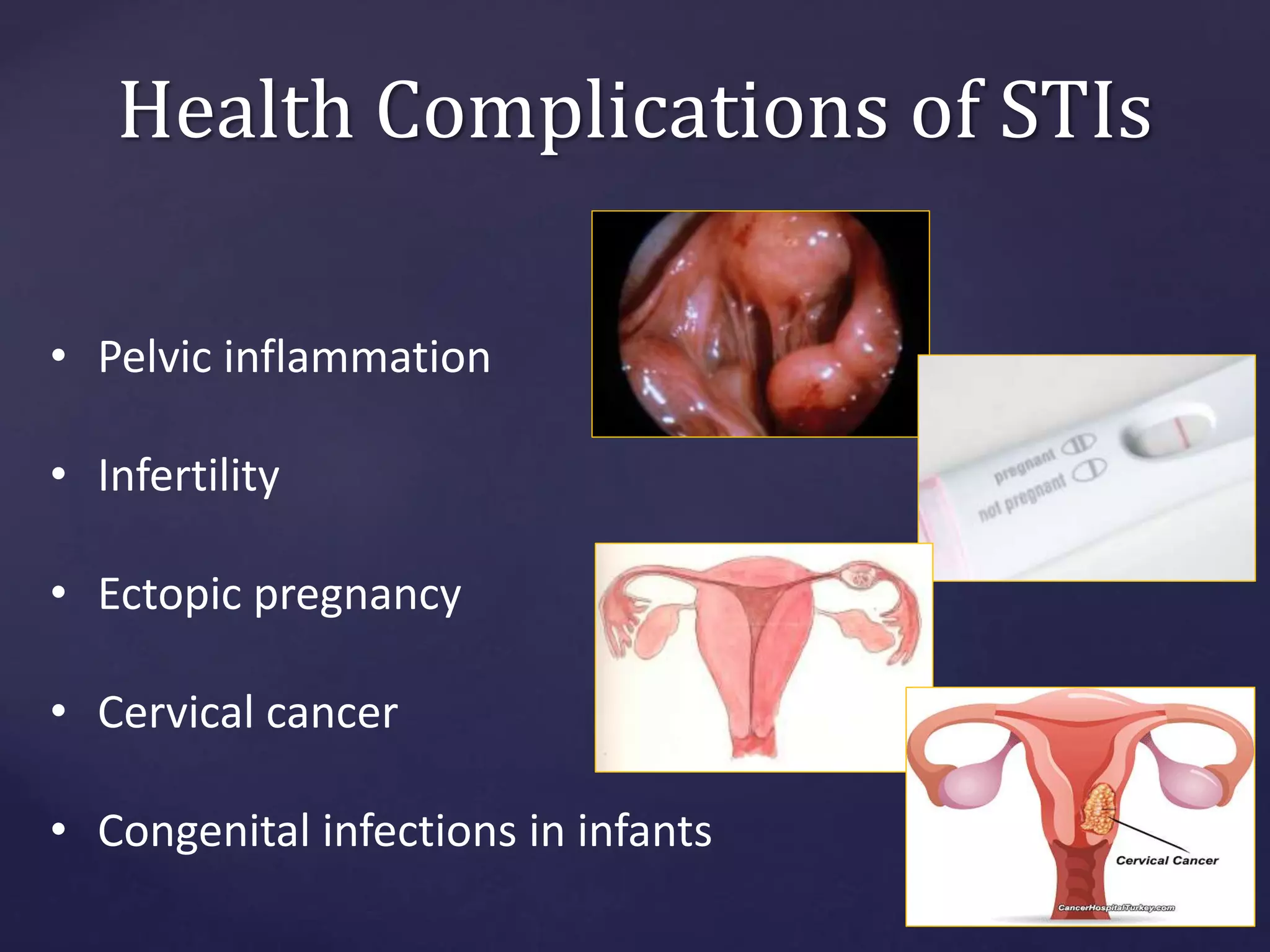
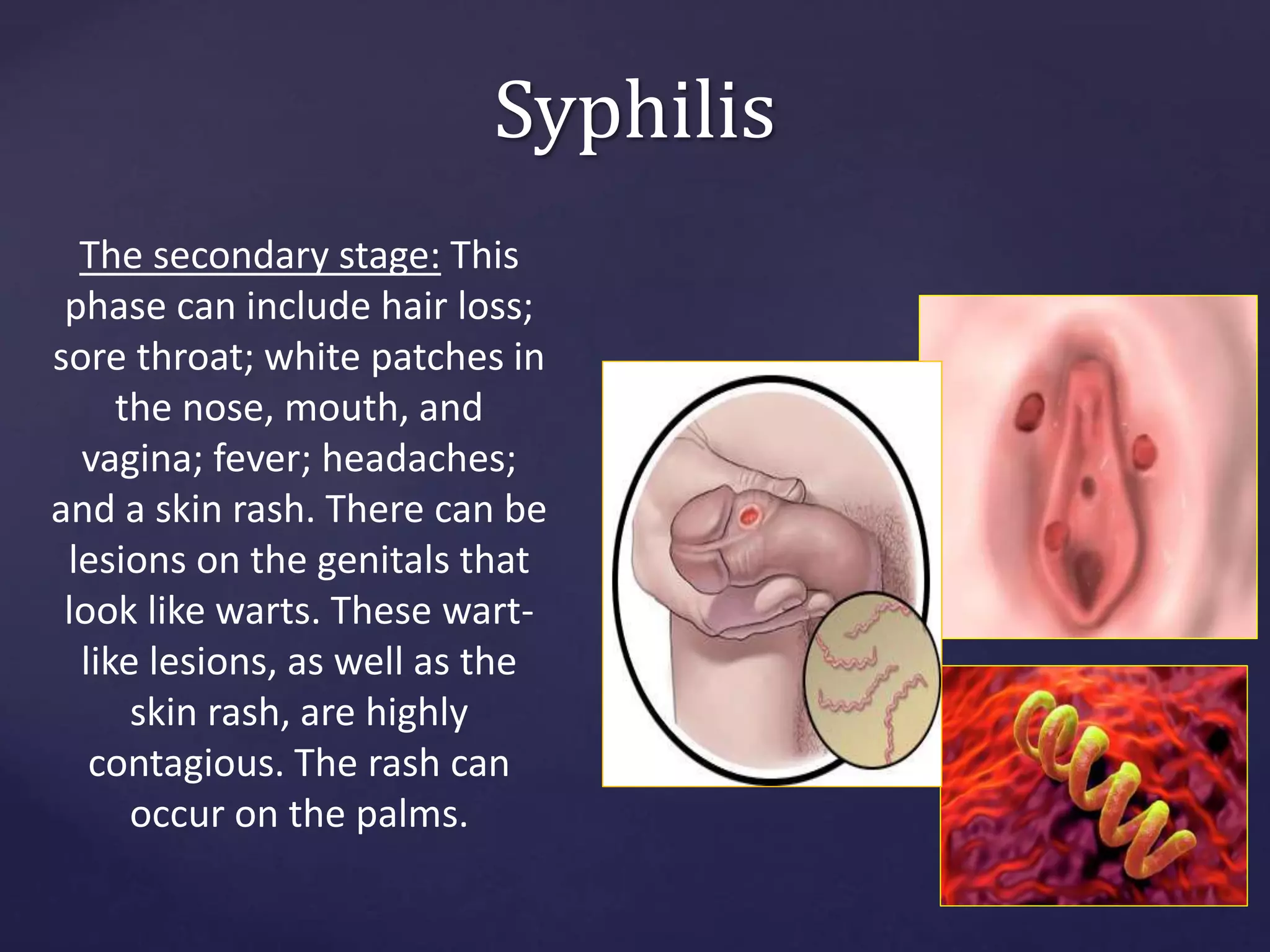
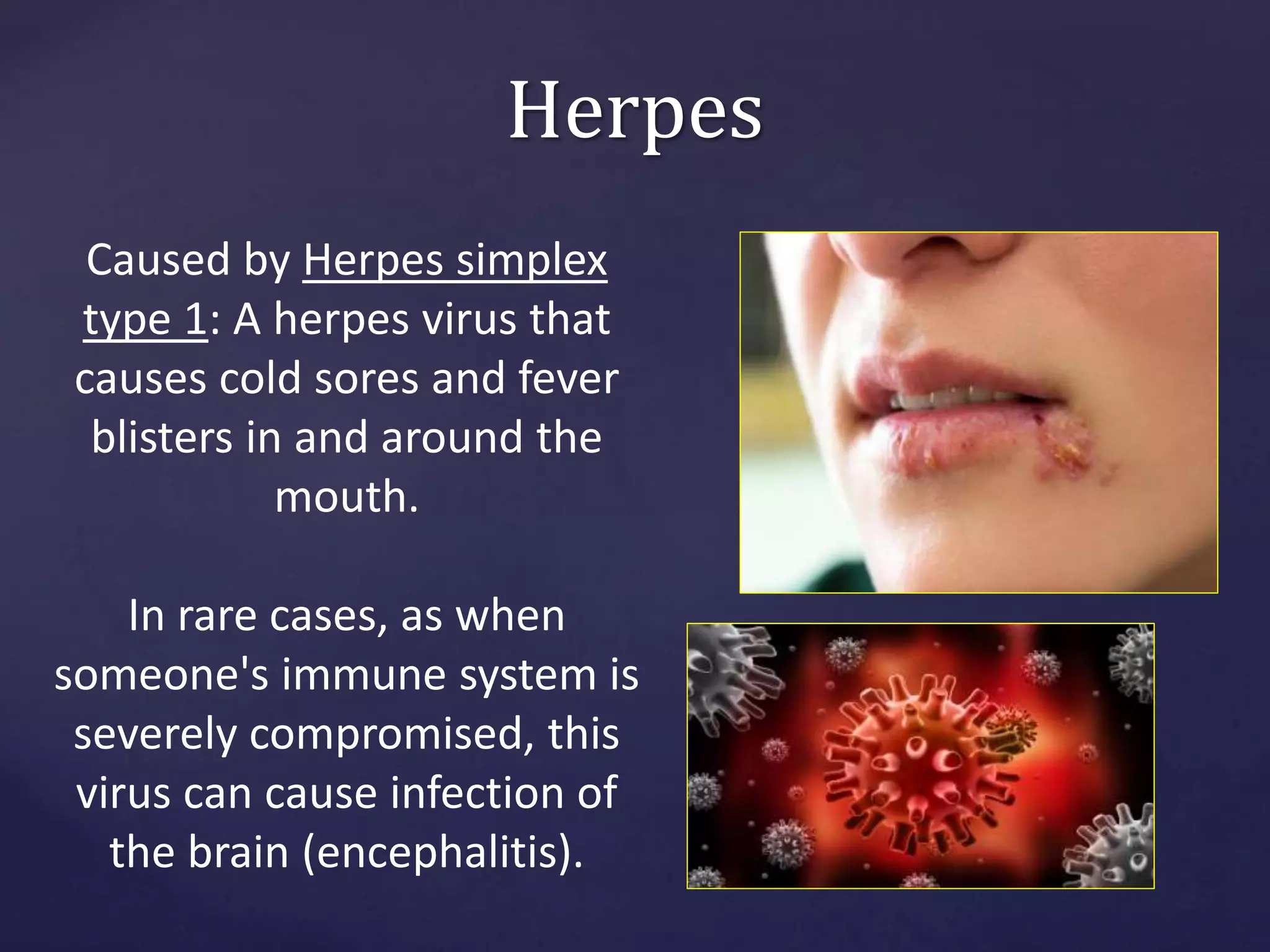
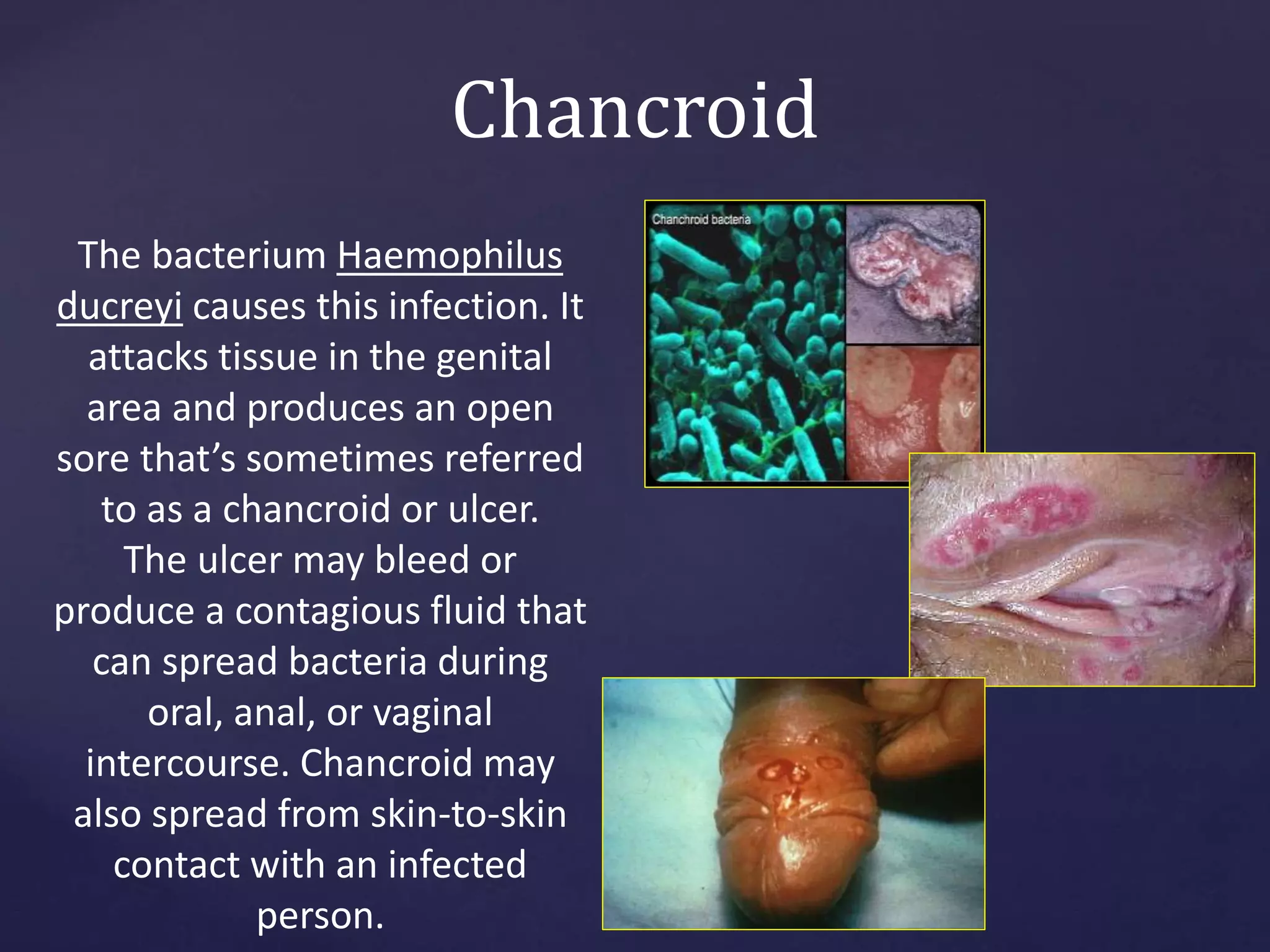
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs), also known as sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), are infections that are transmitted from one person to another through sexual contact. STIs can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. Common STIs include gonorrhea, chlamydia, syphilis, genital herpes, human papillomavirus (HPV), chancroid, and pubic lice. STIs are treated with antibiotics, antiviral drugs, or other medications depending on the specific infection. It is important to complete all treatment and abstain from sex until fully healed to avoid spreading the infection.