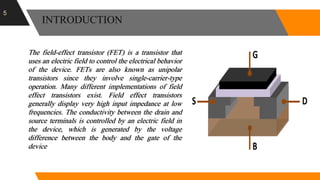
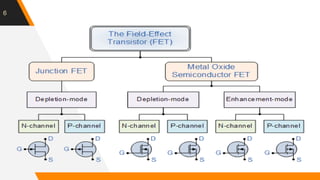
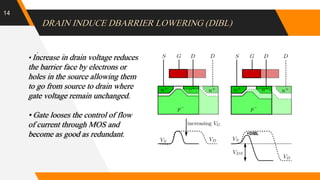
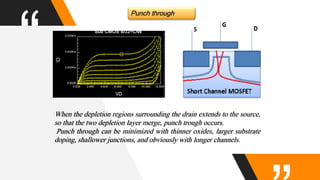
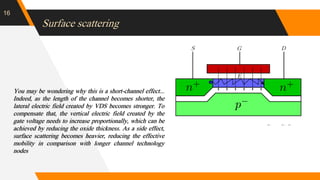
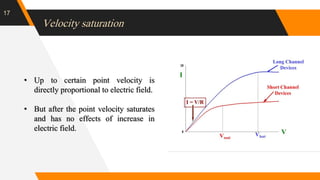
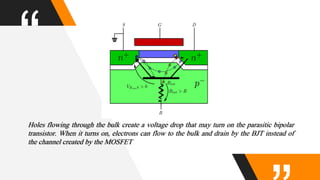
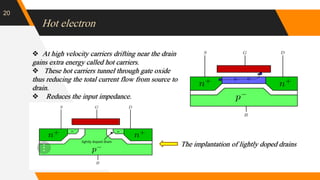
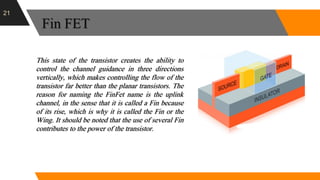
The document discusses the short channel effect in field-effect transistors (FETs), particularly focusing on the challenges posed by miniaturization such as drain-induced barrier lowering and punch through. It highlights the importance of controlling electric fields in both vertical and horizontal dimensions to mitigate performance degradation in miniaturized devices. Additionally, the implementation of FinFET technology offers improved control over channel guidance, enhancing transistor performance compared to traditional planar designs.