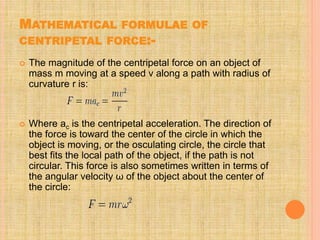
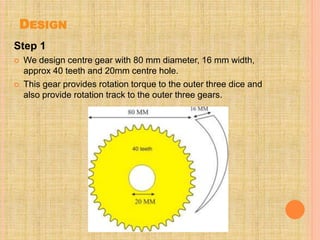
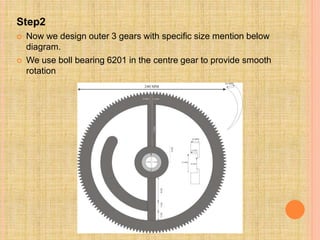
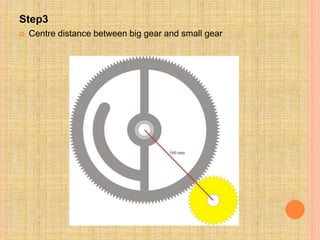
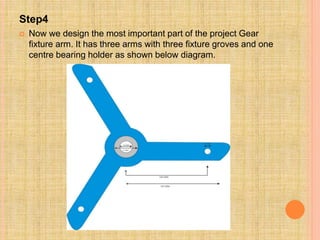
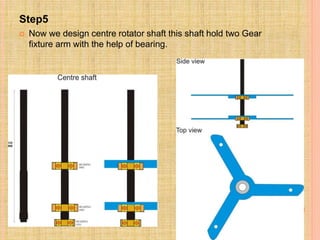
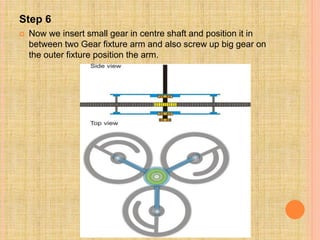
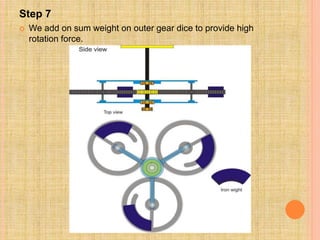
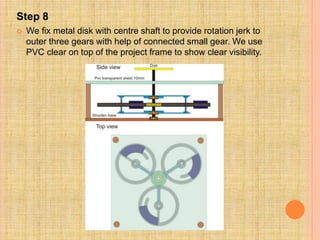
This document describes a semi-perpetual motion machine designed by Harsh Gupta. It works on the principle of centripetal force using a system of gears, shafts and bearings. The central gear provides rotation to three outer gears. Weights are added to the outer gears to provide a high rotational force from a small manual input. While perpetual motion violates thermodynamics, this design aims to generate more power output than input using centrifugal and rotational forces. Potential applications include power generation for irrigation in times of drought.