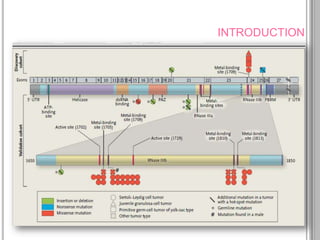
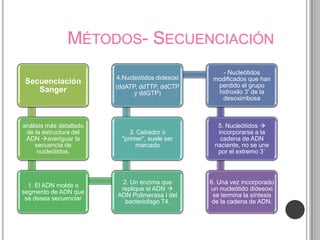
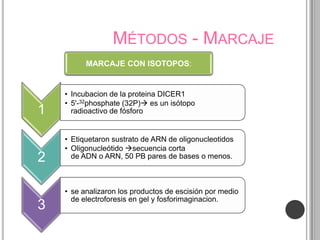
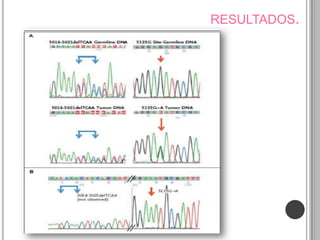
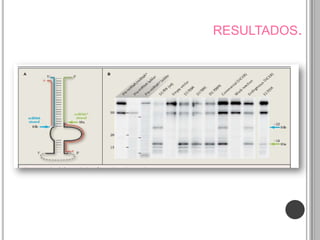
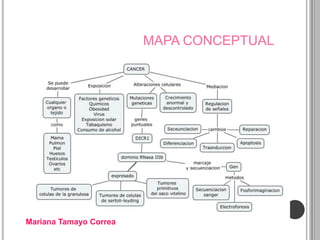
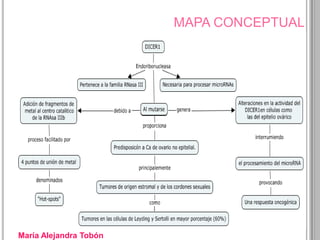
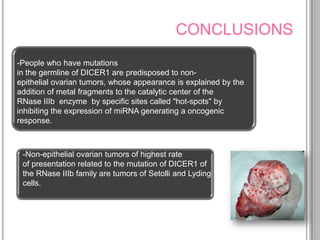
Recurrent somatic DICER1 mutations were found in nonepithelial ovarian cancers. These mutations occurred in codons encoding metal binding sites within the RNase IIIb catalytic centers of DICER1. The mutations were restricted to these sites and did not completely abolish DICER1 function, but instead disrupted microRNA processing in a cell-type specific manner, leading to oncogenesis in certain cell types like ovarian epithelial cells. Validation studies found these DICER1 mutations in a high percentage of additional nonepithelial ovarian tumor samples.