1. The document discusses electrostatic equilibrium and how excess charge accumulates on the outer surfaces of conductors, especially at points with smaller radii of curvature.
2. It then explains how static electricity builds up in storm clouds and the process of how lightning occurs when the electrical fields become strong enough to ionize the air and allow a discharge between the cloud and the ground.
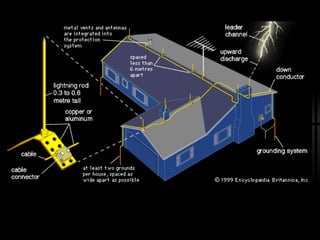
3. Lightning rods are described as providing a path for lightning to safely discharge into the ground and avoid going through buildings.