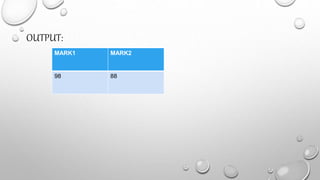
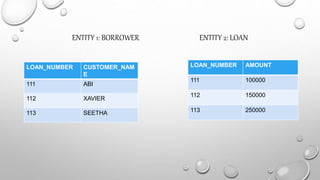
SQL is a database query language used to store and manage data in relational database management systems (RDBMS). The basic structure of an SQL query includes a SELECT clause to specify the attributes to retrieve, a FROM clause to specify the tables to query, and an optional WHERE clause to filter rows. Common SQL operators allow queries to select, filter, order, rename, and relate data across multiple tables in a database.