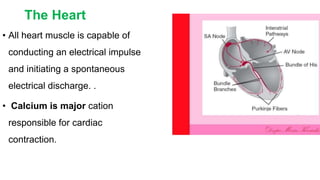
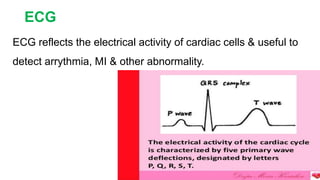
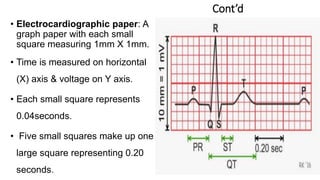
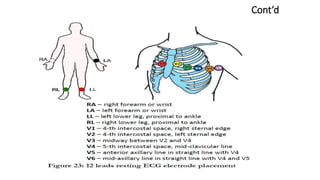
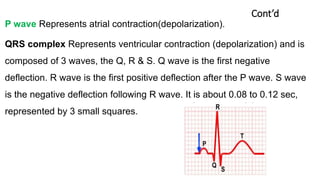
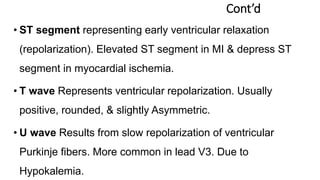
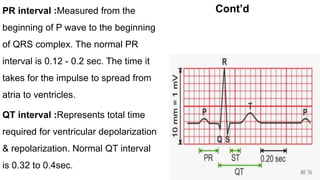
The document discusses electrocardiography (ECG). ECG reflects the electrical activity of the heart and is useful for detecting arrhythmias, myocardial infarction, and other abnormalities. It involves recording the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the limbs and chest. The recording is done on graph paper and represents time on the horizontal axis and voltage on the vertical axis. Key aspects of the ECG waveform like the P, QRS, and T waves are described along with what each represents in terms of cardiac electrical activity and muscle function. Normal values for intervals like the PR and QT intervals are also provided. Finally, some common indications for ECG are listed.