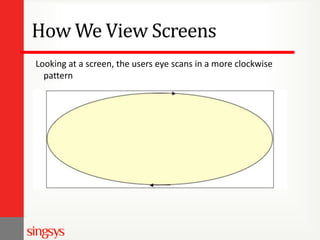
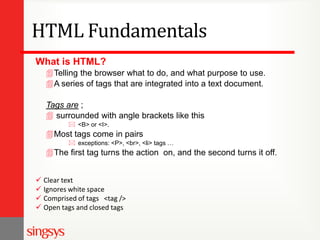
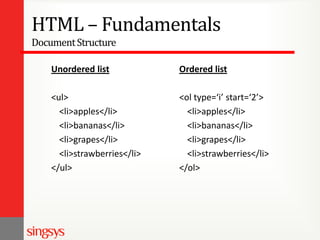
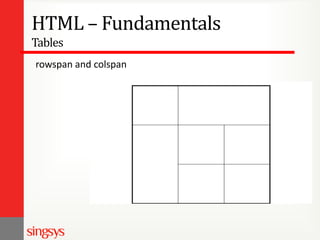
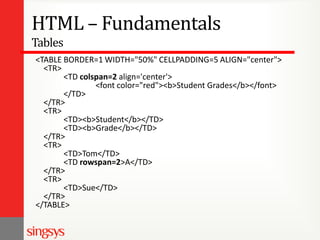
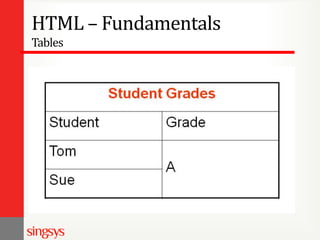
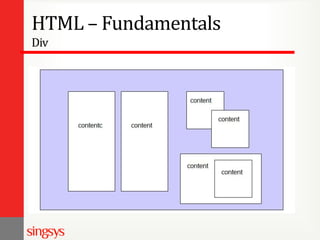
The document provides an overview of basic web design and HTML fundamentals. It defines web design as creating hypertext or hypermedia content delivered through a web browser. It discusses how users read text and view screens, and principles of good web design like having a clear purpose and intuitive navigation. The document also covers HTML tags for headings, lists, links, tables, and divisions (div), as well as attributes and formatting. It emphasizes thinking about the purpose and audience before design and researching other websites for ideas.