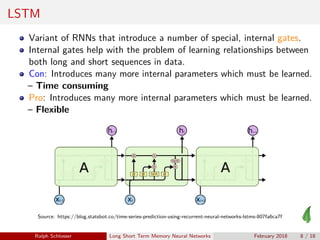
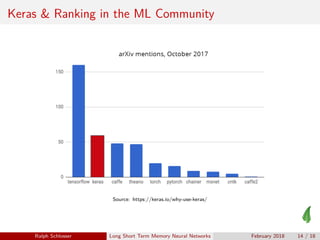
The document provides an overview of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neural networks, highlighting their advantages over traditional Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) in handling sequence data, while addressing challenges like the vanishing and exploding gradient problems. It explains the internal gating mechanisms of LSTMs that aid in managing long-range dependencies in input data and introduces Keras as a user-friendly framework for implementing these neural networks. Recent advances indicate that LSTMs can function as universal program approximators, prompting discussions on the future of software development.