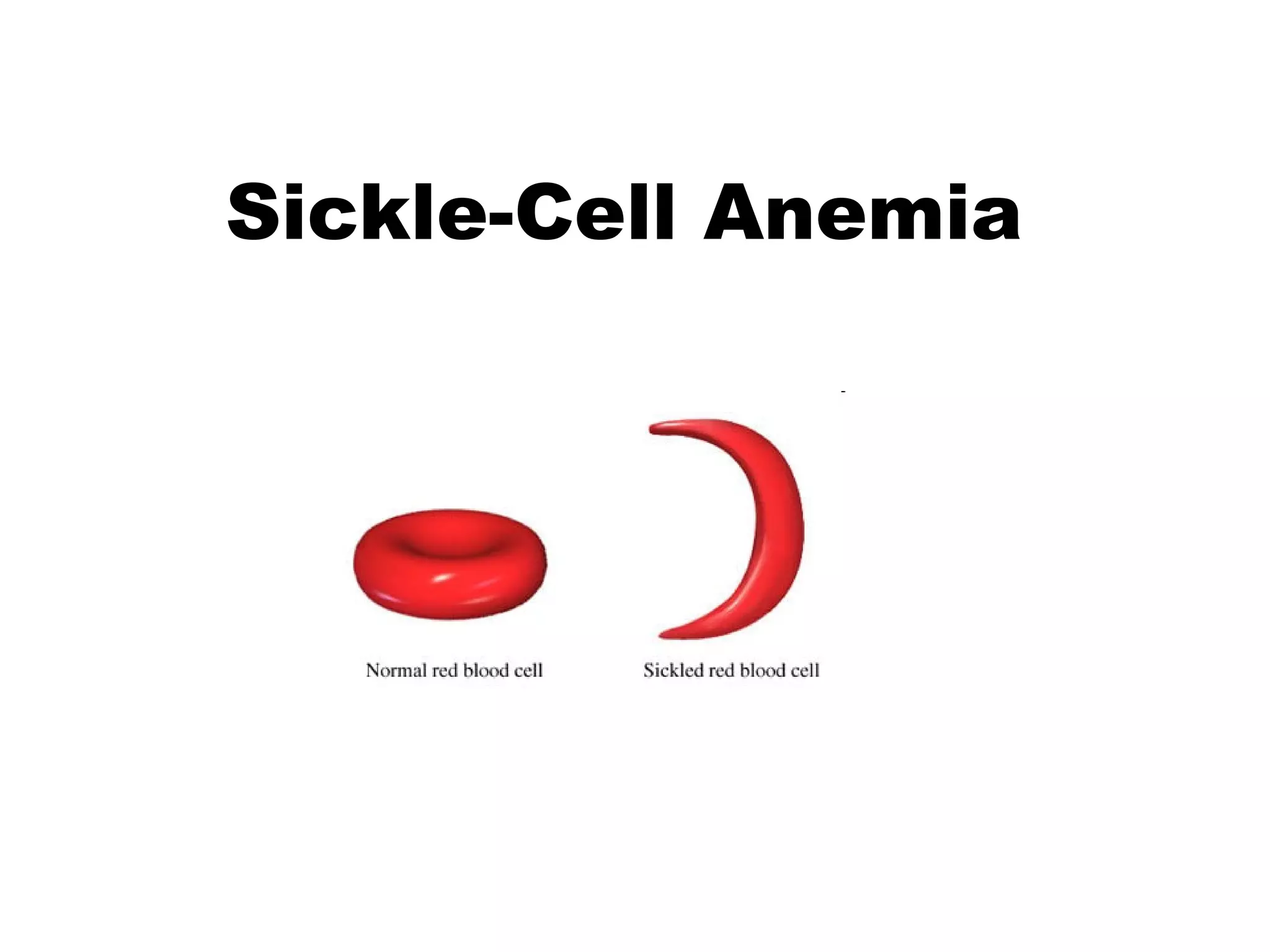
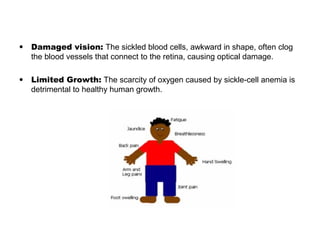
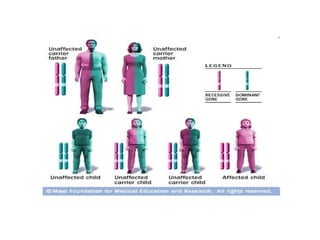
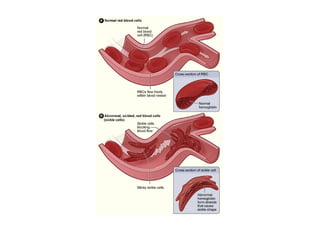
Sickle-cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder caused by an autosomal recessive trait where the normal hemoglobin A is replaced with abnormal hemoglobin S. Symptoms include anemia from the breakdown of red blood cells, frequent pain from blockages in blood vessels, jaundice from liver damage, and limited growth from low oxygen levels. Treatments involve folic acid, pain medications, and procedures for complications, but there is no cure. It predominantly affects those of African descent, and while carriers are resistant to malaria, full sickle-cell anemia can have severe symptoms.