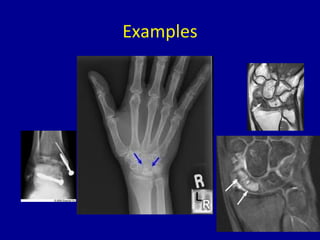
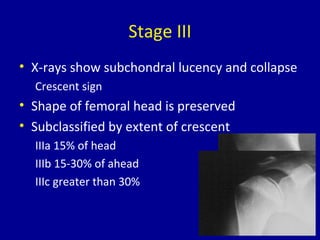
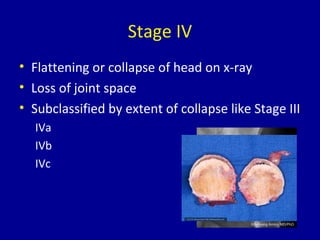
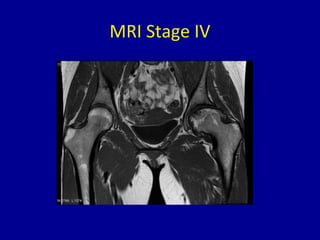
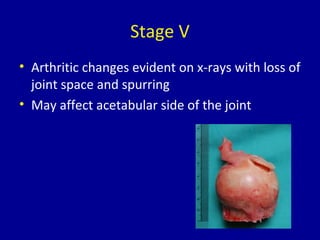
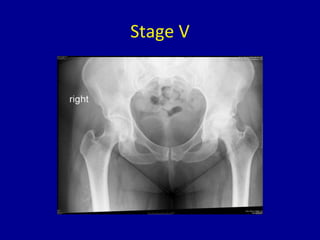
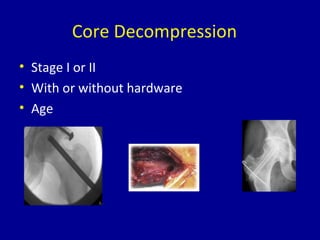
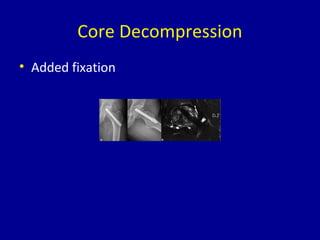
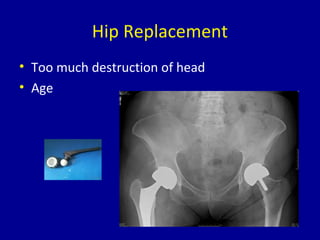
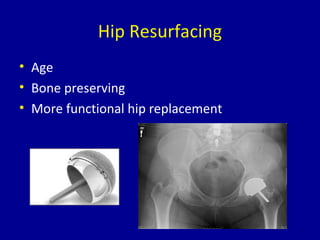
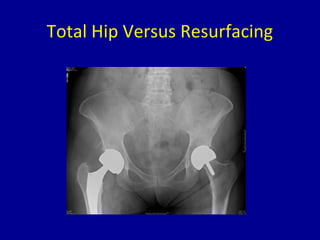
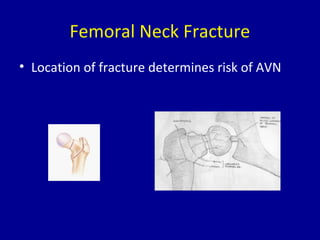
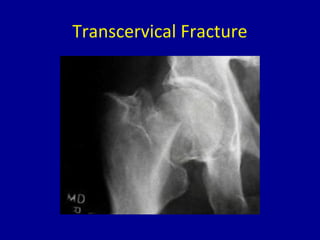
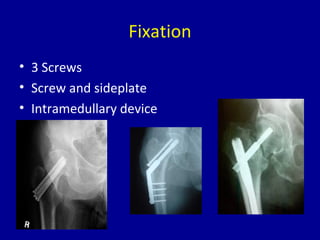
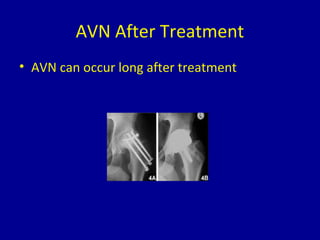
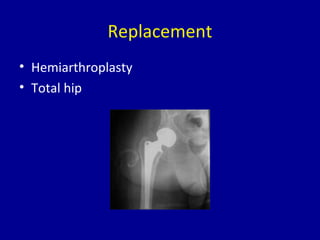
Avascular necrosis, also known as osteonecrosis or bone infarction, is the death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply. It most commonly affects the femoral head. There are many potential causes including trauma, alcohol use, steroid use, and idiopathic cases. Diagnosis is made through imaging like x-rays, CT scans, MRIs, and bone scans. Treatment depends on the stage of necrosis and other factors, and may include observation, core decompression, vascularized bone grafts, partial or total hip replacement, or hip resurfacing. Staging is important for determining treatment and can range from pre-symptomatic changes visible only on MRI to complete femoral head destruction indistinguishable from osteo