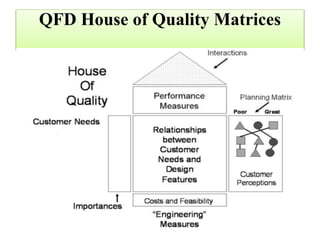
This document discusses concepts related to new service development and measuring service quality. It covers the following key points:
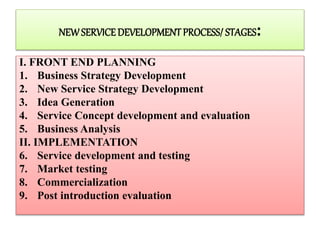
1. New service development involves bringing a new service to market and includes service design and various business considerations. The process involves idea generation, concept development, business analysis, implementation including development and testing, and post-introduction evaluation.
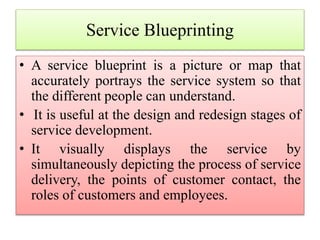
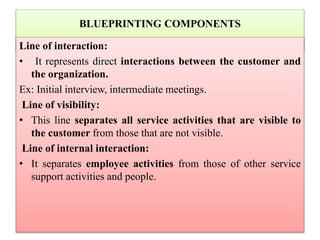
2. Service blueprinting is a useful tool used in service design and redesign. It visually maps out customer interactions, internal processes, and support functions to understand a service from different perspectives.
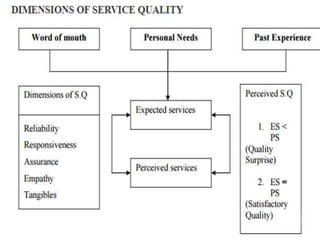
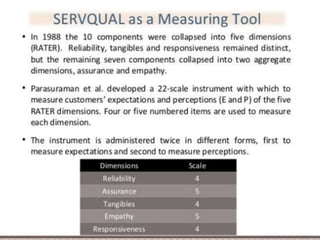
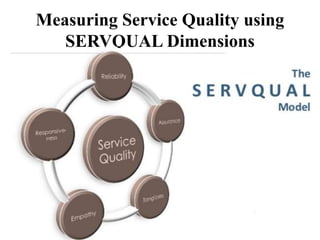
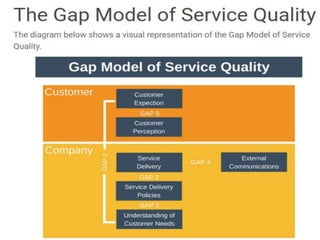
3. Service quality is determined by how well a service meets customer expectations and is influenced by factors like service environment (service scape) and employee performance. Models like SERVQUAL and