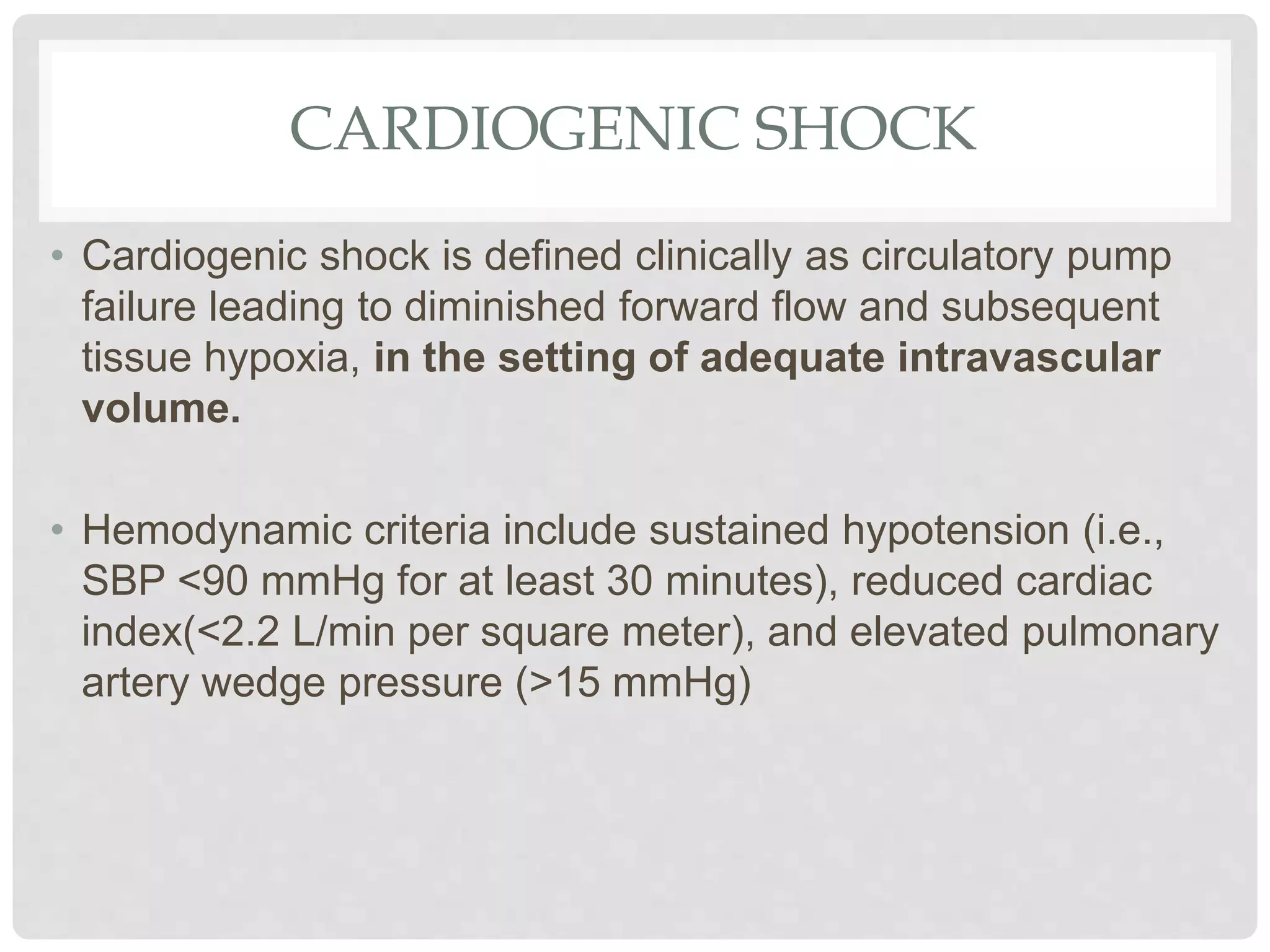
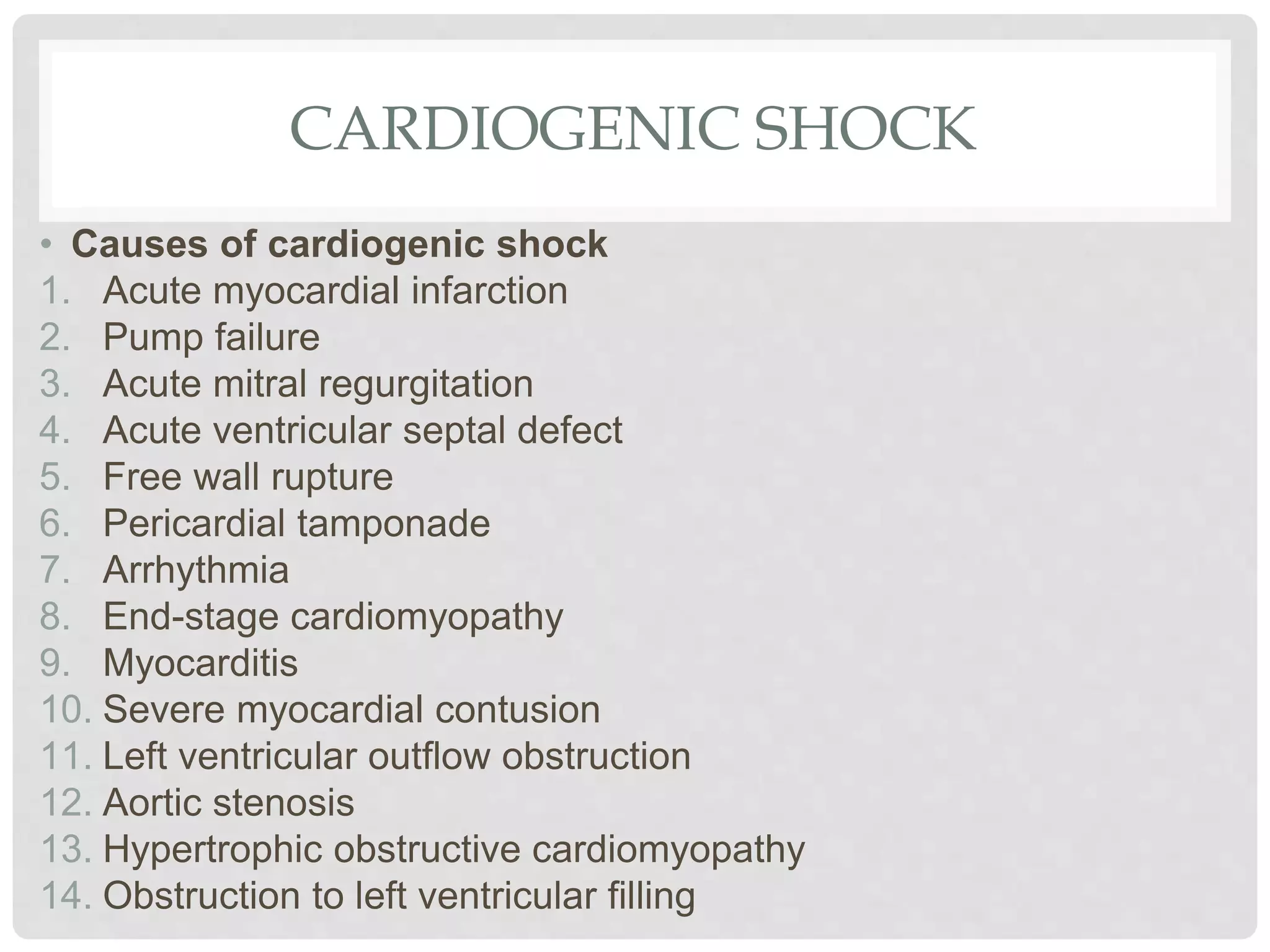
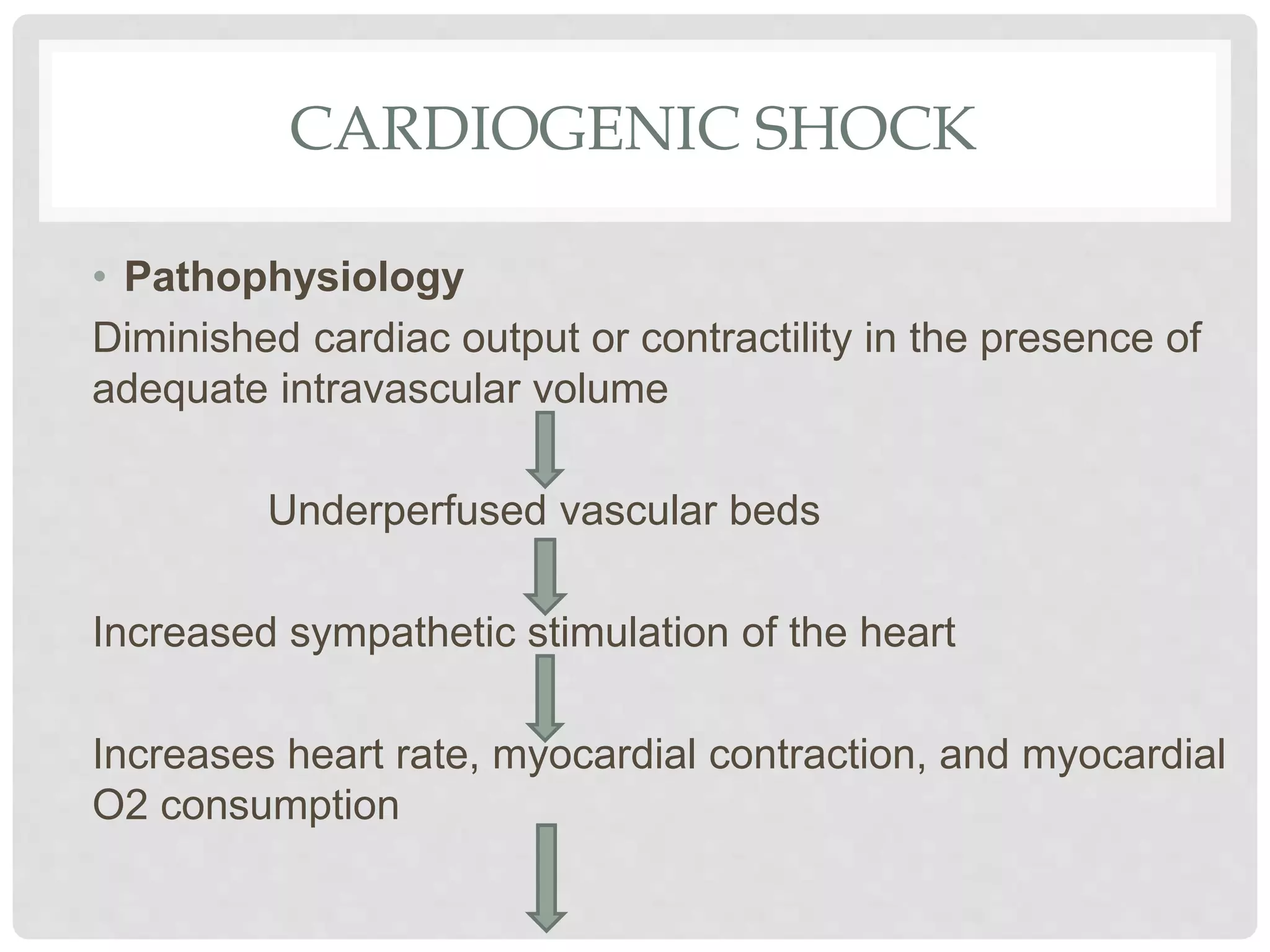
1. Shock is defined as inadequate tissue perfusion resulting from decreased delivery of oxygen and nutrients and inadequate removal of waste from cells.
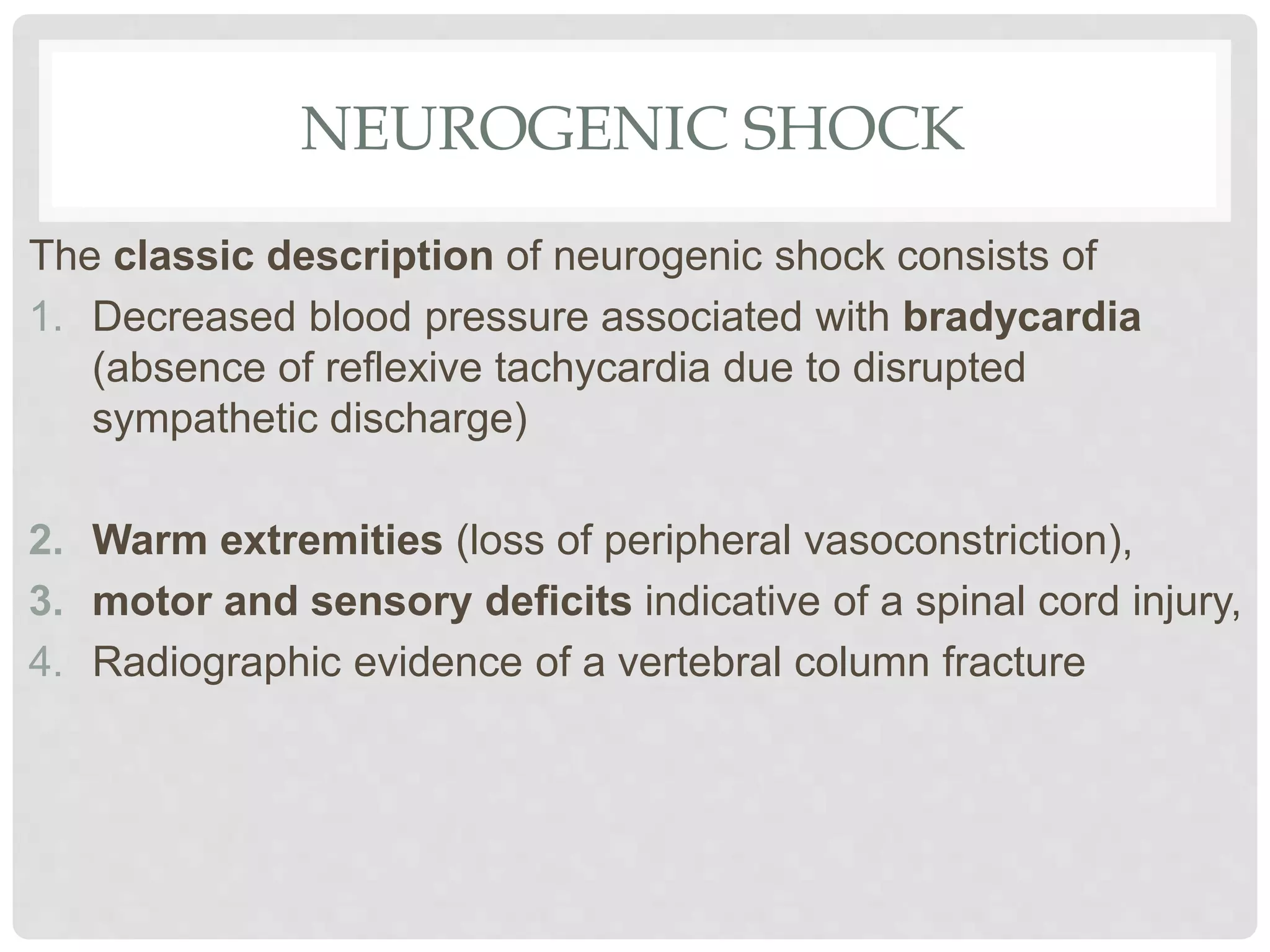
2. There are four main types of shock: hypovolemic, distributive, cardiogenic, and obstructive.
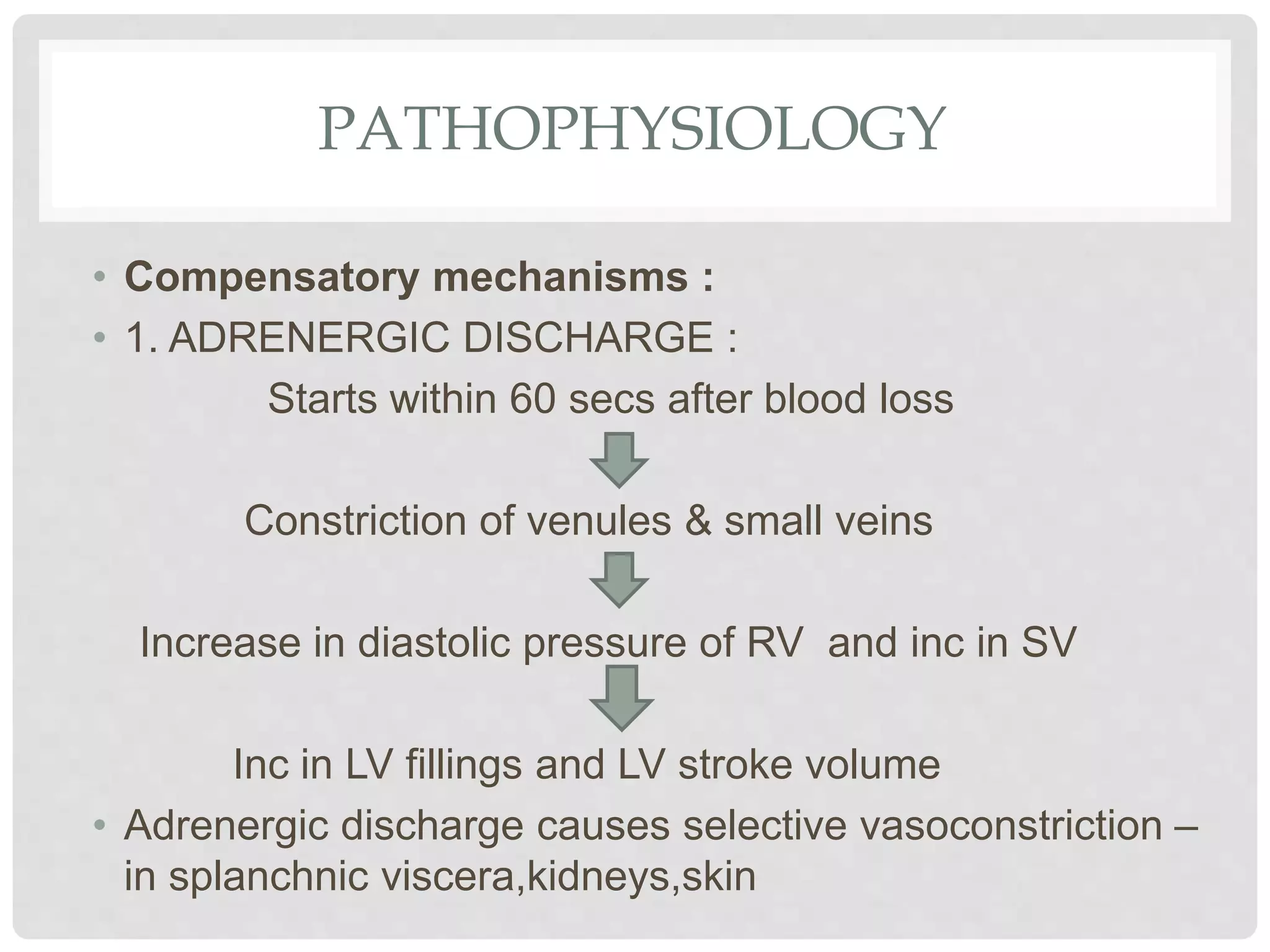
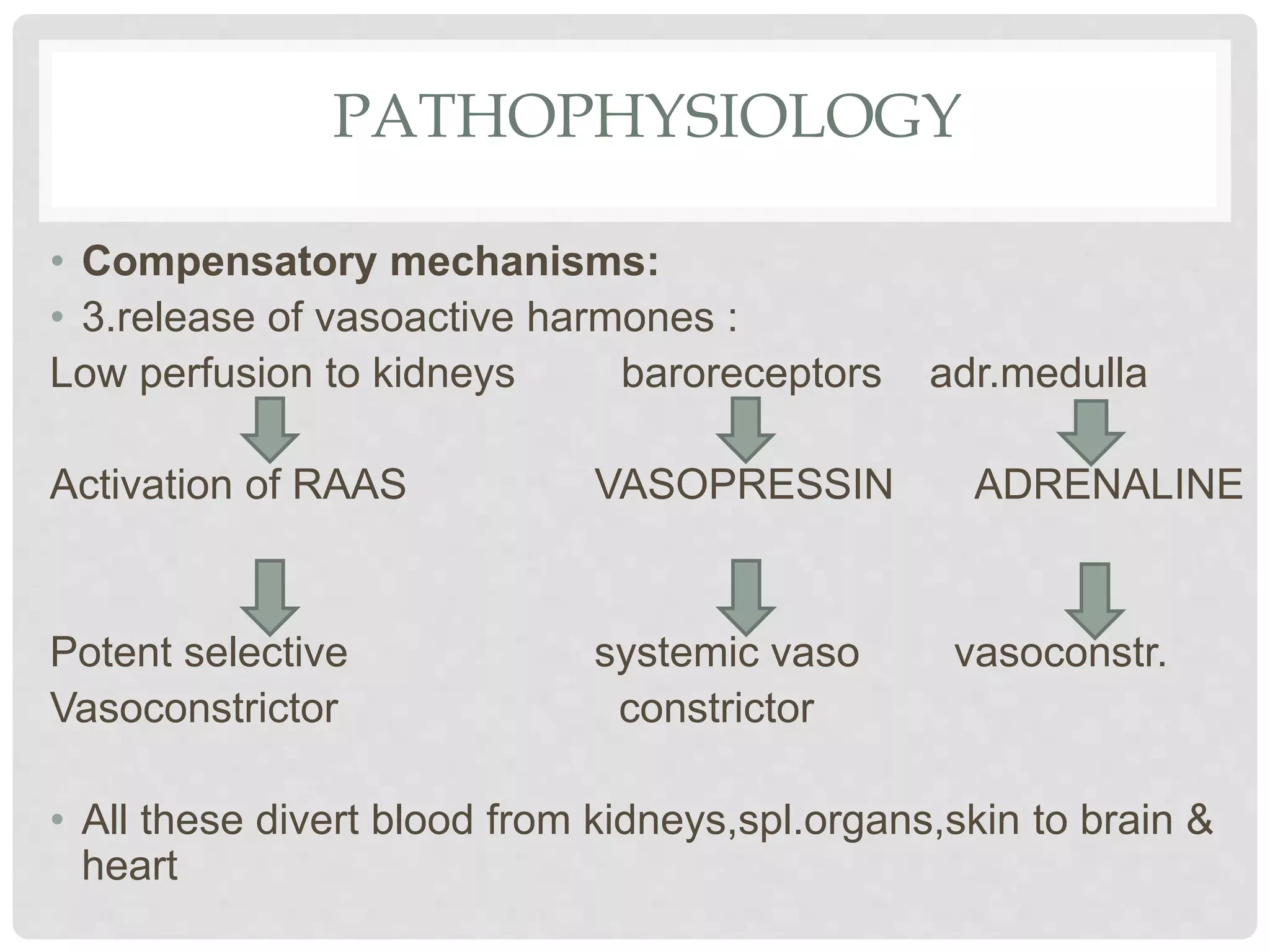
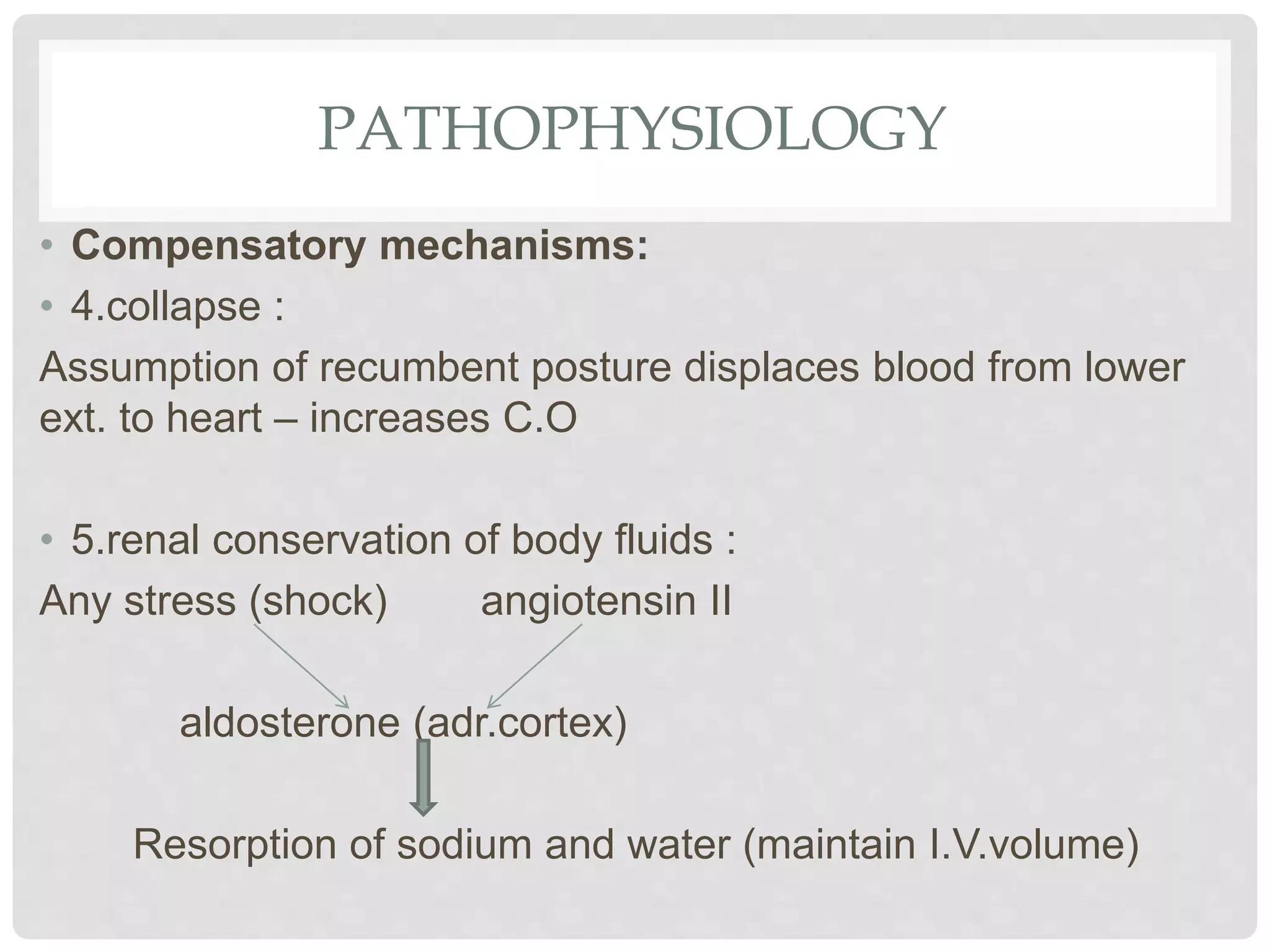
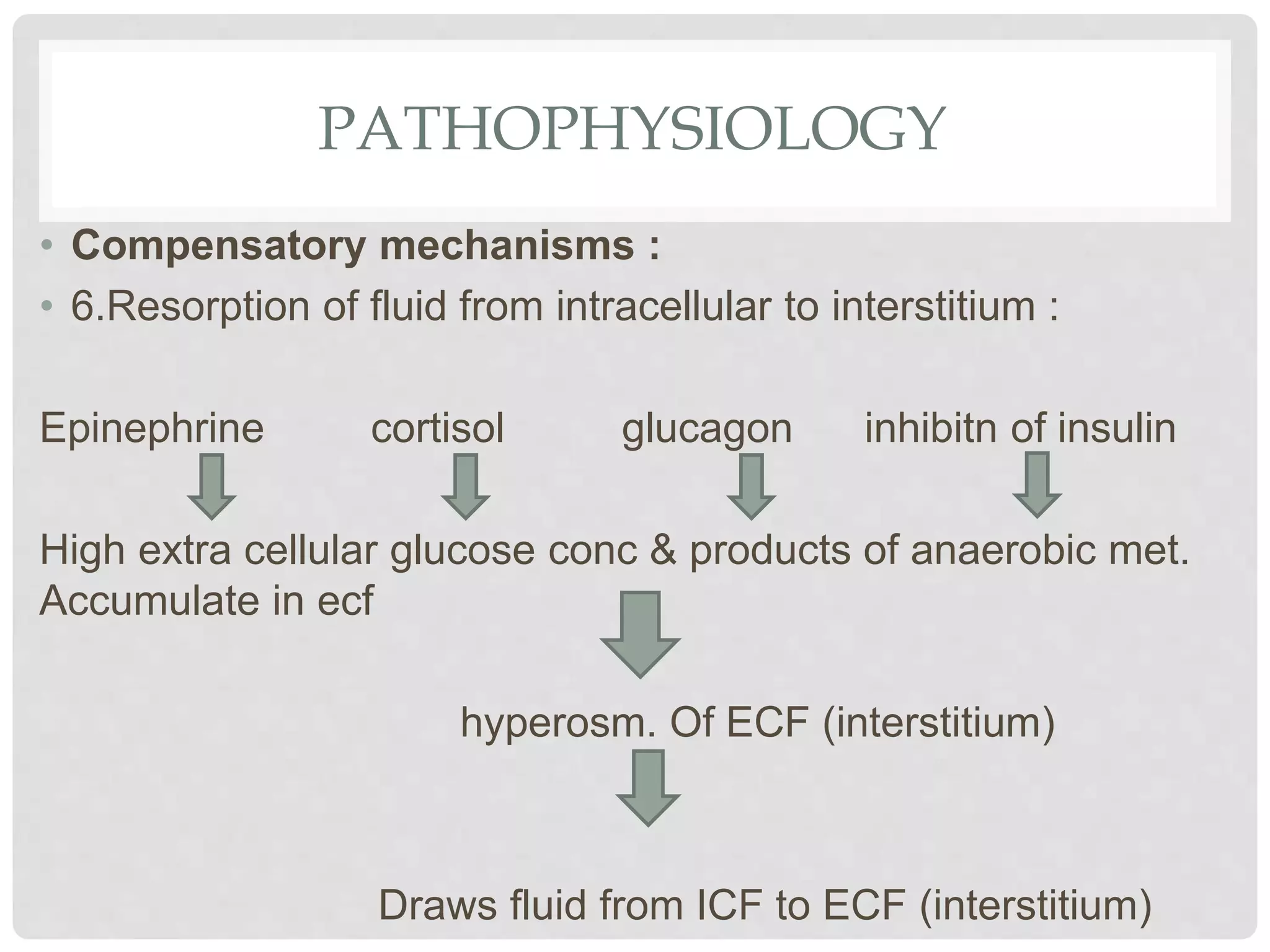
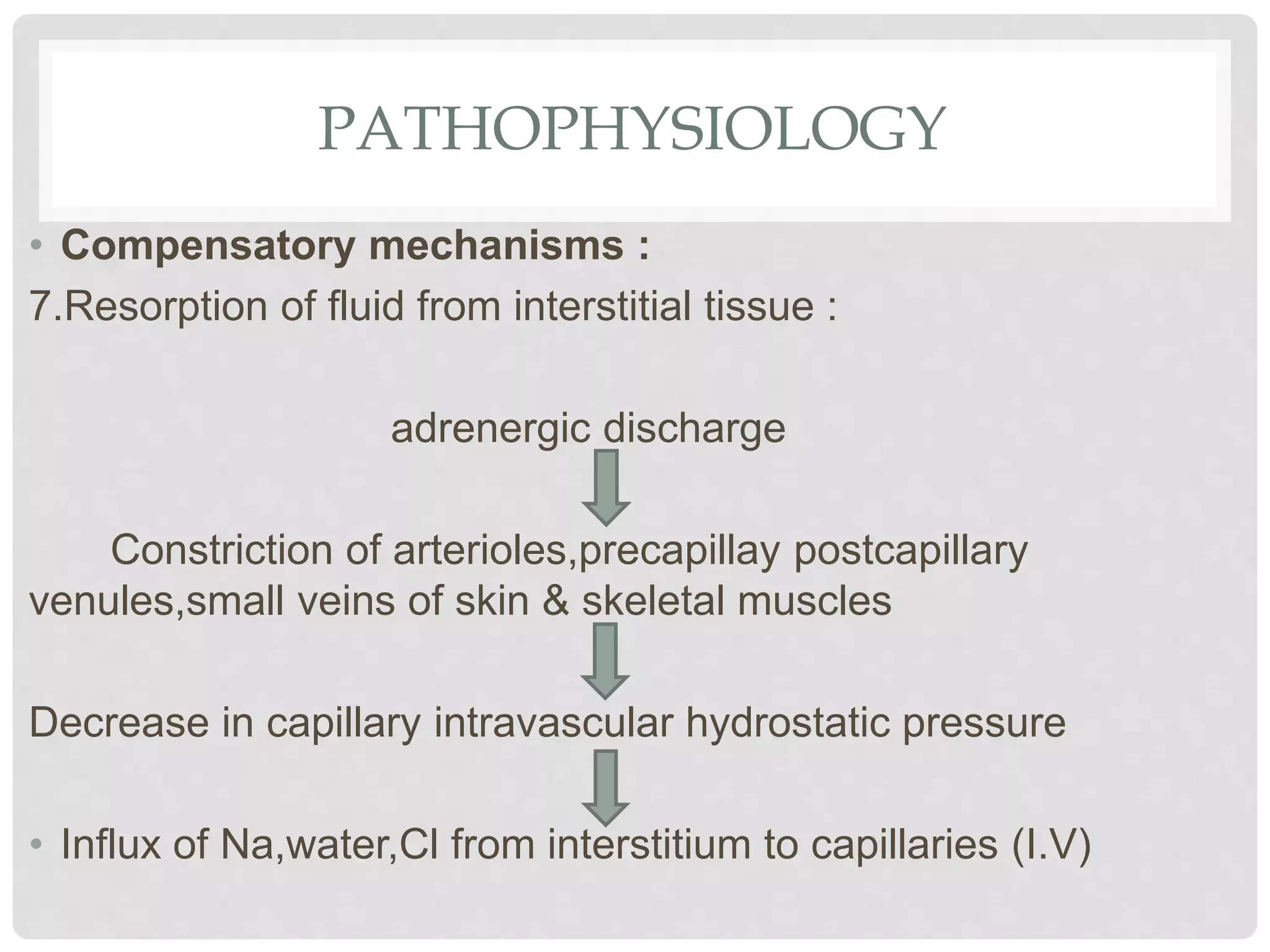
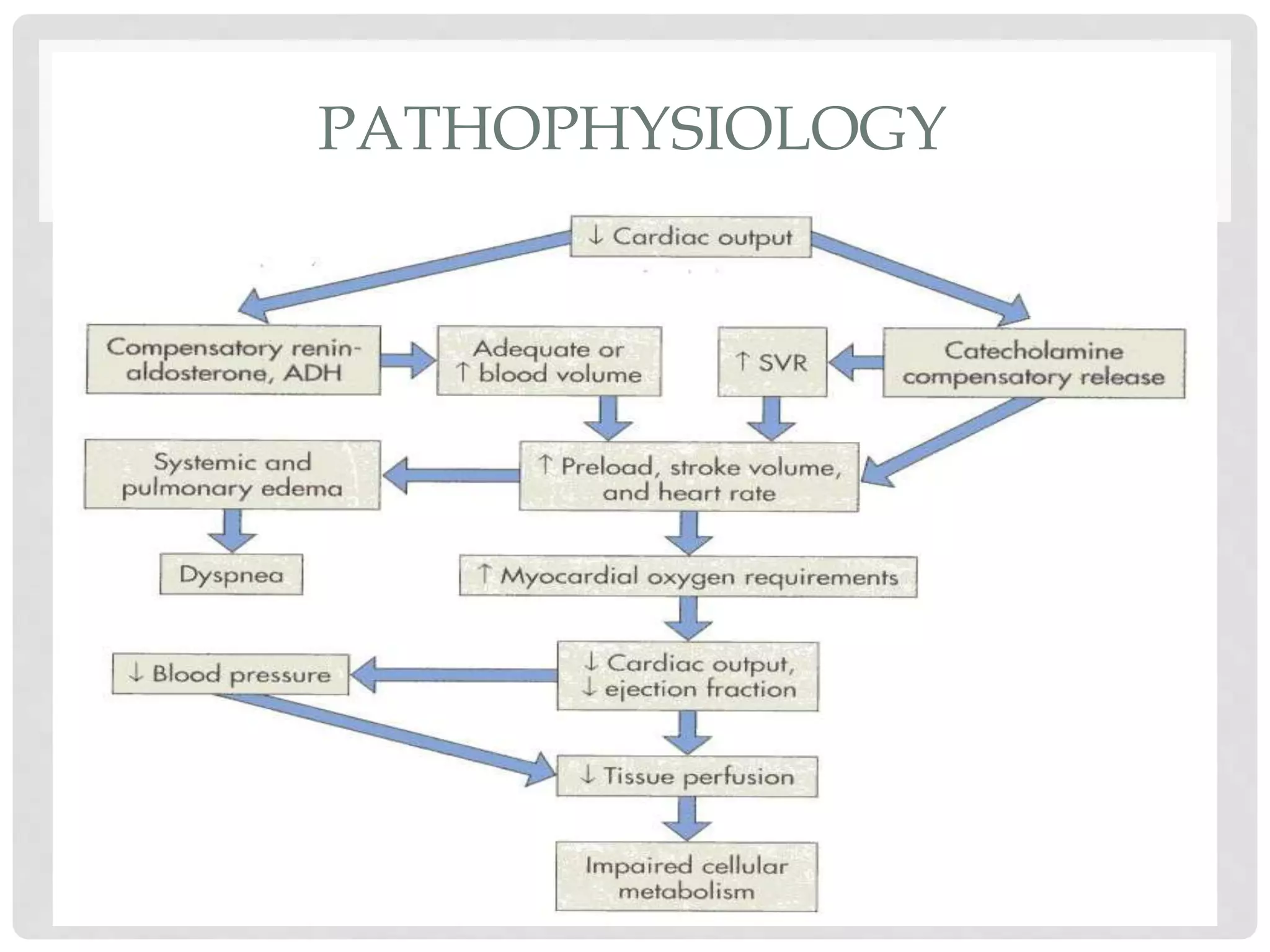
3. Hypovolemic shock results from loss of intravascular volume from bleeding, vomiting, or diarrhea leading to decreased blood pressure and organ perfusion. Compensatory mechanisms aim to maintain perfusion to vital organs but eventually fail.