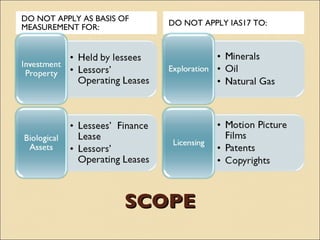
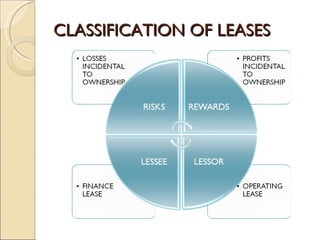
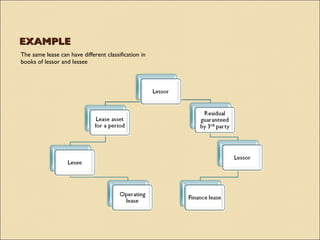
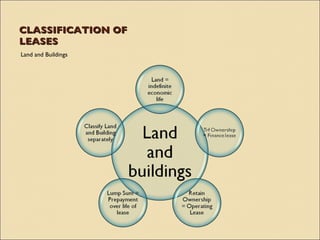
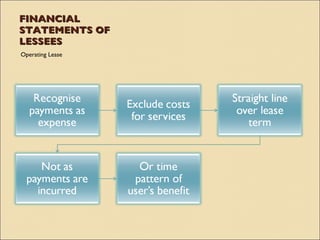
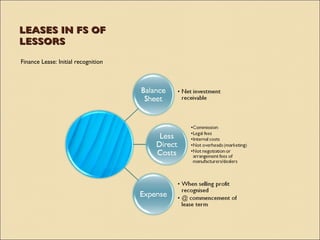
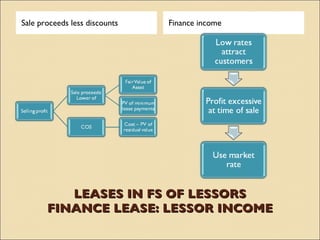
IAS 17 provides guidance on accounting for leases. Key aspects include classifying leases as either finance or operating based on transfer of risks and rewards of ownership. Lessees account for finance and operating leases differently, with finance leases requiring recognition of leased assets and liabilities on the balance sheet. Lessors also account for finance and operating leases differently, with finance leases requiring recognition of a net investment receivable that is amortized over the lease term to achieve a constant rate of return. Sale and leaseback transactions are also addressed.