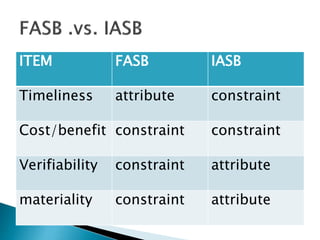
The document discusses the constraints on the relevance and reliability of accounting information, focusing on attributes such as timeliness, cost-benefit analysis, materiality, and verifiability. It highlights the importance of balancing these qualities to ensure that information provided is useful for decision-making while also weighing the costs involved in maintaining reliability. Additionally, it addresses user-specific constraints and the challenges external users face in verifying financial statements.