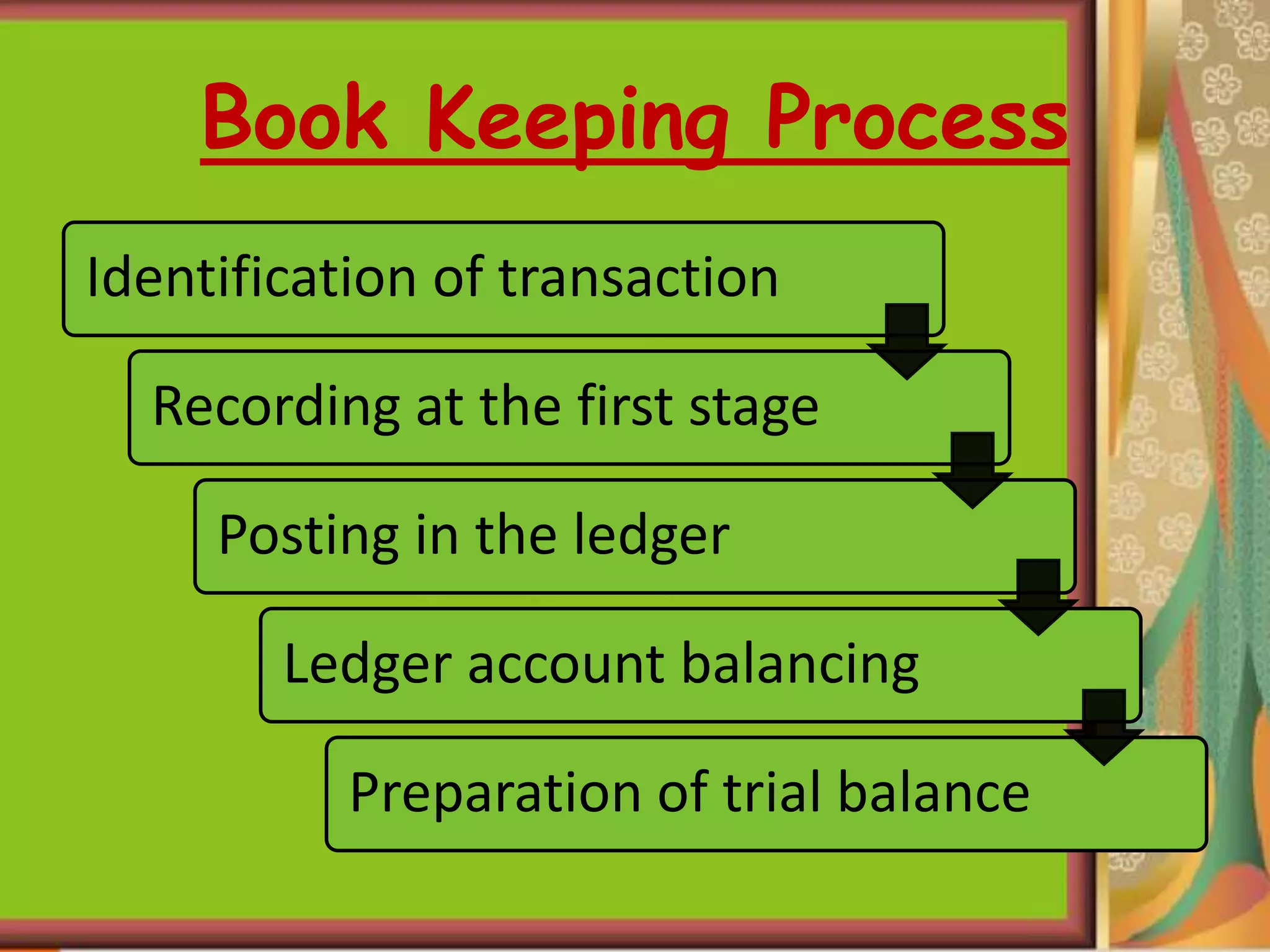
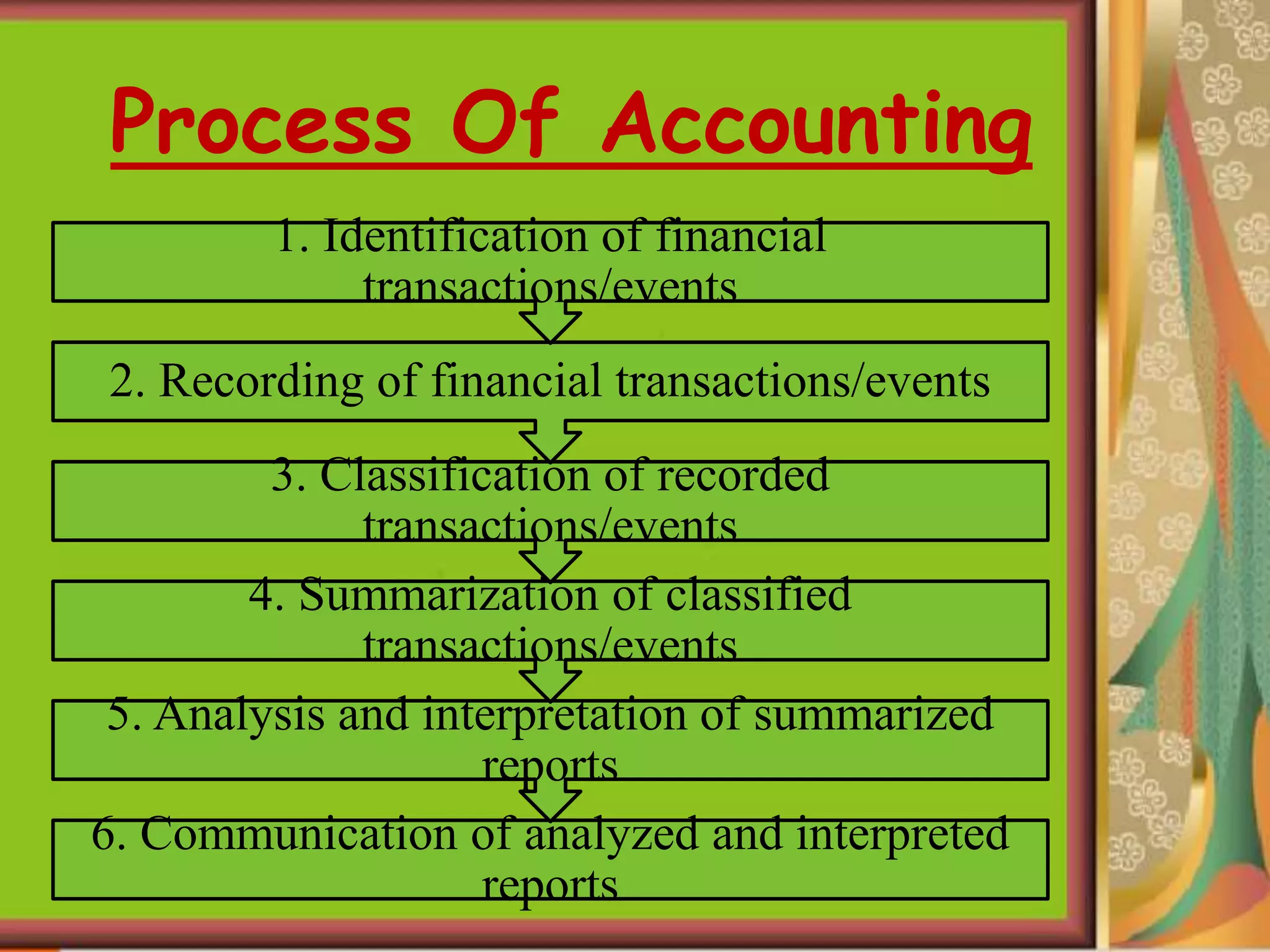
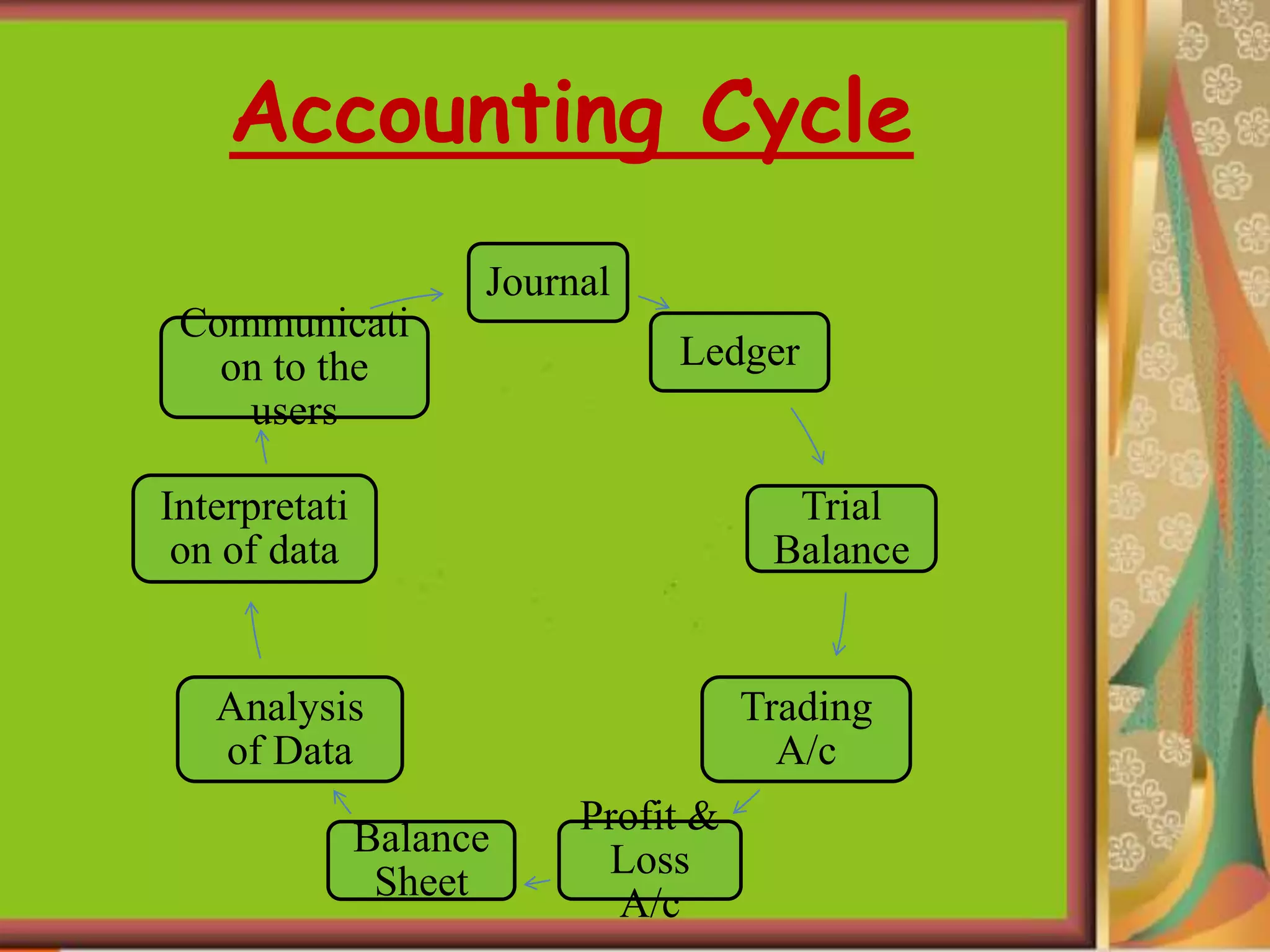
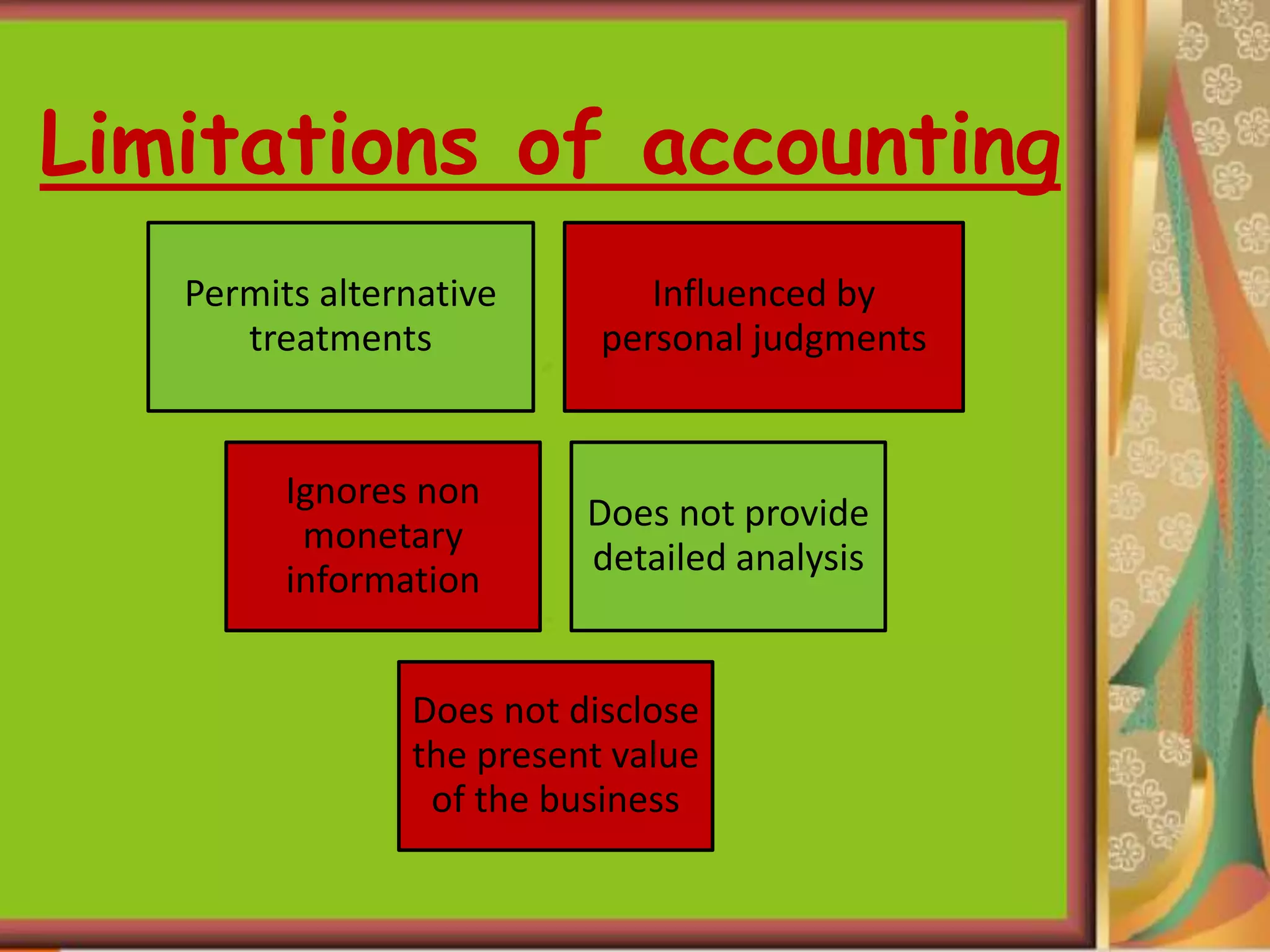
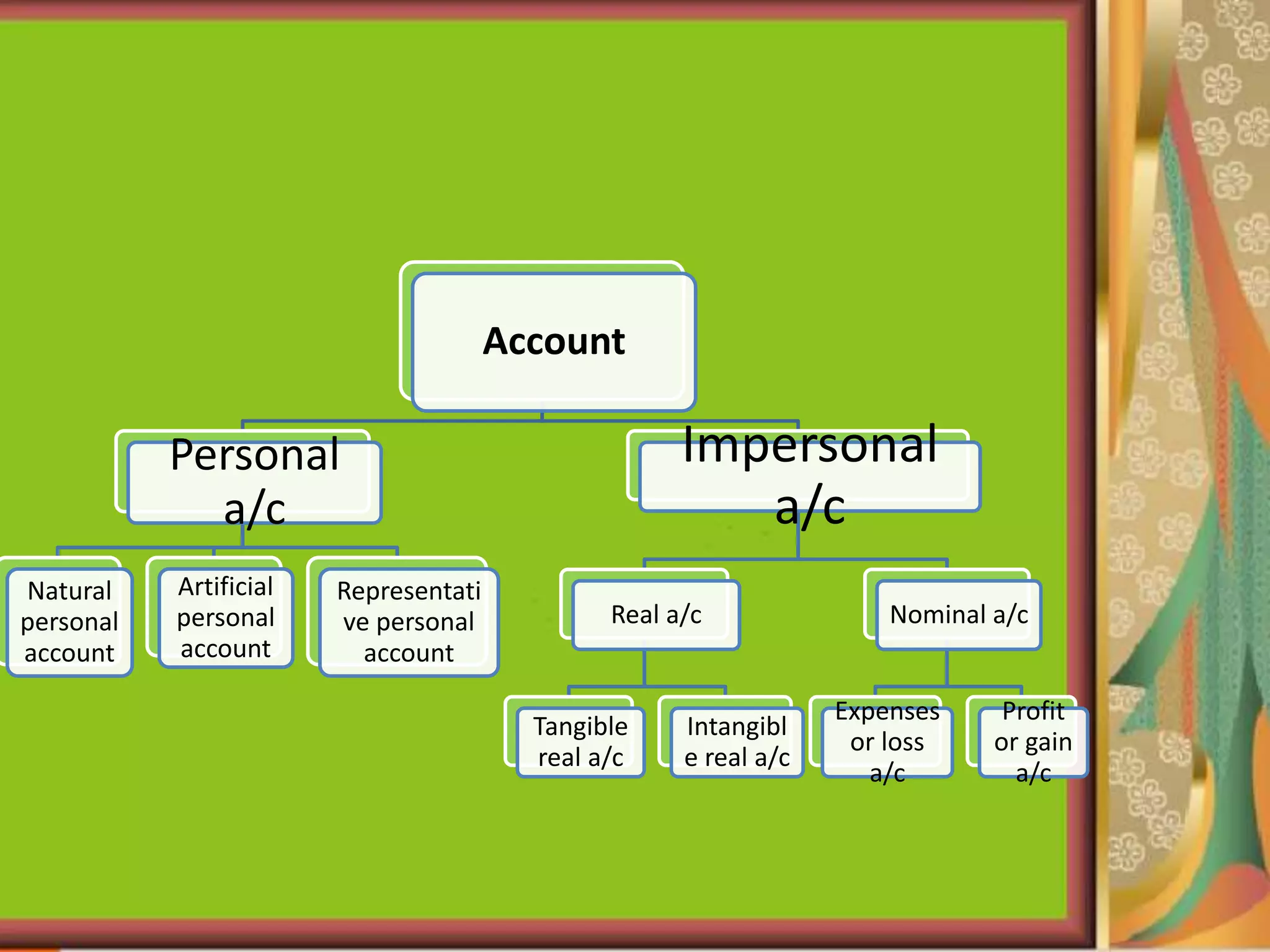
This document provides an introduction to accounting and bookkeeping. It defines accounting as recording, classifying, and summarizing financial transactions and events to determine a business's financial position. Bookkeeping is the fundamental process of accurately recording business transactions, while accounting analyzes and interprets the summarized financial information. The key users of accounting information are internal management as well as external potential investors, creditors, and tax authorities. The objectives and advantages of accounting are maintaining financial records, calculating profits and losses, and providing information to users about a business's performance and financial position.