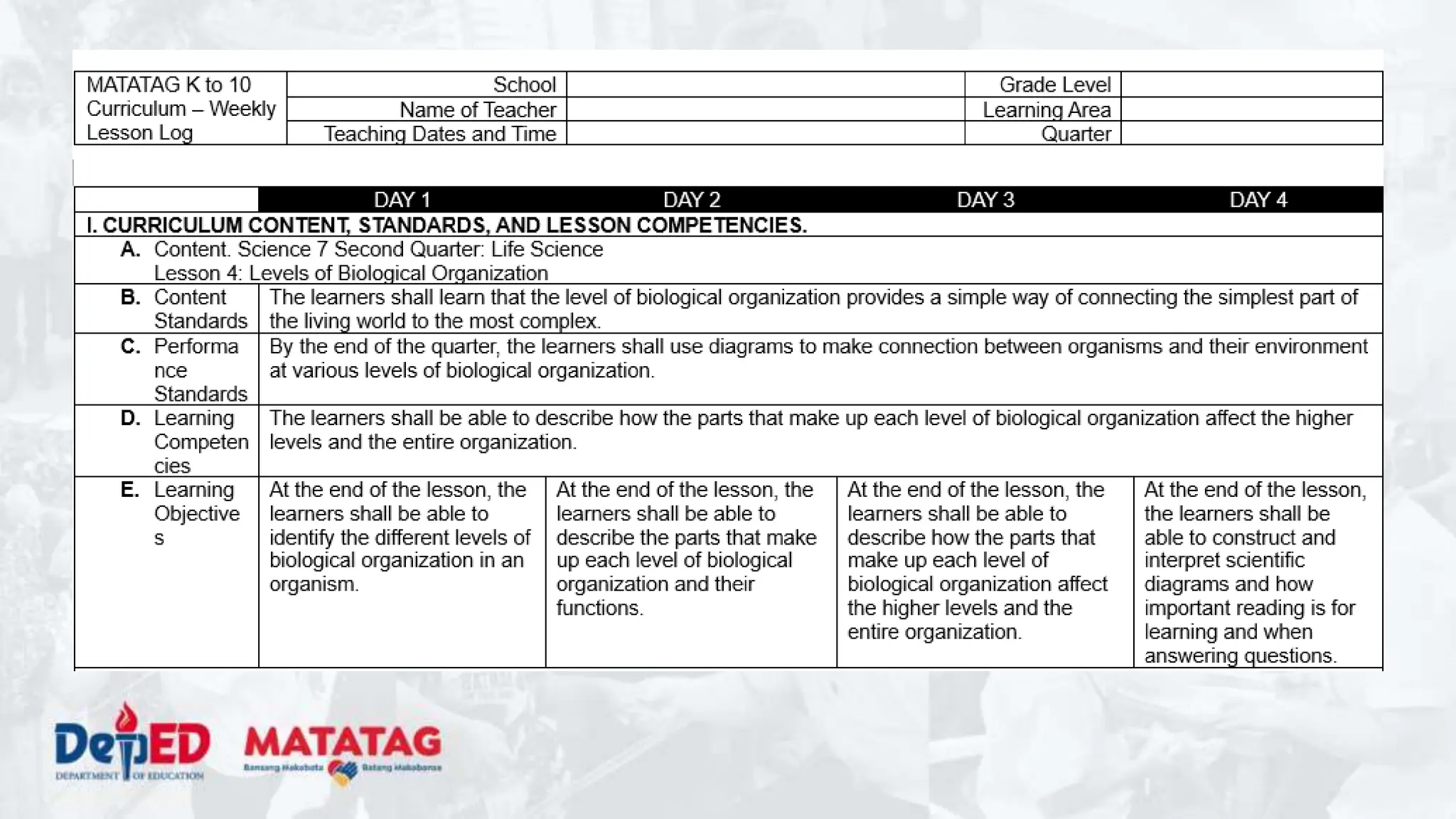
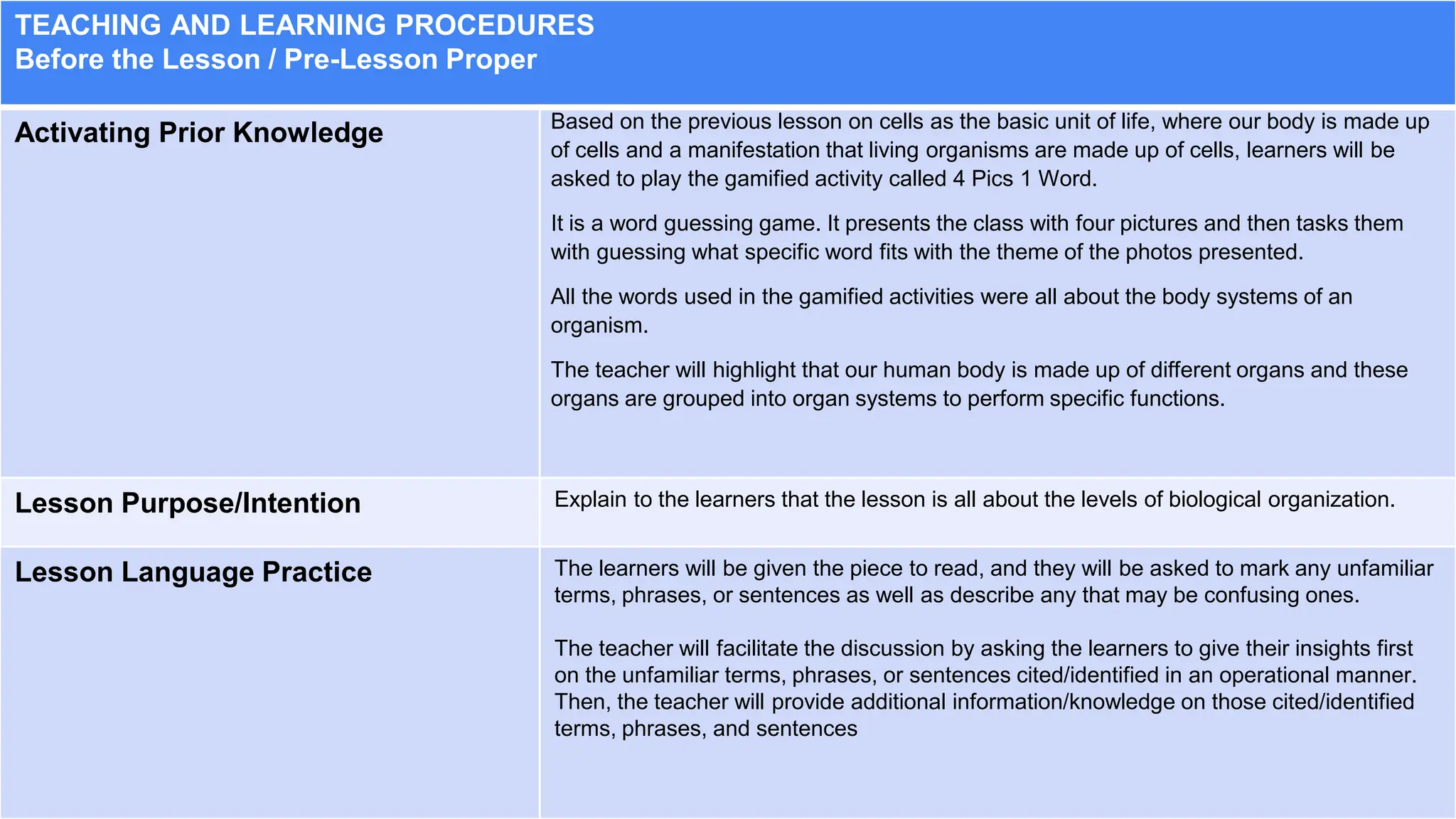
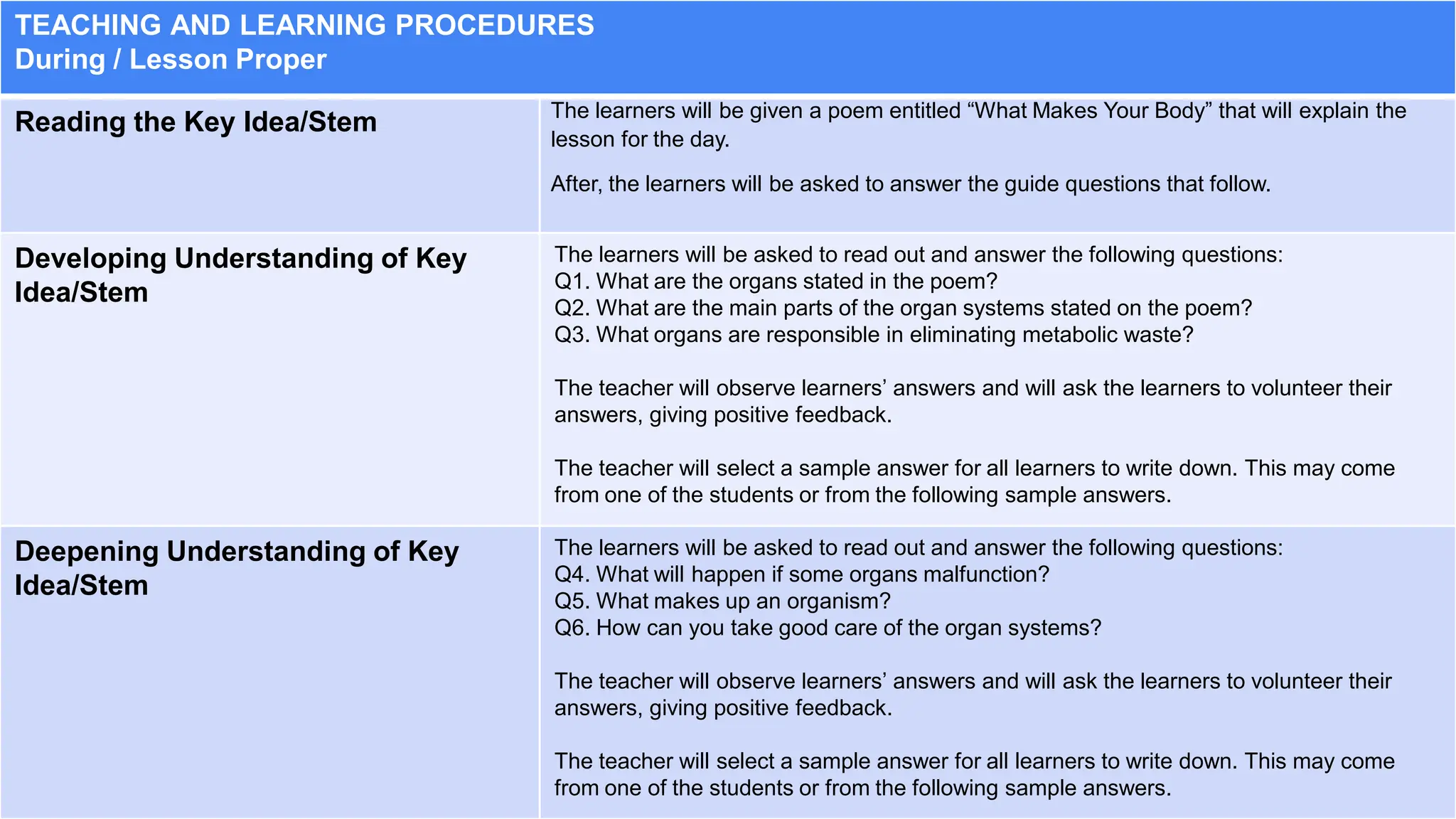
This document provides an overview and sample of a lesson exemplar for teaching biological organization. It includes sections for curriculum content and standards, learning resources, teaching procedures, and assessment. The teaching procedures section details the steps to be taken before, during, and after the lesson. This includes activating prior knowledge, explaining the lesson purpose, conducting the lesson proper through developing understanding of key ideas, and making generalizations after. The goal is for learners to understand the different levels of biological organization in an organism and how each level is interconnected and important for the sustainable development goals.