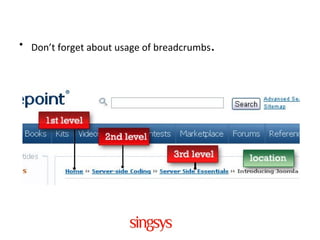
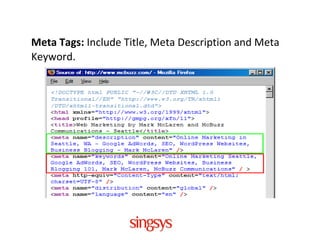
Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to optimizing on-page and off-page ranking factors to achieve high search engine rankings. SEO is important because 85% of internet traffic comes from search engines, and users rarely view results past the first page. Search engines rank pages using algorithms that consider on-page factors like titles, headers, and content, as well as off-page factors like links and anchor text. Proper use of titles, meta tags, headings, images, URLs, and internal linking helps websites rank higher in search results.





![Points for Design and Development of
SEO friendly websites
• Canonicalization Issues: Sites make the same HTML content or files
available via different URLs
for ex: http://xyz.com/, http://www.xyz.com/index.php and
http://www. xyz.com/home.php URLs must redirect to http://www.
xyz.com/
• Search Engine Friendly URLs: Search Engine Friendly (SEF) URLs are
beneficial to both users and search engines, helping to clarify what
a page is about and what category it can be found in. See below for
an example of a search engine friendly and non-search engine
friendly URL.
SEF-URL: [domain.com/category/]
Non-SEF: [domain.com/index.php?catid=321&prodid=123] or
[domain.com/ node/58]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/seo-130910071341-phpapp02/85/Points-for-Design-and-Development-of-SEO-friendly-websites-7-320.jpg)