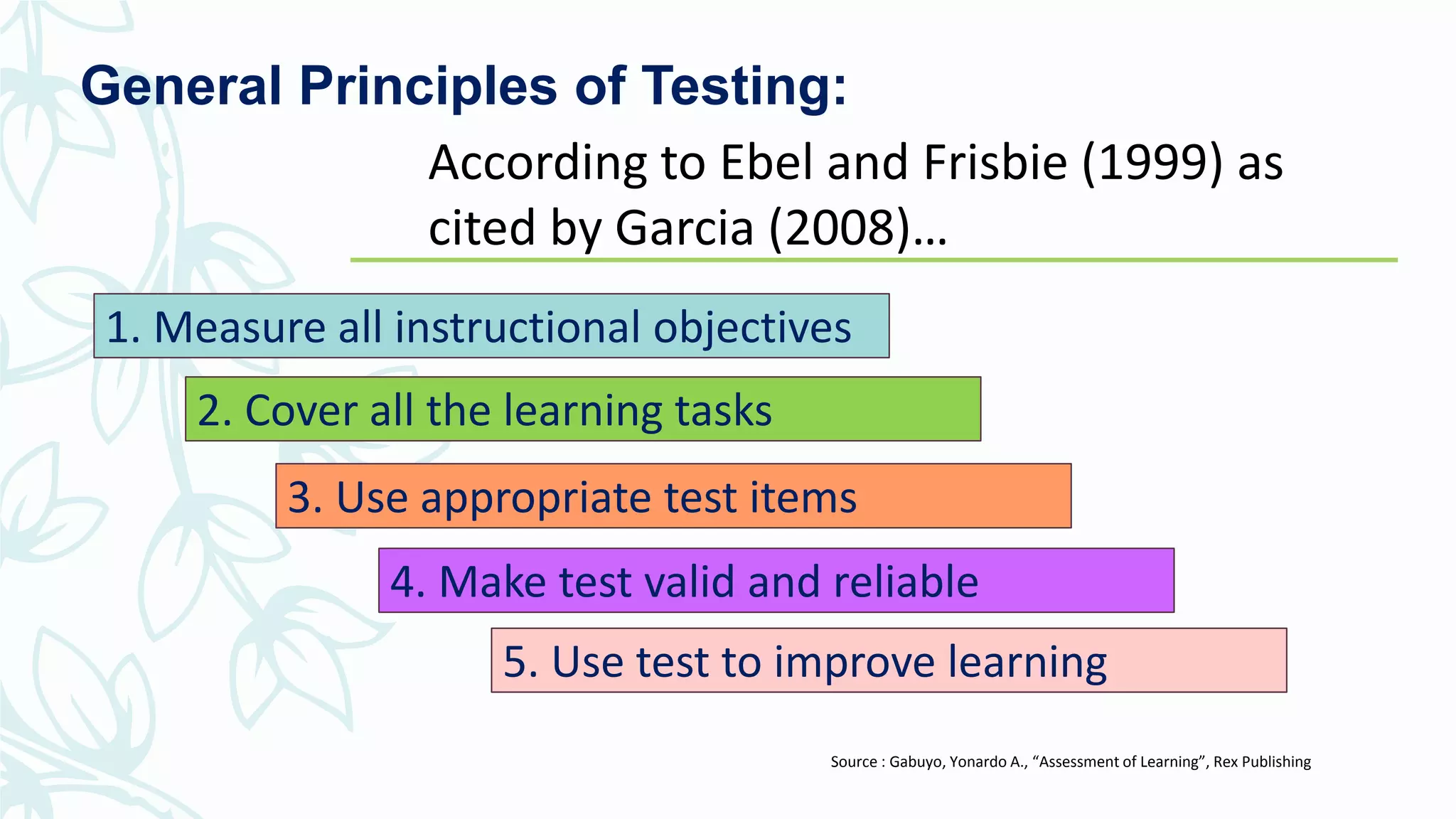
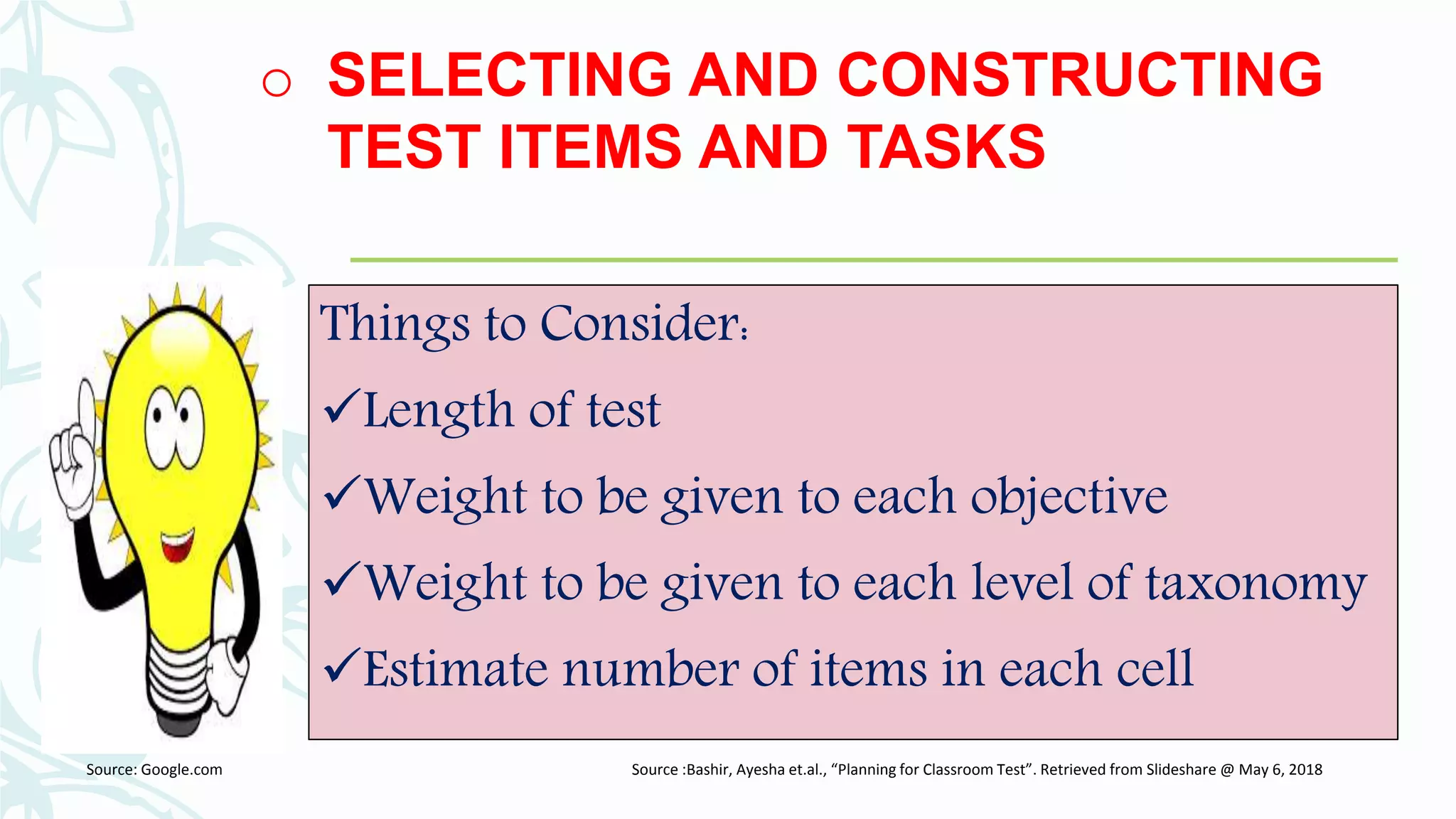
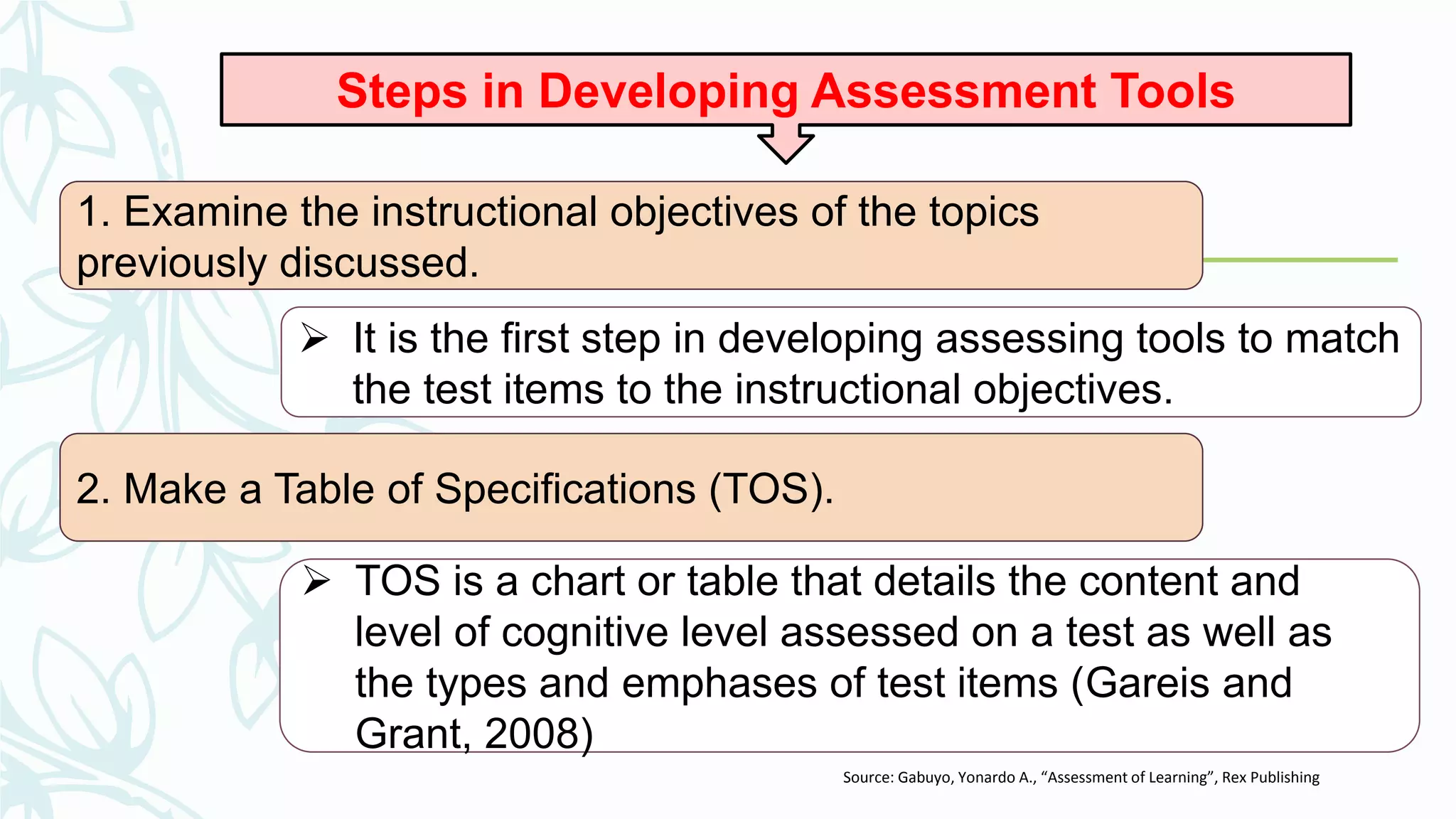
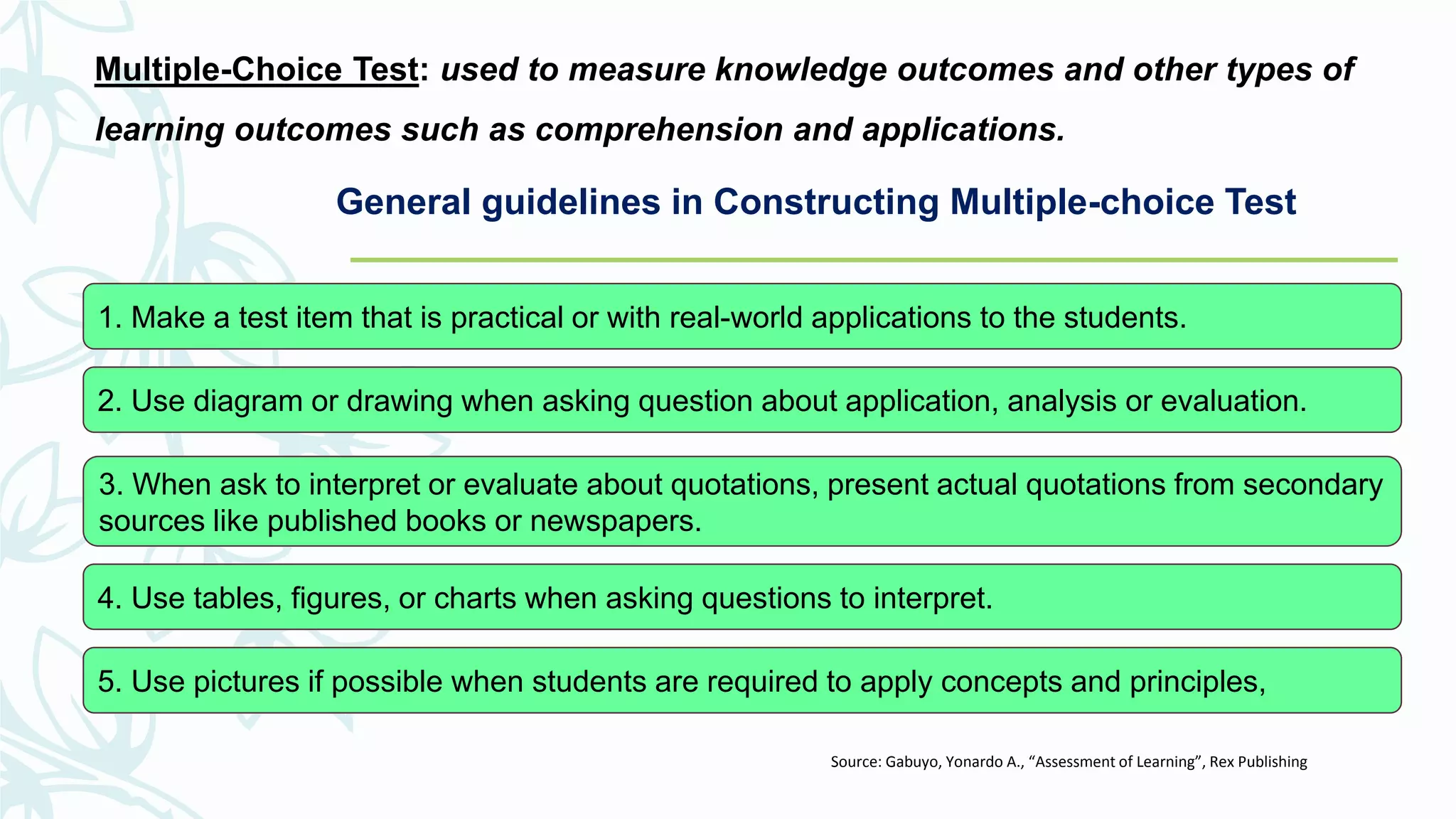
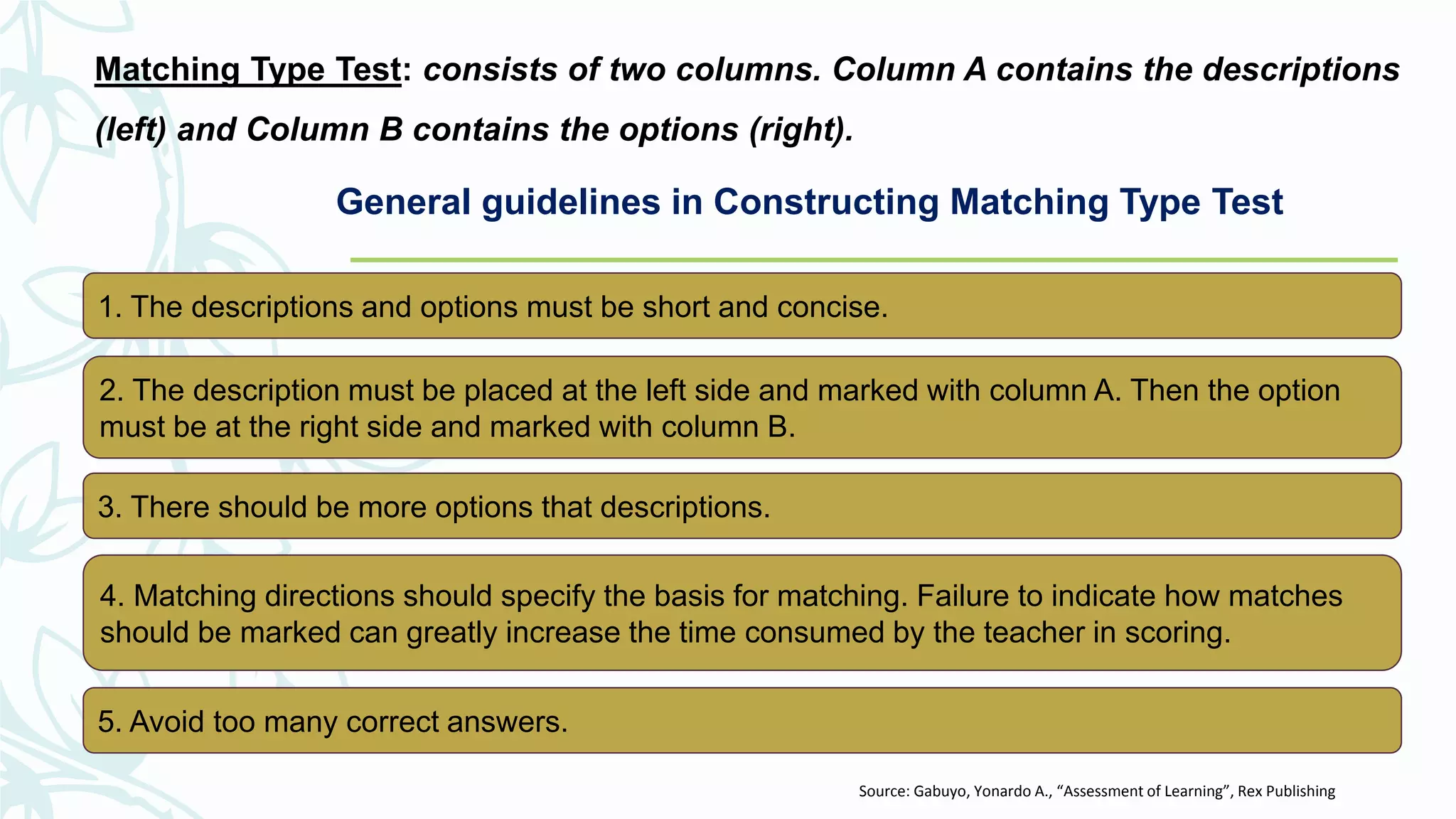
The document discusses developing and improving classroom-based assessments. It provides definitions of assessment and classroom-based assessment, noting that assessment is an integral part of instruction that enhances student learning. Various types of assessment tools are described, including tests, performance assessments, portfolios, observations, and self-reports. Guidelines are provided for planning assessments, selecting test items, constructing different item types like multiple choice and essay, and improving assessments through analysis and collaboration with colleagues.