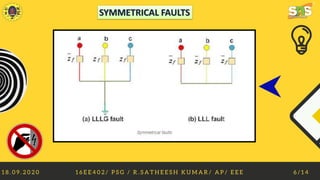
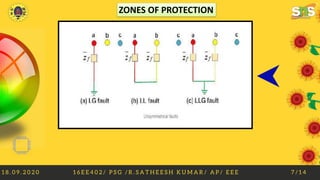
This document discusses faults in electrical power systems. It defines a fault as any abnormal electric current, such as a short circuit. There are two main types of faults: symmetrical faults, which are severe but rare, including line-to-line-to-ground and line-to-line faults; and unsymmetrical faults, which are more common and less severe, including line-to-ground, line-to-line, and double line-to-ground faults. Faults can be caused by weather conditions, equipment failures, human errors, or fires. Effects of faults include overcurrent, danger to personnel, equipment loss, and electrical fires. Fault limiting devices like fuses, circuit breakers, and relays are