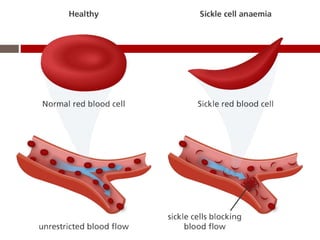
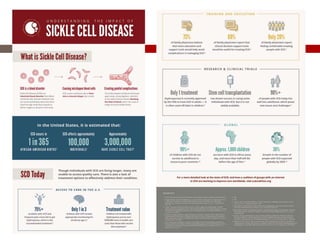
Zola, a 2-year old girl from Southern Africa recently moved to the US and has been experiencing numerous health issues including painful wounds that are slow to heal, swollen fingers and toes, fever, paleness, and pneumonia-like symptoms. An initial diagnosis would be anemia, and blood tests such as hemoglobin electrophoresis would be performed to diagnose sickle-cell anemia, which is caused by a genetic mutation resulting in abnormal sickle-shaped hemoglobin. Treatment options include medications, blood transfusions, and potentially a bone marrow transplant.