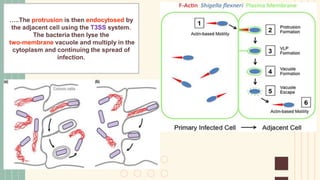
Shigella is a Gram-negative bacterium that causes the infectious disease shigellosis or bacillary dysentery. It is transmitted via the fecal-oral route and infects the colonic epithelium. Clinical symptoms include abdominal cramps, bloody mucus in the stool, and fever. S. dysenteriae produces a Shiga toxin that can damage kidney and brain cells. The bacterium uses a type III secretion system and effector proteins to invade intestinal cells, spread intracellularly, and induce inflammation. Treatment involves rehydration and antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin. Prevention relies on hand washing and water sanitation.