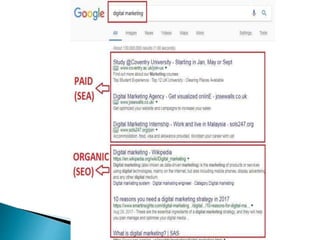
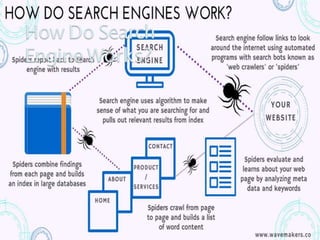
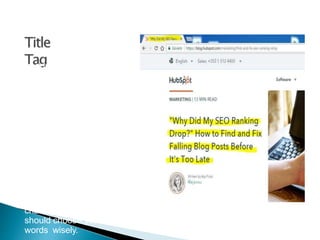
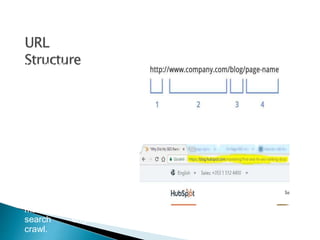
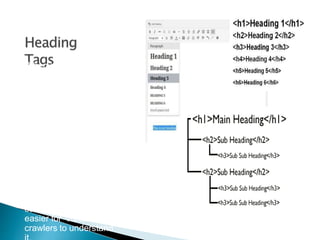
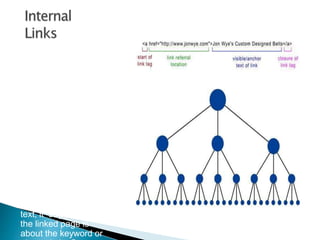
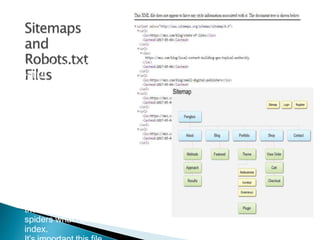
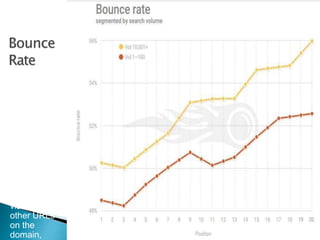
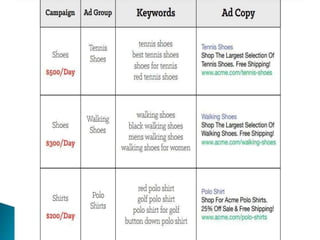
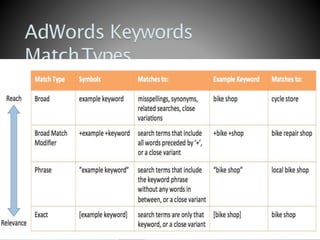
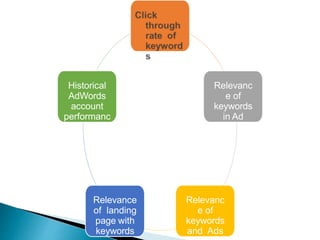
The document discusses search engine optimization (SEO) best practices. It covers how Google finds and ranks websites, on-site optimization factors like content, site structure, and keywords, and off-site factors like links. It also discusses techniques for link building, social media optimization, blogging, mobile SEO, analytics, and paid search advertising. The goal of SEO is to help websites achieve better organic search rankings and traffic.