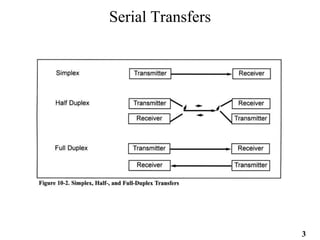
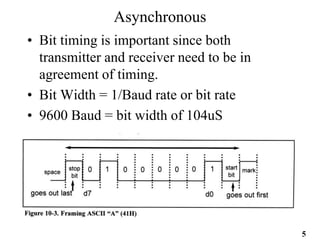
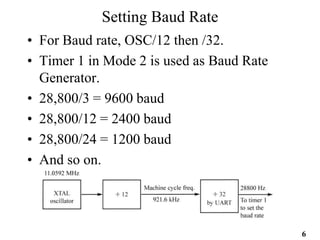
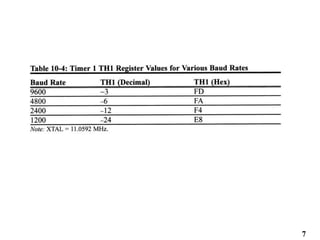
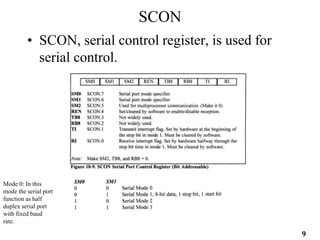
The document provides an overview of 8051 microcontroller serial communications, discussing essential concepts such as asynchronous and synchronous data transfers, baud rate settings, and the operation of serial control registers. It includes programming examples for data transmission and reception, along with the necessary configurations for enabling serial communication. Additionally, it outlines problems related to serial data transfer, such as transferring characters and using ports for input.