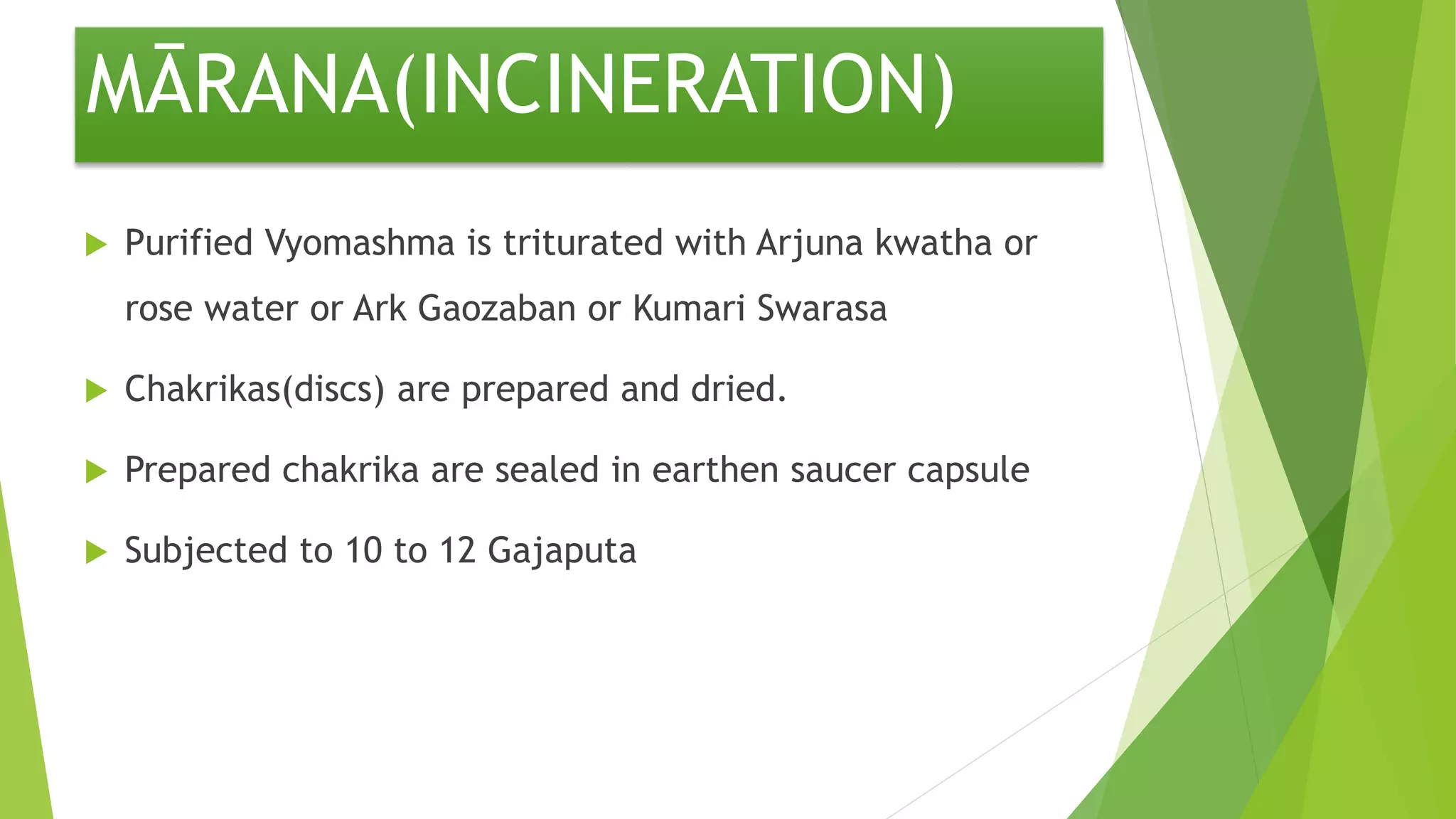
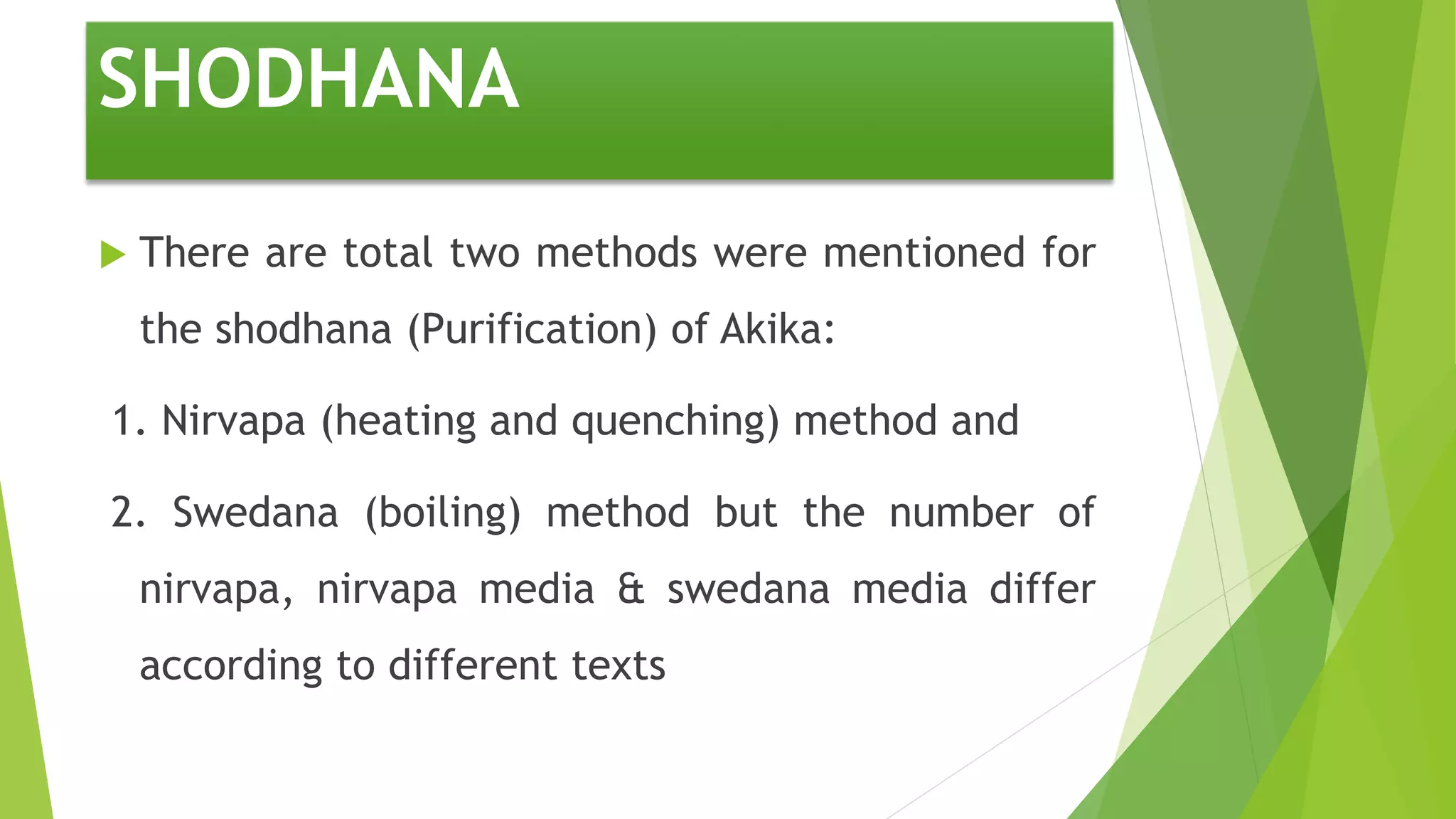
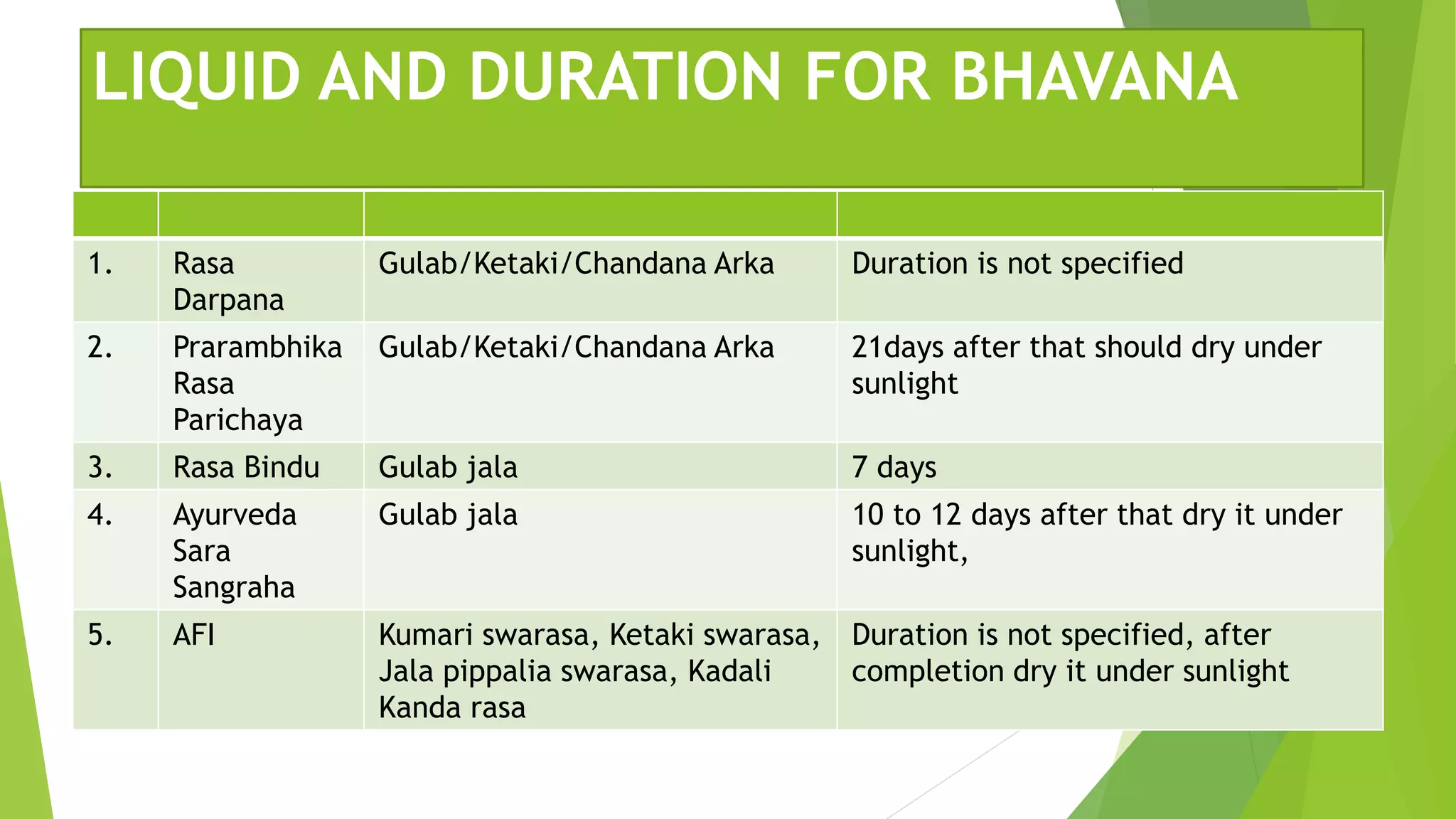
The document provides information on various types of Sikata varga drugs. It discusses Sikata (sand), Dugdhapashana (talc), Nagapashana (serpentine), and Badarashma (fossil norinite). For each drug, it describes synonyms, properties, therapeutic uses, formulations, and in some cases, purification processes. It traces the historical references of Sikata varga in ancient texts and provides taxonomic classifications developed in the 20th century. The document aims to enumerate and describe the key drugs classified under Sikata varga according to Ayurvedic literature.