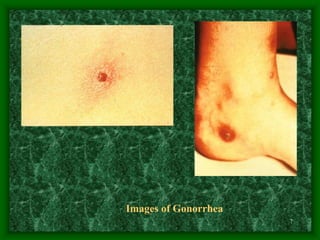
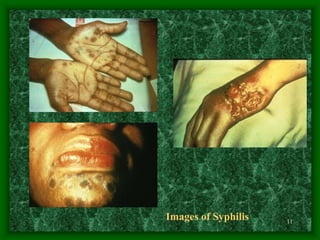
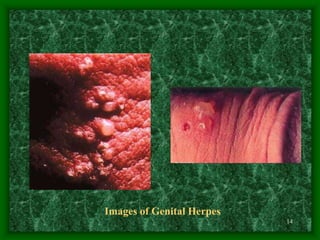
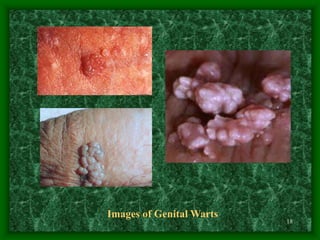
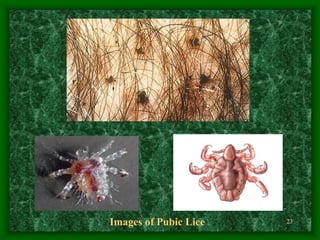
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, trichomoniasis, pubic lice, genital herpes, and genital warts. Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that often has no symptoms but can cause reproductive health issues if left untreated. Gonorrhea is also a bacterial infection that may cause discharge and pain when urinating. Syphilis is a bacterial infection with stages including chancres, rashes, and potential long-term organ damage. Genital herpes and genital warts are caused by viruses that remain in the body indefinitely.