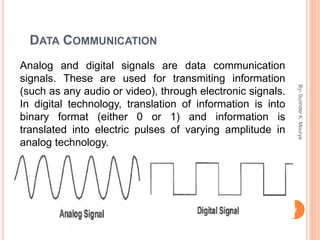
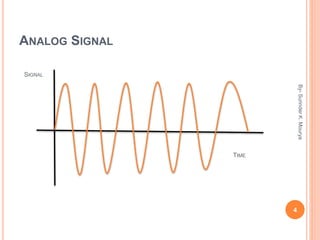
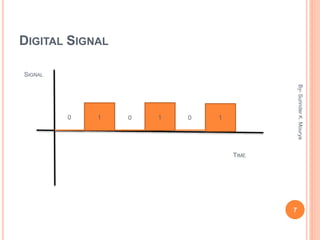
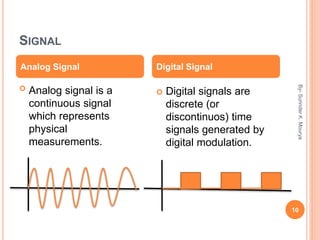
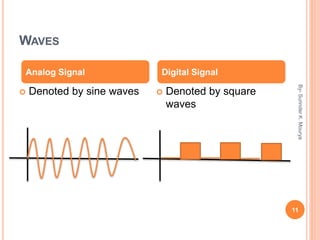
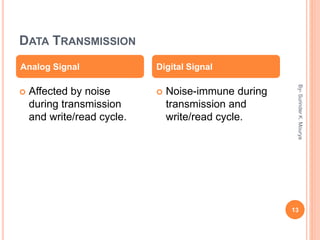
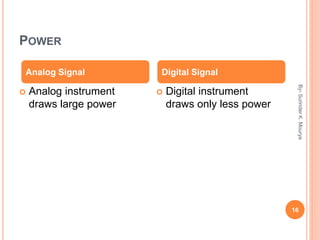
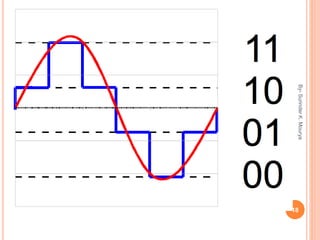
This document discusses analog and digital signals used for data communication. Analog signals are continuous over time and value, while digital signals are discrete using binary numbers. Some key differences are that analog signals can be affected by noise during transmission while digital signals are noise-immune, analog devices typically draw more power than digital, and digital signals are better suited for computing and memory storage while analog is used for audio/video. Examples of analog signals include voices and speedometers, while digital examples include computers, cameras and watches.