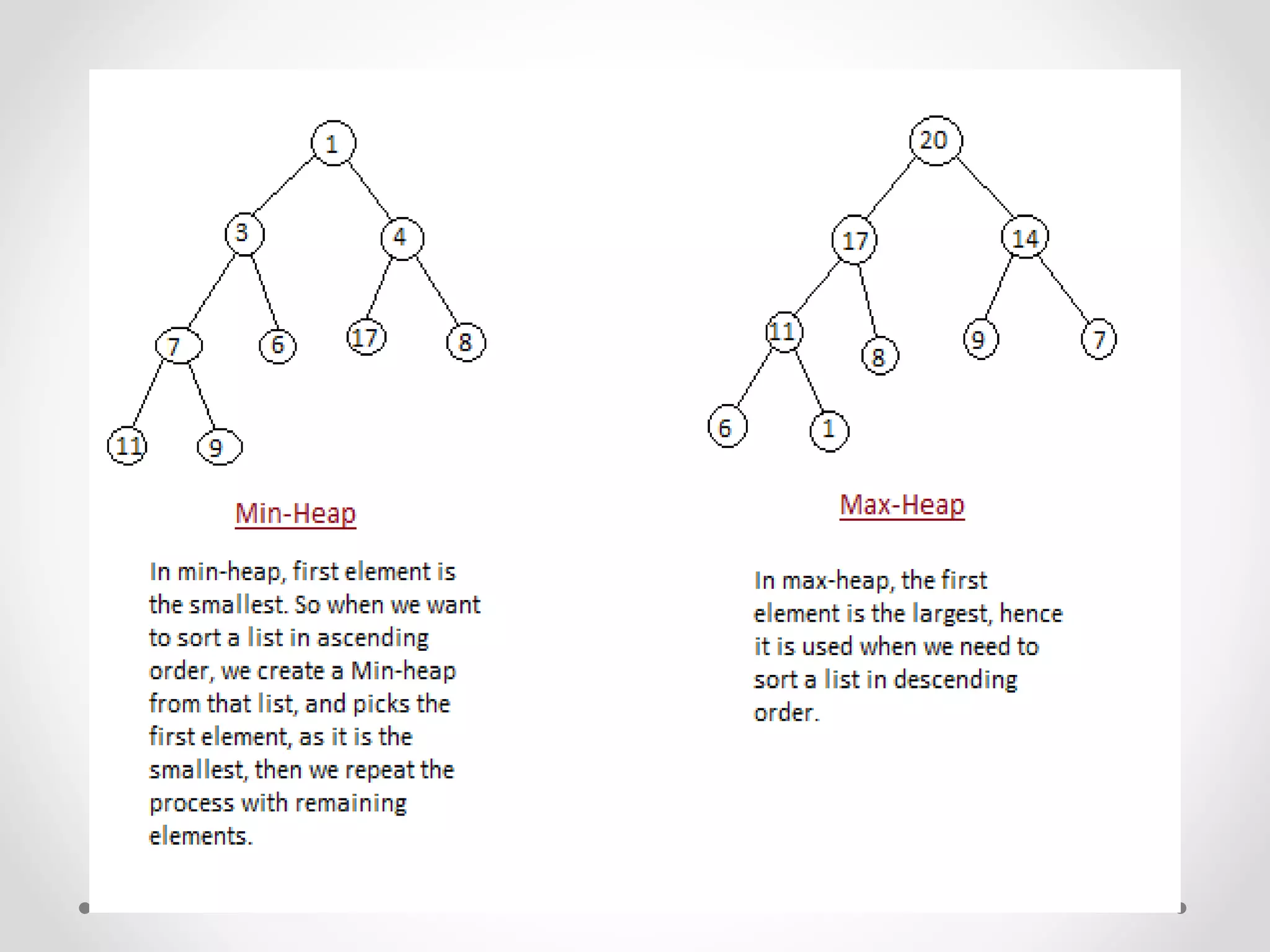
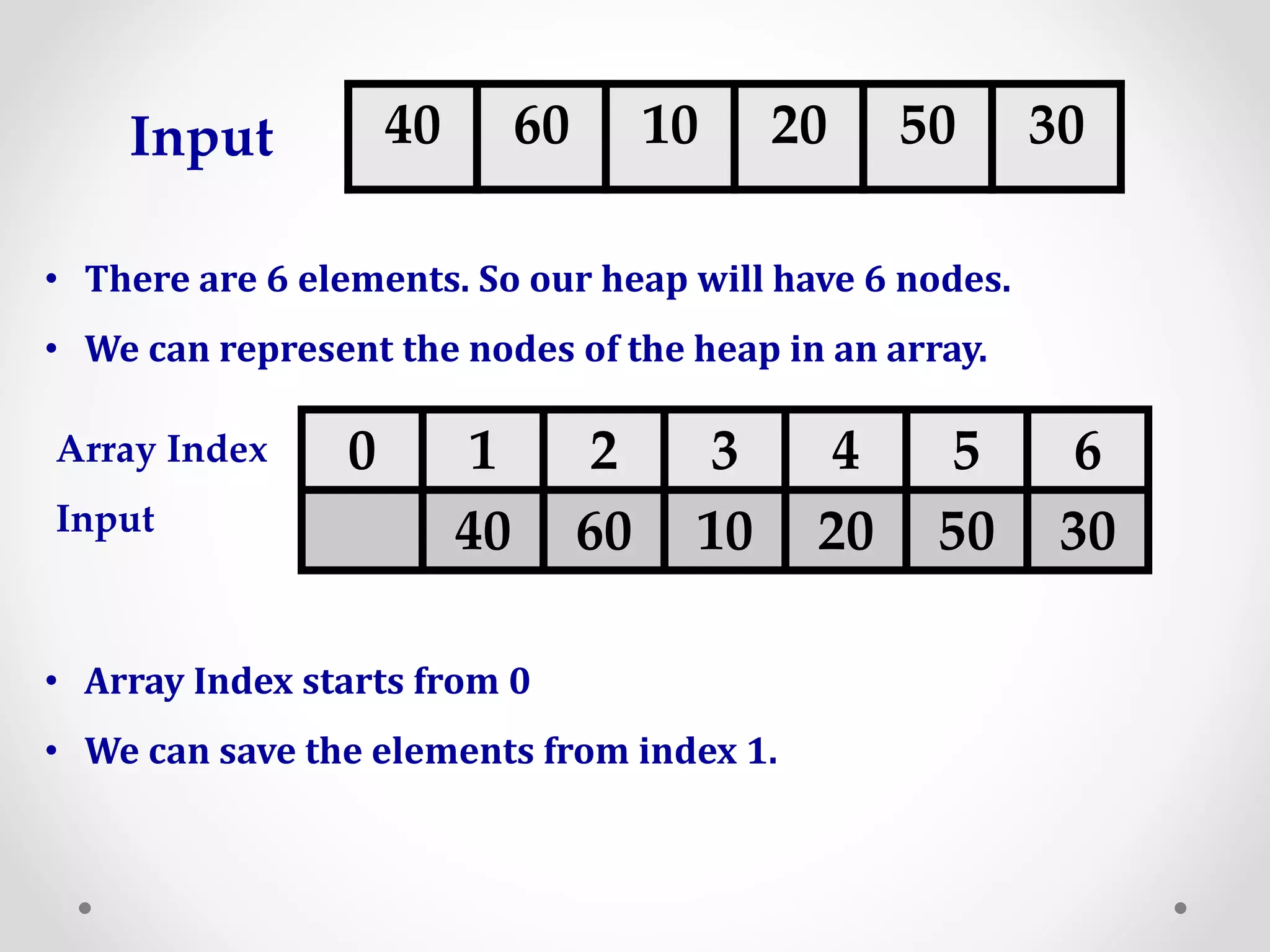
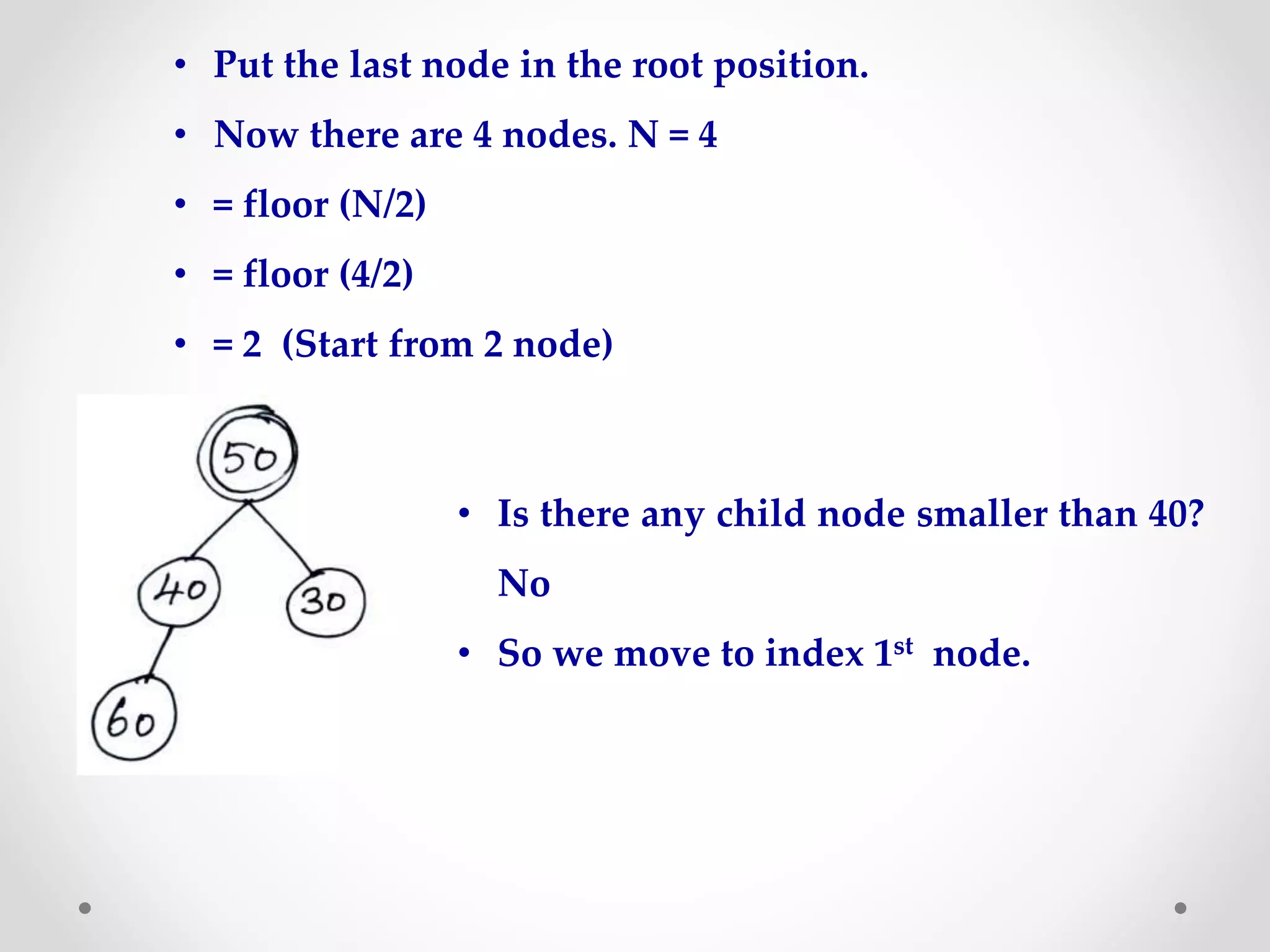
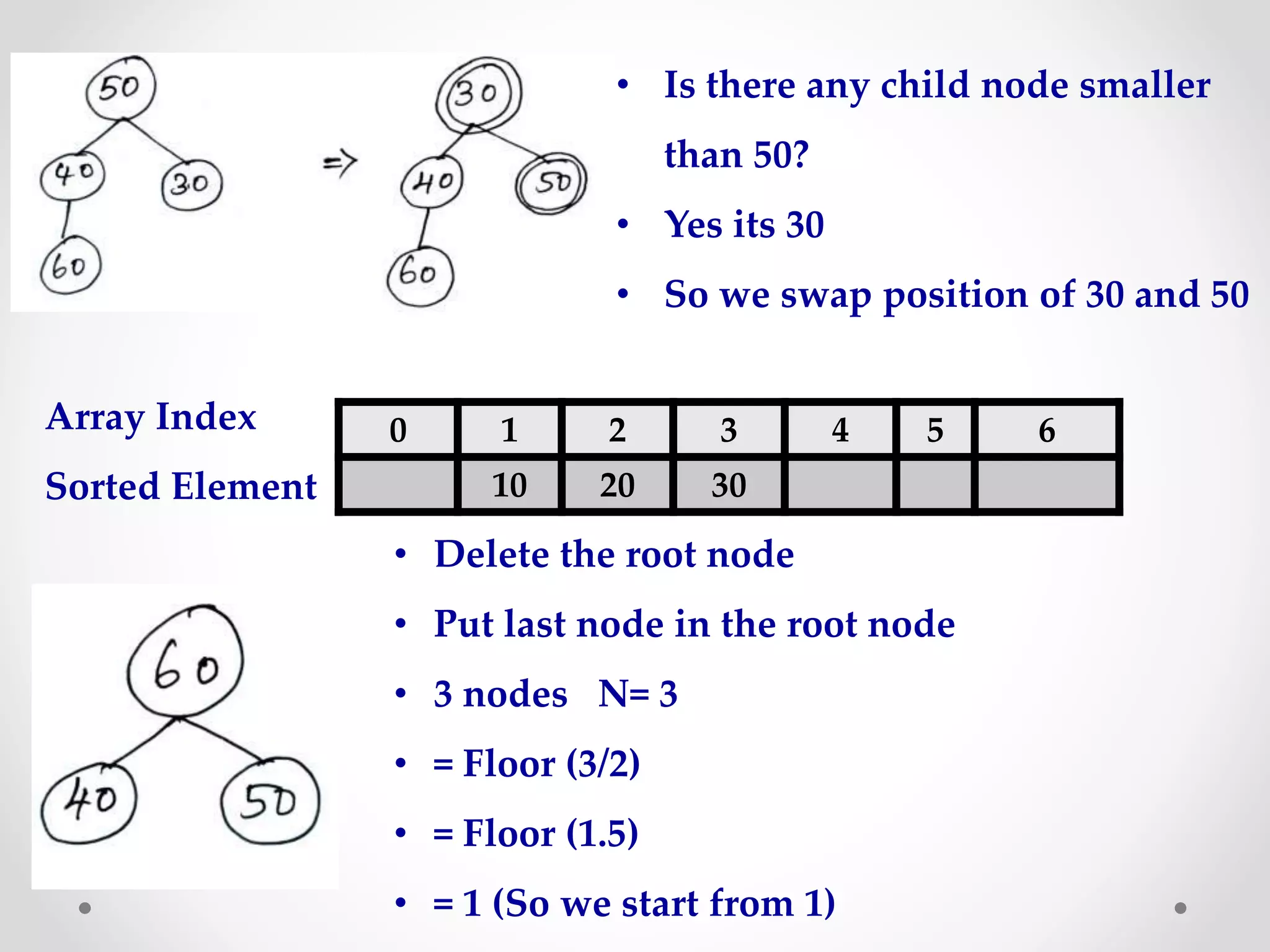
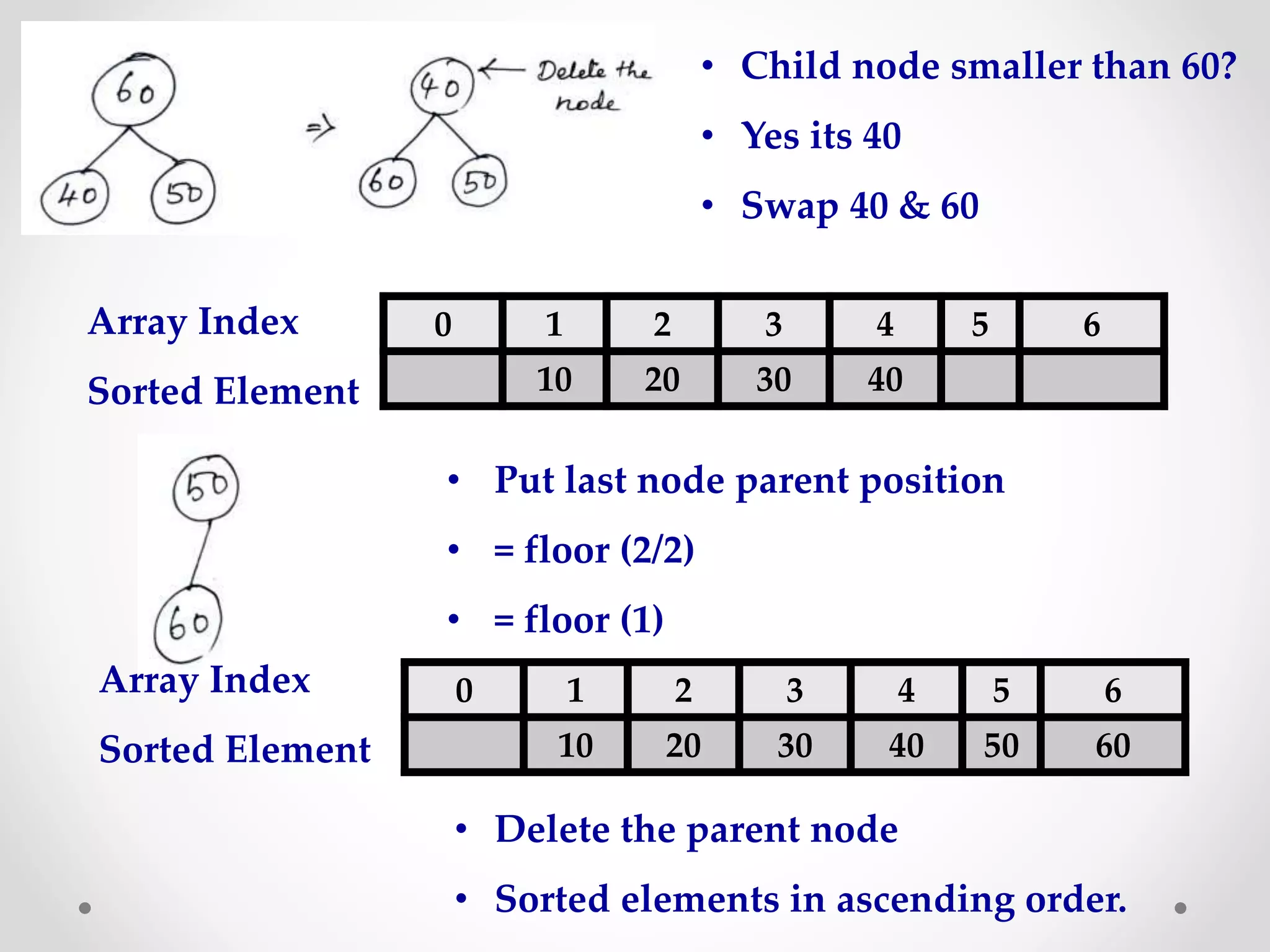
Heap sort is a sorting algorithm that uses a heap data structure. It first builds a max or min heap from the input elements. For ascending order, it builds a min heap where each parent node is smaller than its children. It then repeatedly removes the root node and replaces it with the last element, maintaining the heap property. This process continues until all elements are sorted. The time complexity of heap sort is O(n log n) as building and maintaining the heap takes O(log n) for each of the n elements.