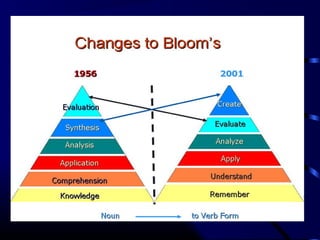
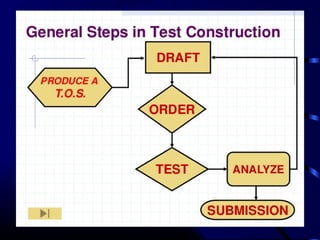
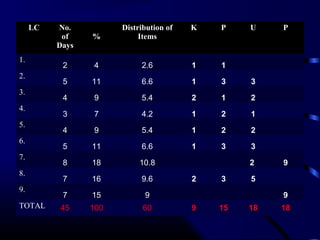
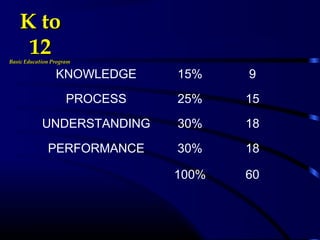
This document provides information and guidance on test construction. It discusses that the purpose of test construction is to improve the educational program and make it more effective. It outlines objectives around identifying cognitive domains of learning and constructing test items. It also discusses Bloom's taxonomy and the six cognitive domains. Various activities are presented to help teachers practice constructing test items aligned to objectives and cognitive domains, including using a table of specifications to plan assessments. The document emphasizes the importance of test construction in evaluating student learning and providing feedback to improve teaching.