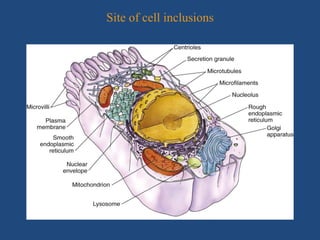
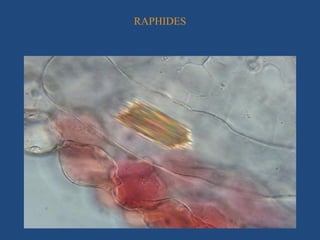
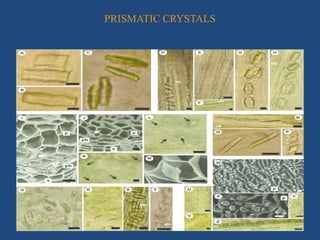
The document discusses plant cell inclusions known as ergastic substances, which are non-living materials that arise from cellular metabolism and are classified into reserve, secretory, and excretory materials. It covers their properties, types, and significance in plant physiology and human welfare, including their roles in food storage, waste disposal, and production of important substances like enzymes and drugs. Overall, ergastic substances are essential for plant health and have substantial benefits for human civilization.