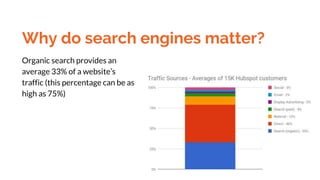
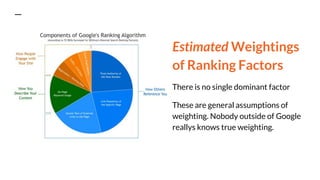
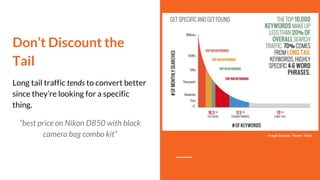
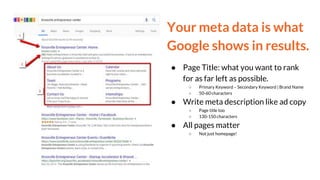
This document provides an overview of search engine optimization (SEO) and inbound marketing. It discusses why SEO matters for businesses, how search engines work, and the various on-page and off-page optimization techniques that can help improve organic search rankings. These include on-page SEO best practices like keyword research, optimizing page titles and content, and off-page factors like link building. Regular audits and measurement of efforts are also recommended to track performance and return on SEO investments. The goal is to understand user intent and provide relevant, high-quality content to both searchers and search engines.