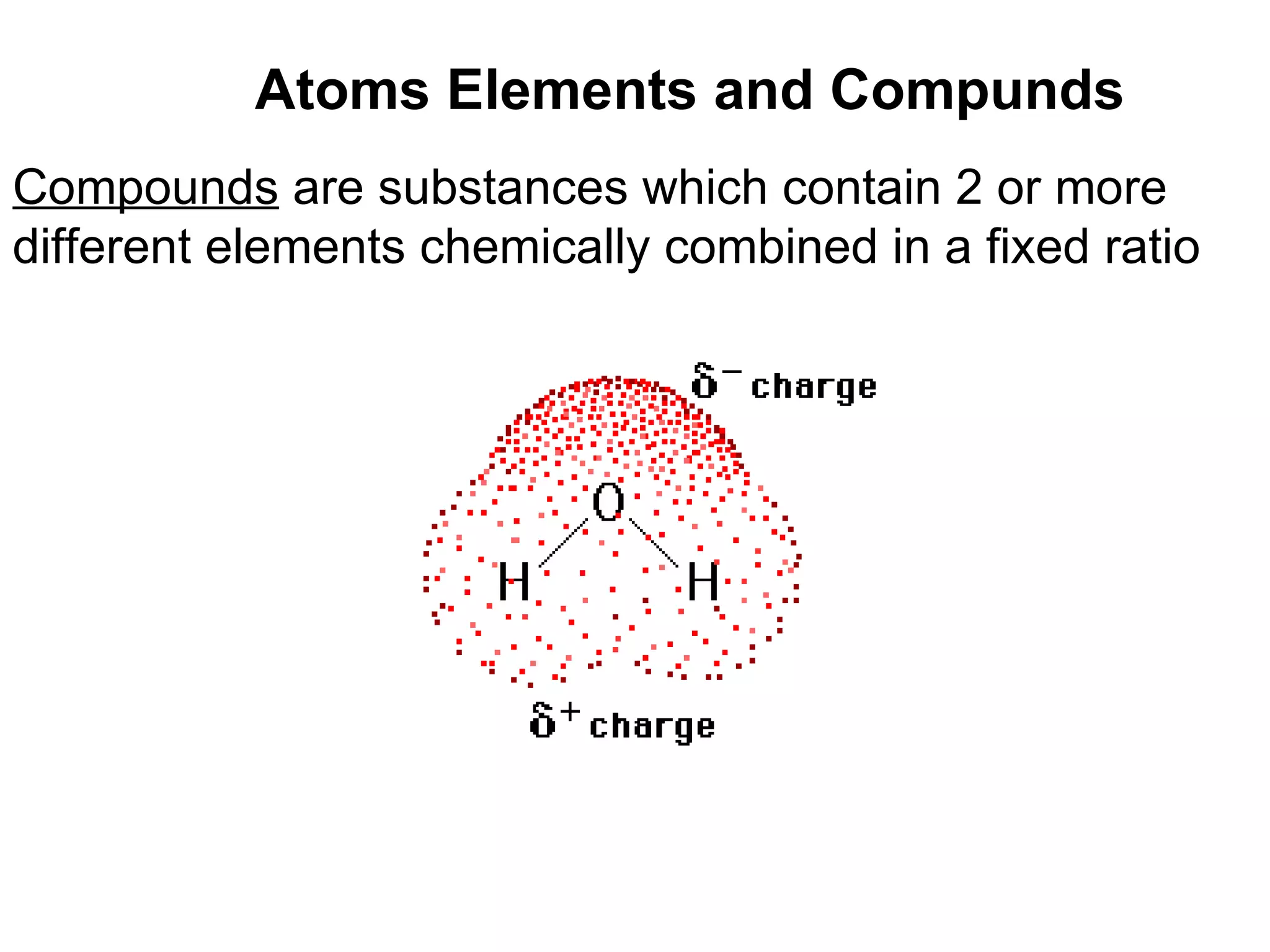
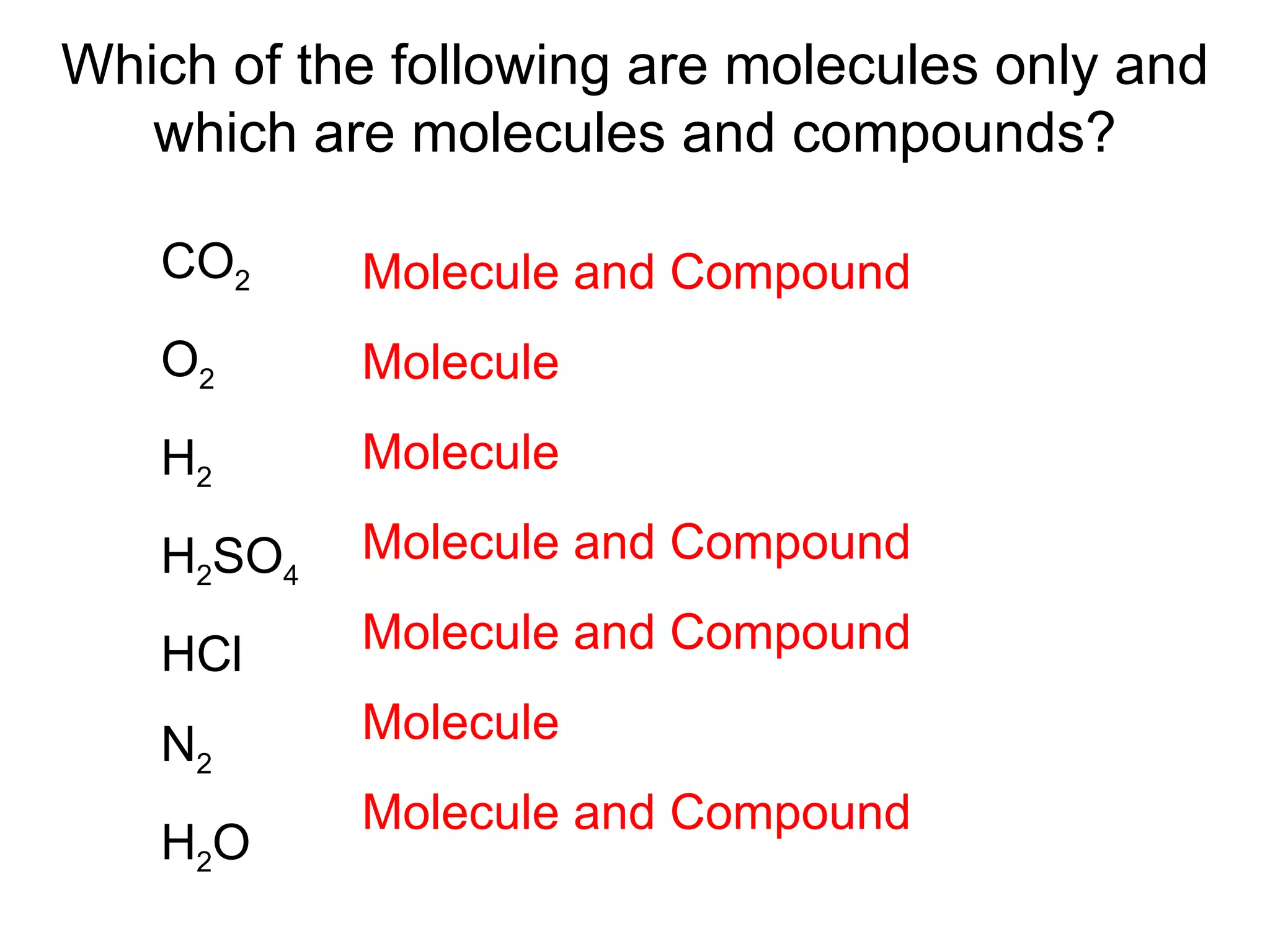
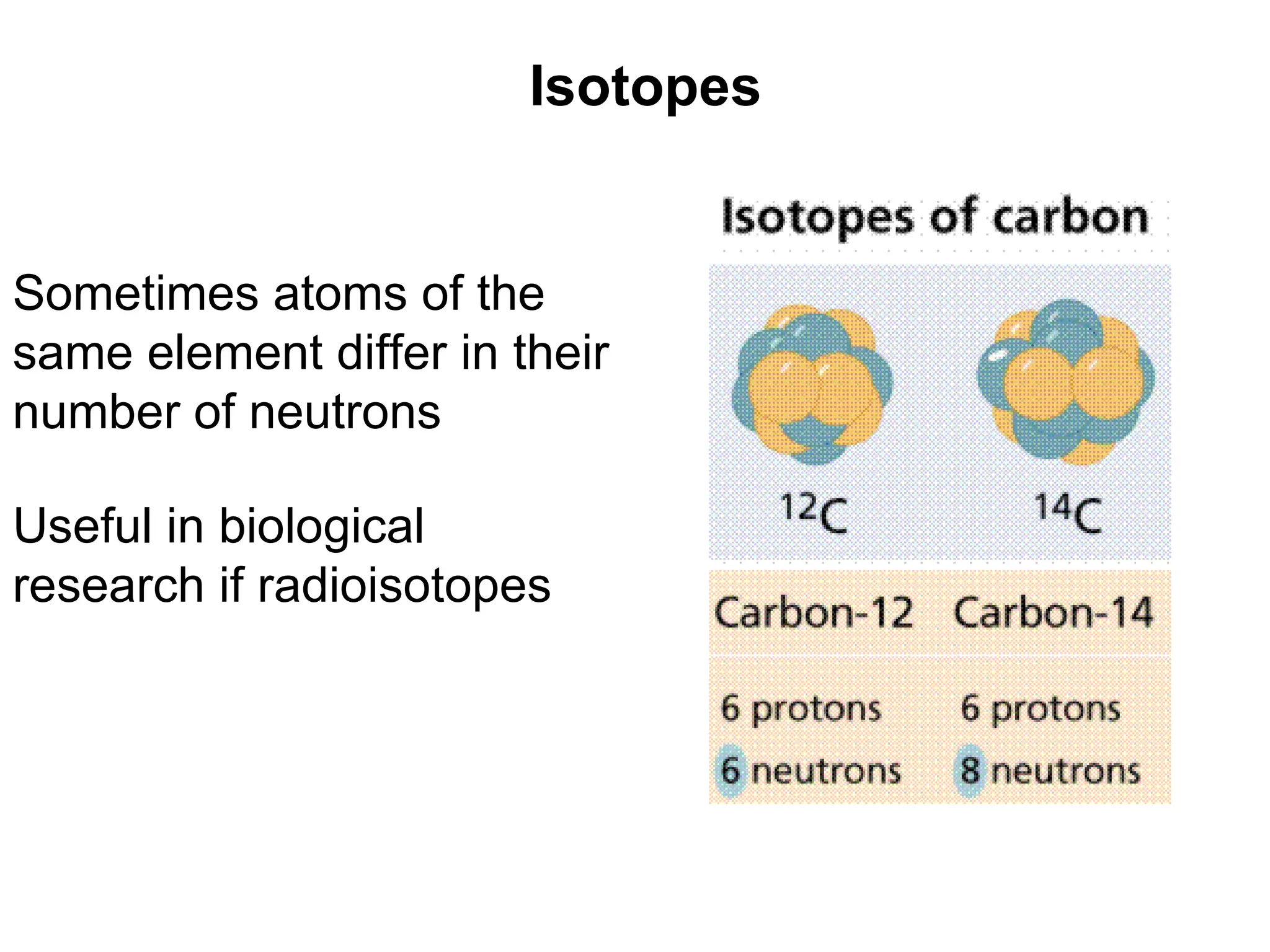
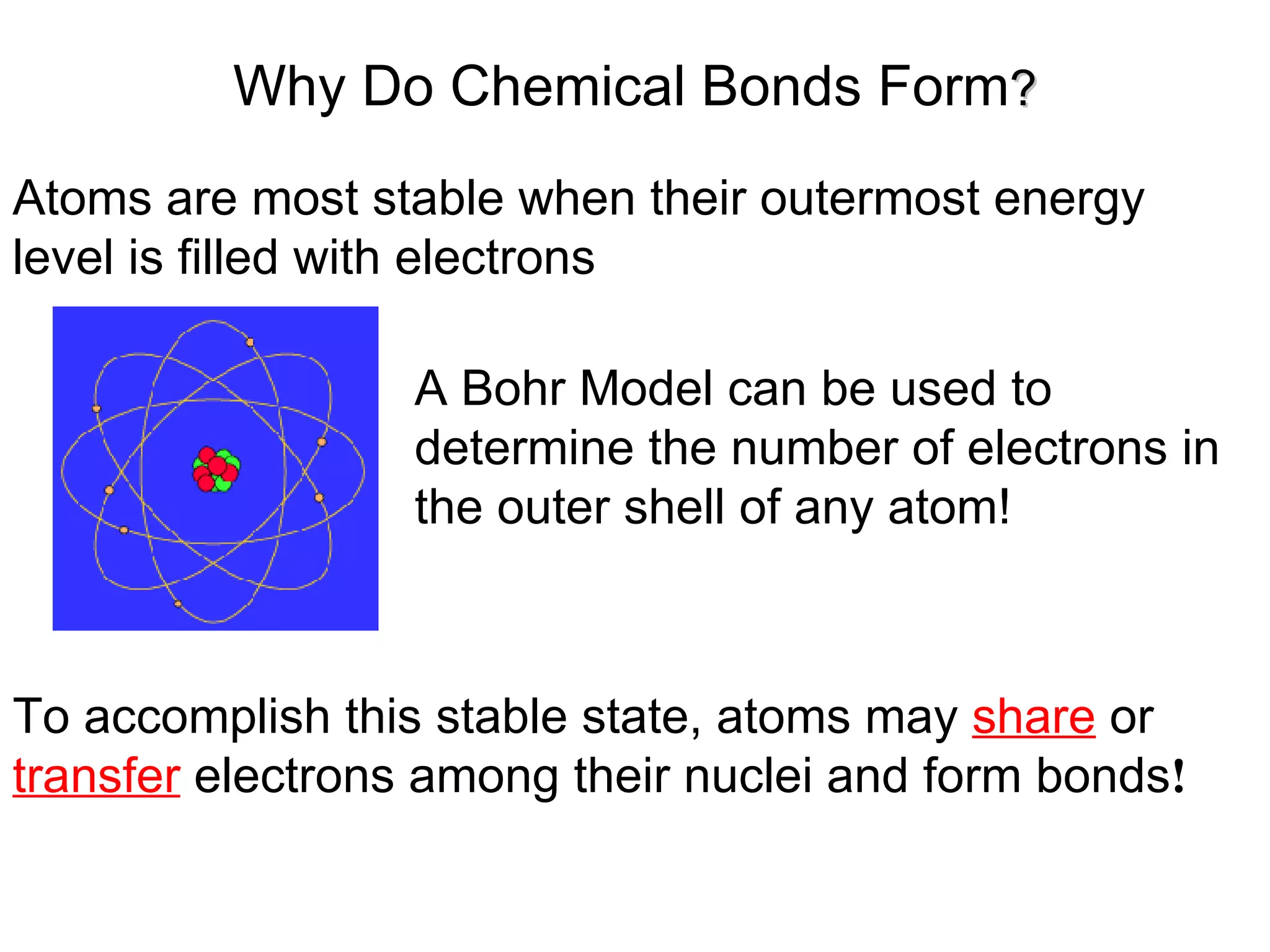
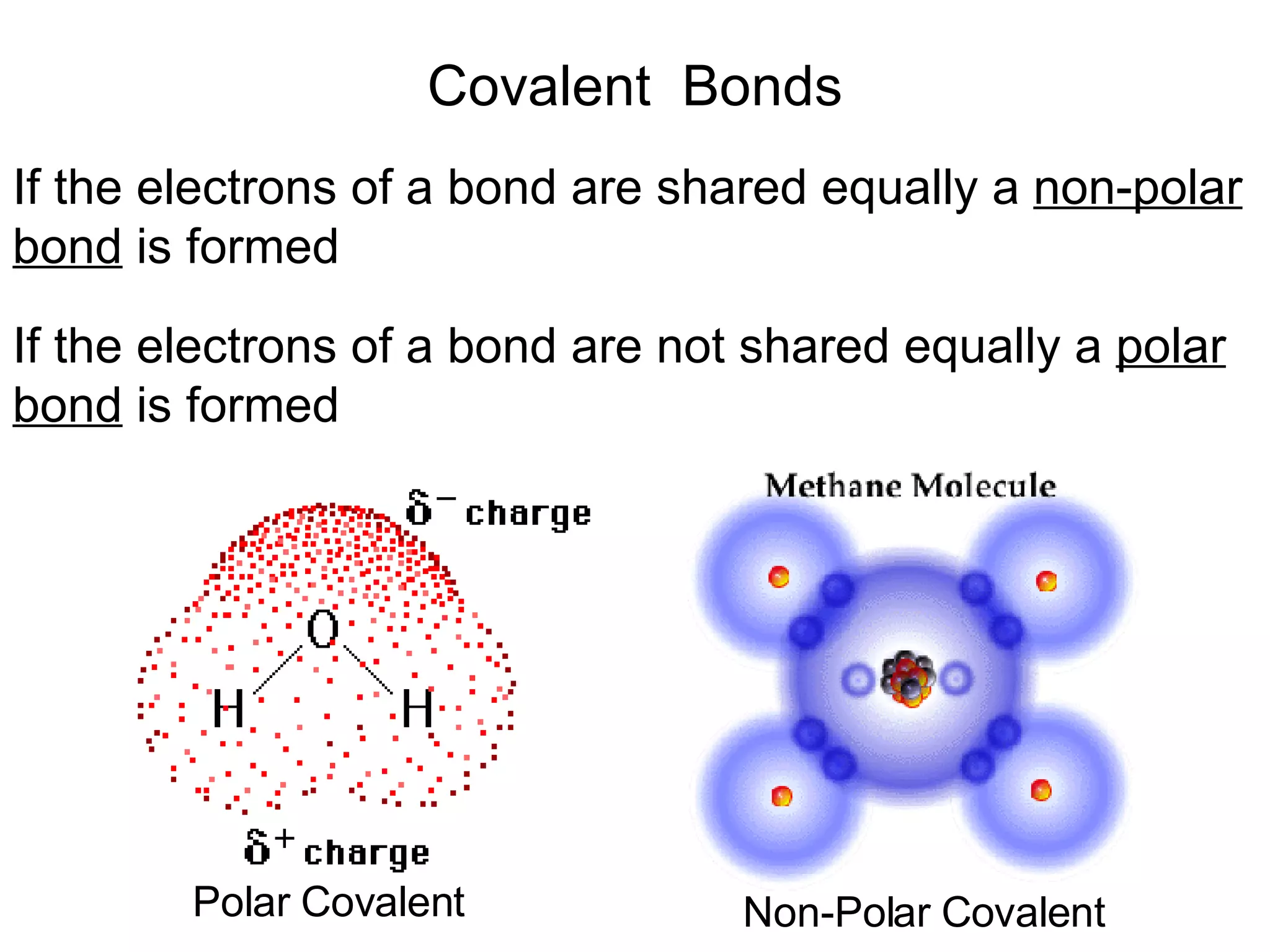
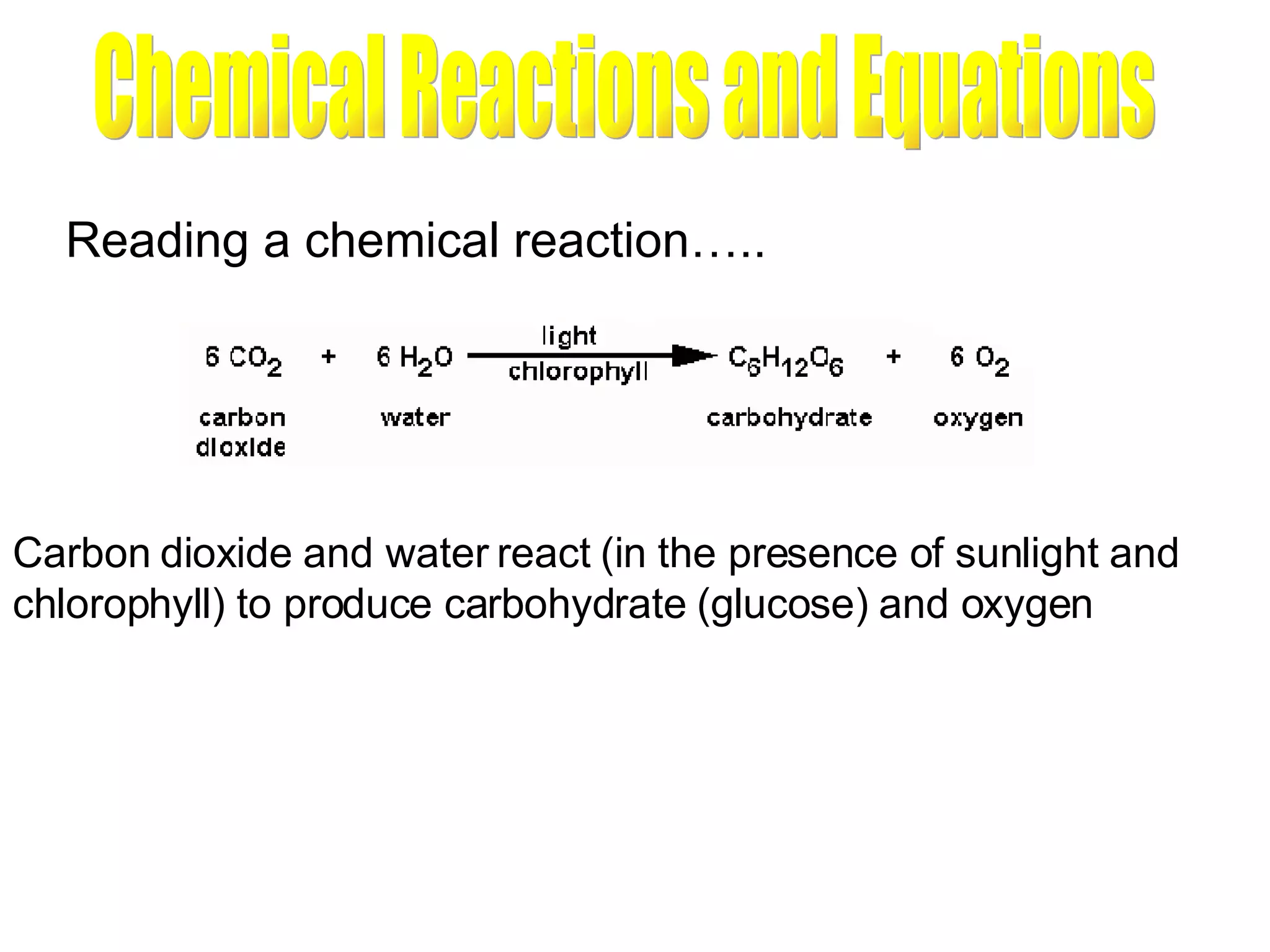
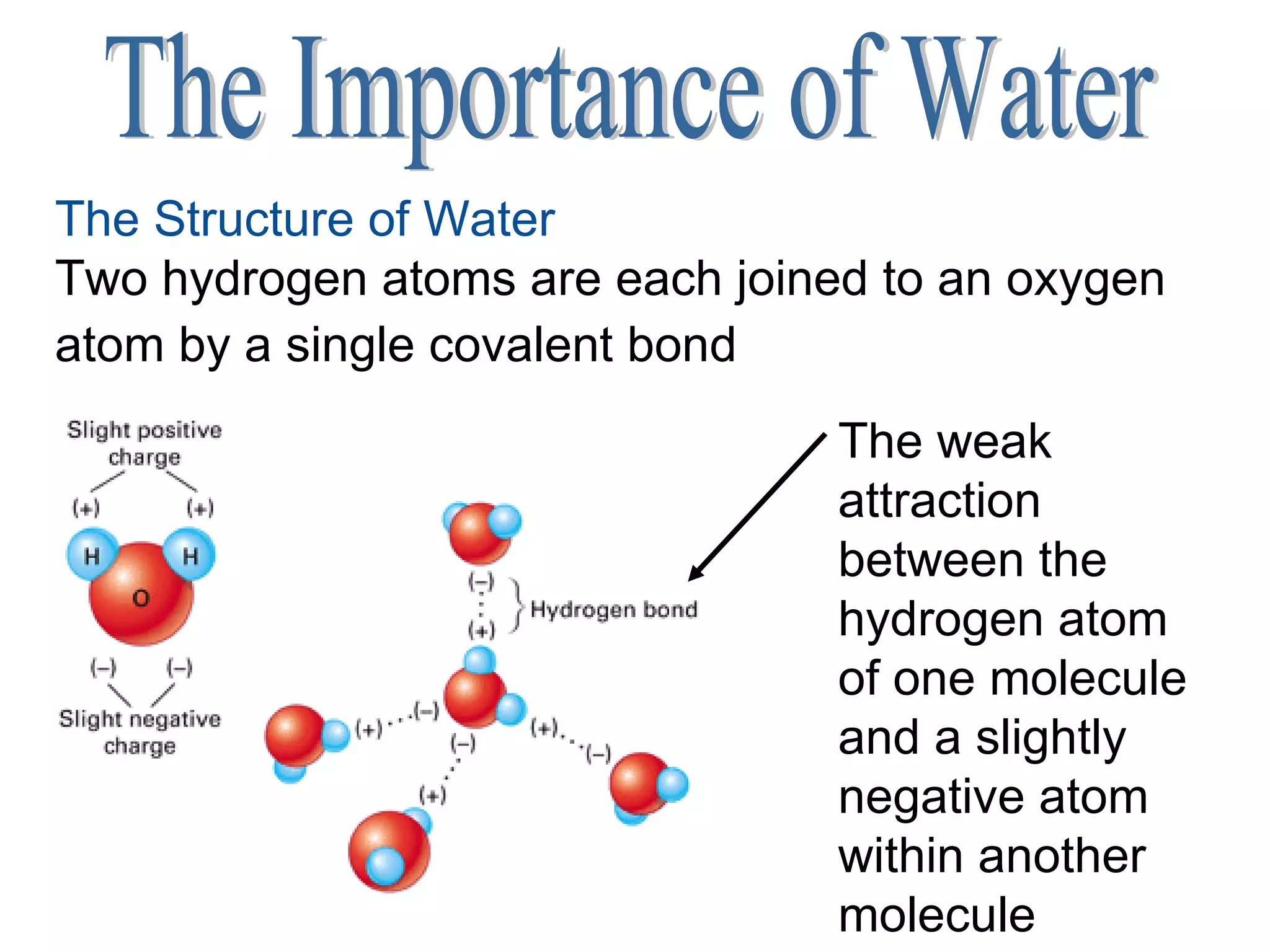
1) All cells and organisms are composed of chemicals and life processes involve chemical reactions. Basic chemistry concepts like matter, atoms, molecules, compounds, and chemical bonds are important for understanding biology.
2) Key concepts covered include the structure of atoms and molecules, ionic and covalent bonds, chemical reactions and equations, the unique properties of water, and the role of ions and pH in living cells.
3) A solid foundation in basic chemistry concepts is necessary for understanding the complexity and elegance of life at the cellular and molecular levels.