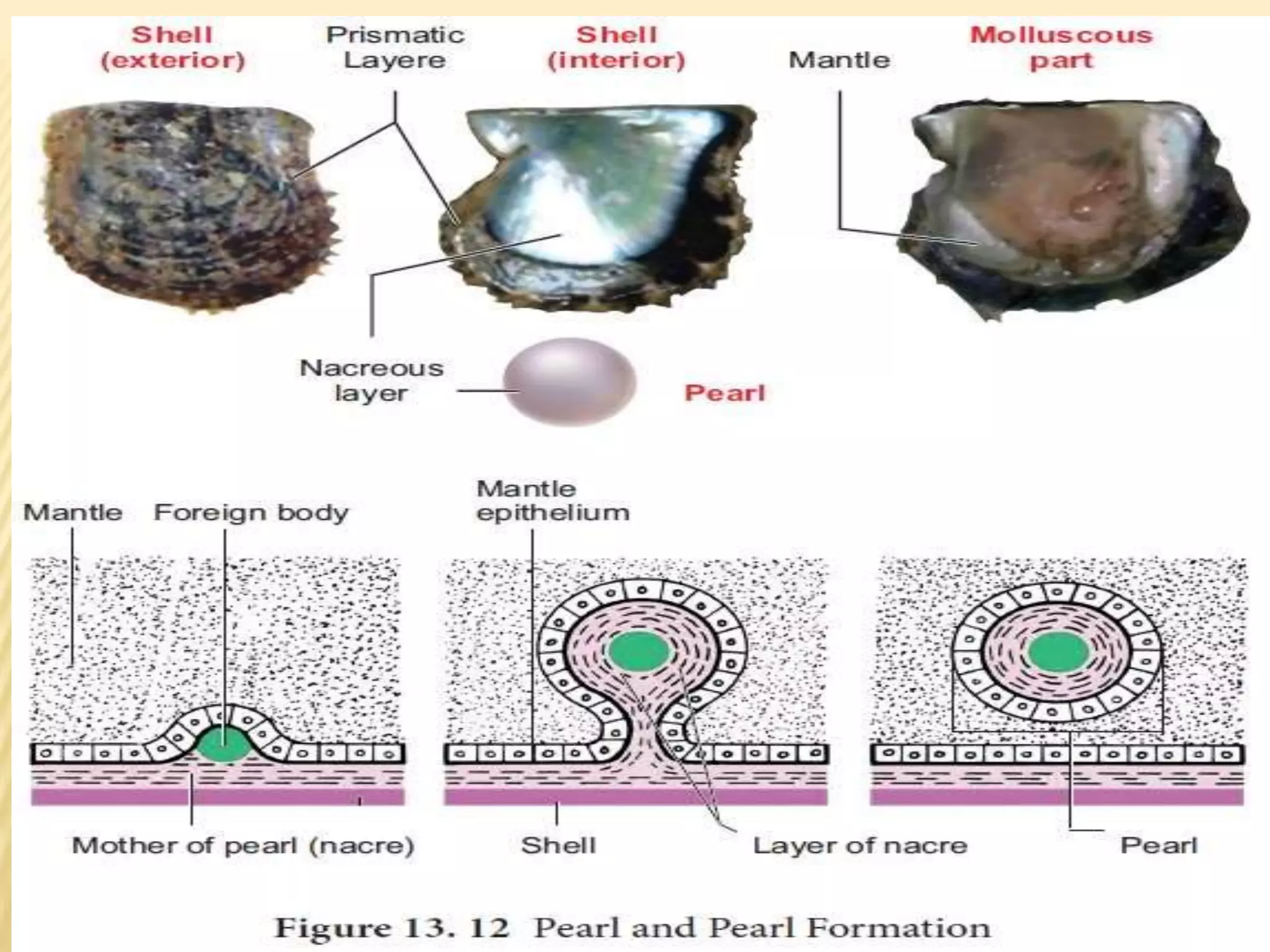
This document provides information on various types of ratnas (gems and precious stones) according to Ayurveda. It begins by defining ratnas as the best gems known for their qualities and properties. Ratnas are divided into animal and mineral products, as well as two main groups - ratna varga and upratna varga. Nine main ratnas are then described - manikya, mukta, parval, taksharya, pukhraaj, hira, neelam, gomeda, and vaidurya. For each ratna, the document provides details on chemical composition, qualities, doshas, shodhana (purification) process, and medicinal