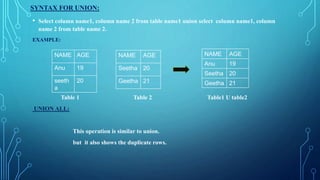
Set operations allow combining results from multiple SELECT statements. There are four main types:
Union combines results and eliminates duplicates. Intersect returns only common records. Union All and Intersect All also show duplicate rows. Syntax involves a SELECT query followed by a set operator and another SELECT query.