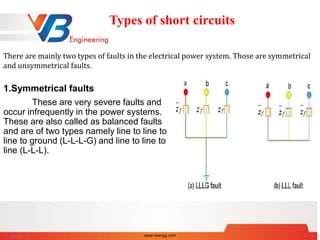
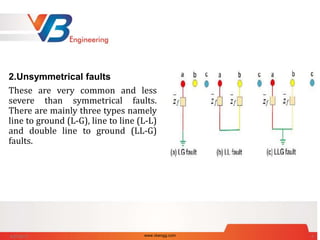
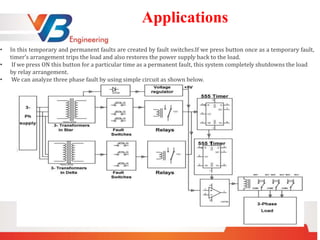
A short circuit is a fault characterized by a low resistance path in a circuit, often caused by loose wires or moisture. Two main types of electrical faults are symmetrical (less common and severe) and unsymmetrical (more common and less severe), with various causes including weather, equipment failures, and human errors. Faults can lead to dangerous overcurrents, equipment damage, and electrical fires, requiring protective devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and relays to mitigate these risks.