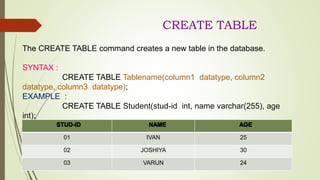
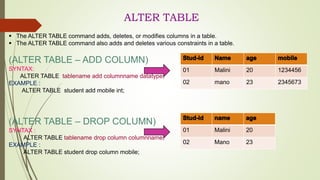
This document provides information about different types of database languages. It discusses database definition languages (DDL) which are used to define the database structure, data manipulation languages (DML) which are used to retrieve and modify data, data control languages (DCL) which control security and access, and transaction control languages (TCL) which manage transactions. Examples of commands for each language type are provided, such as CREATE, ALTER, and DROP for DDL and SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE for DML.