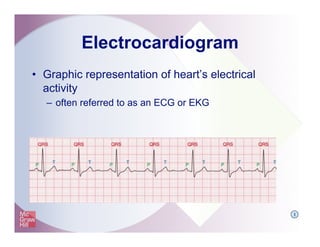
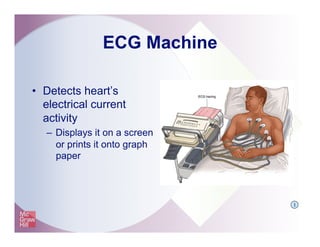
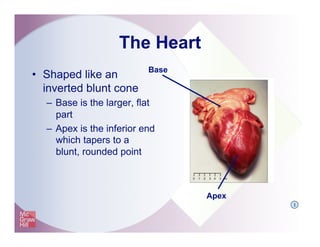
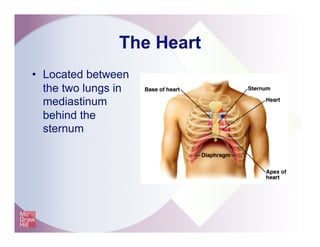
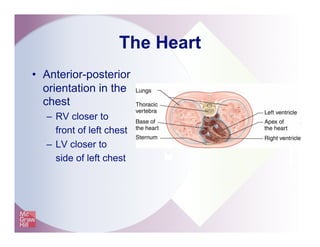
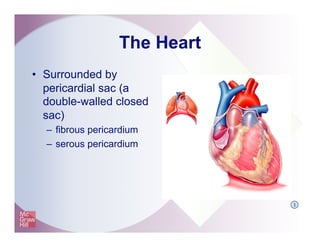
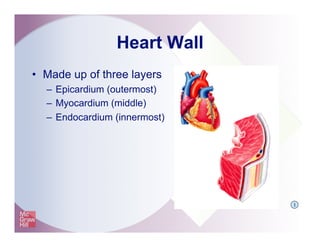
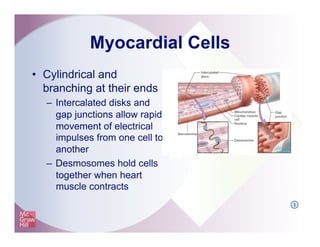
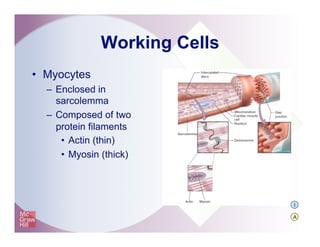
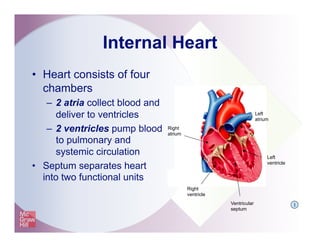
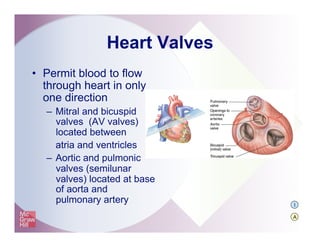
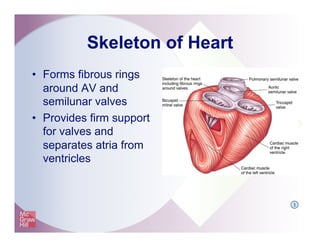
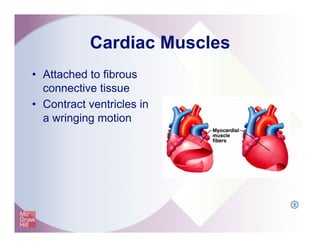
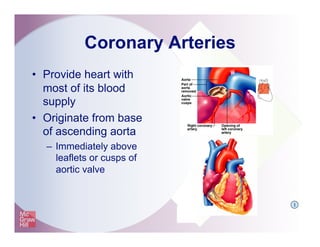
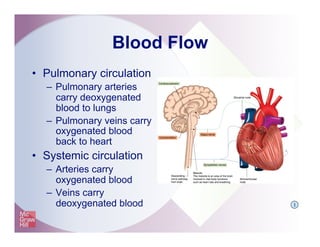
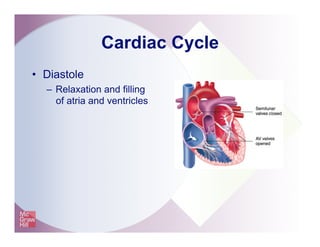
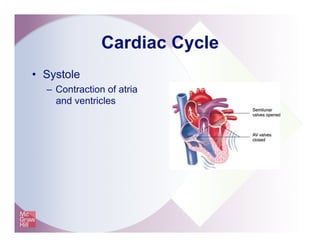
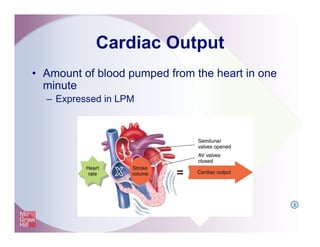
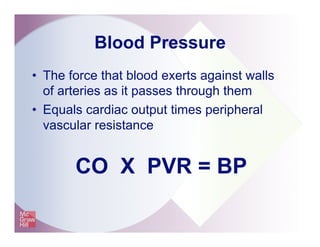
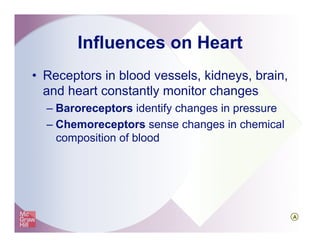
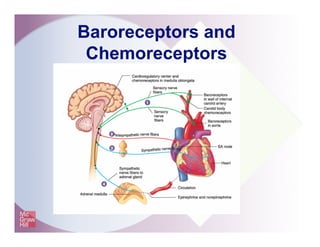
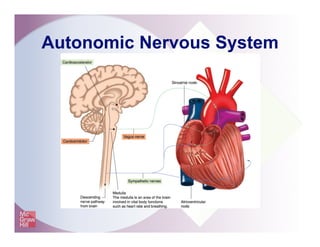
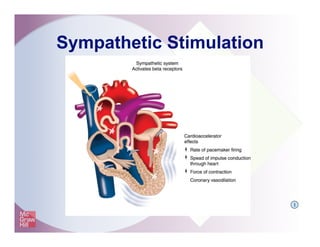
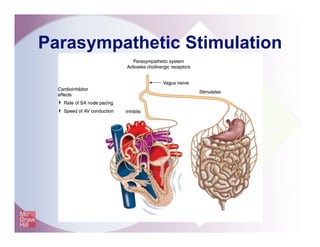
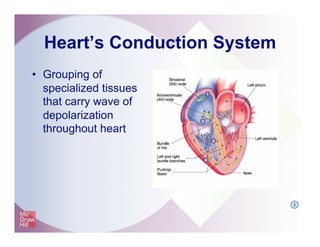
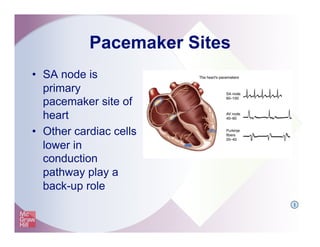
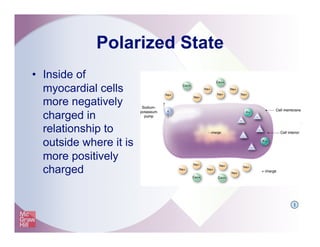
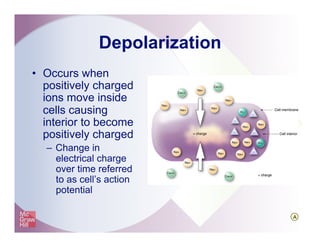
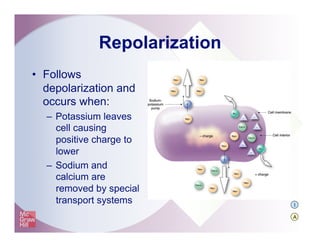
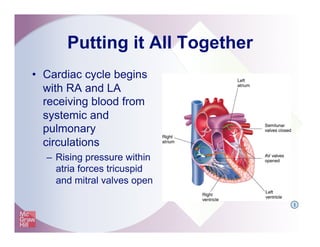
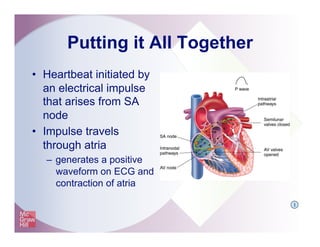
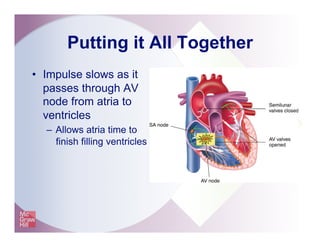
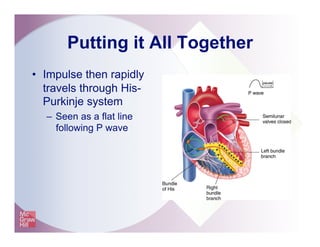
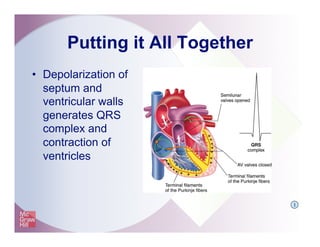
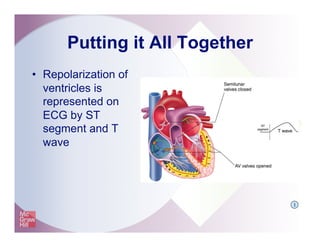
The document provides an overview of electrocardiography and the heart's electrical conduction system. It describes how an ECG works to detect and record the heart's electrical activity. It explains the anatomy of the heart including its chambers, valves, blood vessels and electrical conduction pathways. Key aspects of the cardiac cycle are outlined such as depolarization, repolarization and the roles of ions in generating electrical impulses that stimulate coordinated contractions of the heart muscle.