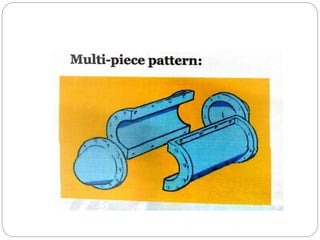
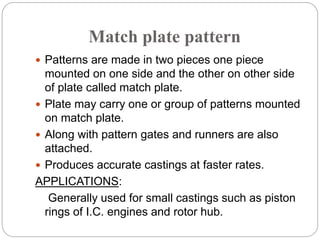
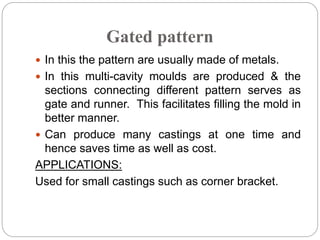
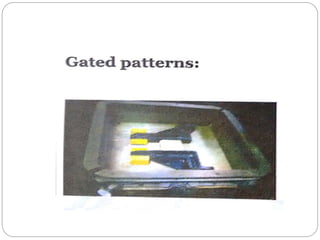
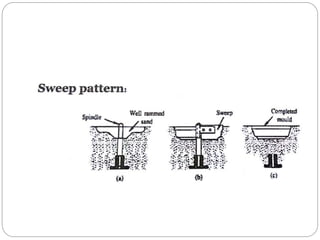
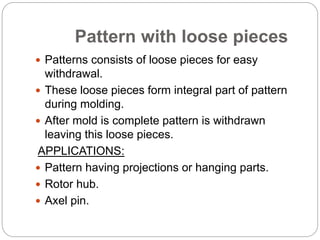
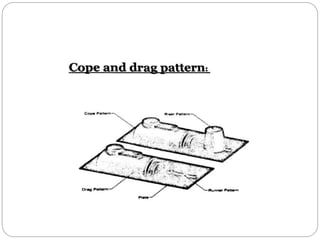
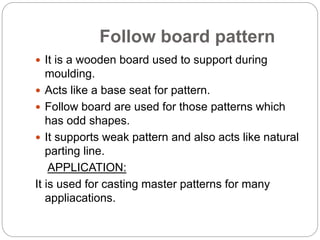
This document discusses different types of patterns used in casting processes and their applications. It defines a pattern as a replica of the component to be manufactured that is used to form a cavity in the mold. There are several types of patterns described, including solid/single piece patterns, split patterns, multi-piece patterns, match plate patterns, gated patterns, skeleton patterns, sweep patterns, patterns with loose pieces, cope and drag patterns, follow board patterns, and segmental patterns. Each type has specific features and is suited for different casting applications.