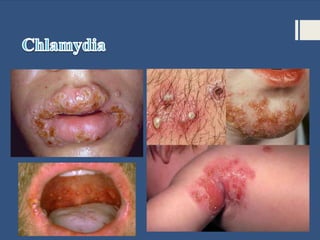
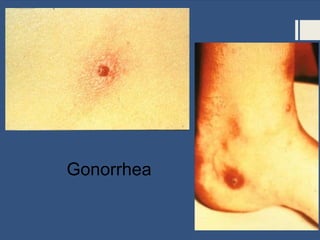
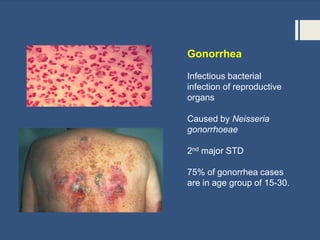
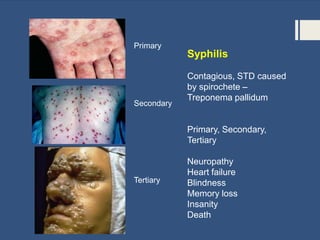
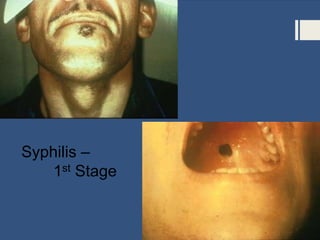
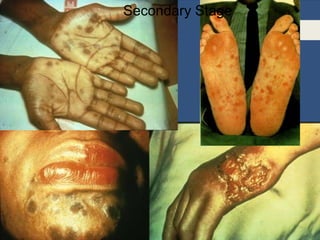
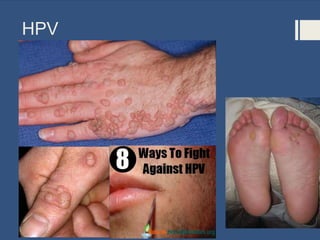
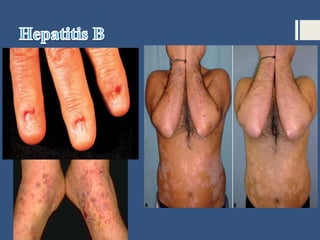
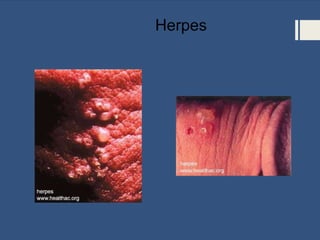
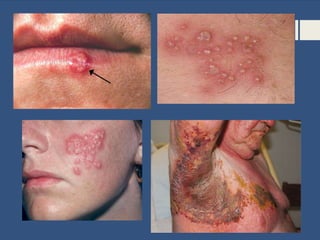
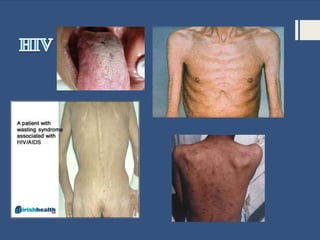
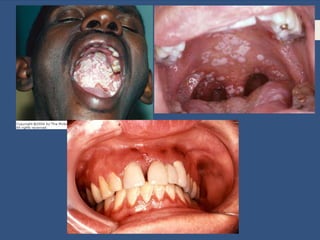
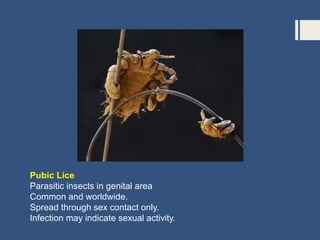
This document provides information about sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) including common types like chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, HPV, hepatitis B, herpes, and HIV. It describes how each infection is transmitted and potential symptoms. Testing and treatment options are outlined for bacterial STDs which can generally be cured with antibiotics, and viral STDs which cannot be cured but can be managed with medication. The importance of preventing STDs through abstinence, monogamy, condom use, and getting tested is also discussed.