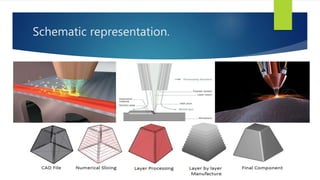
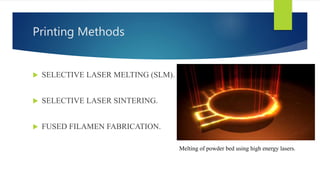
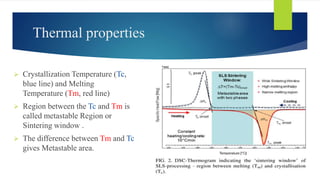
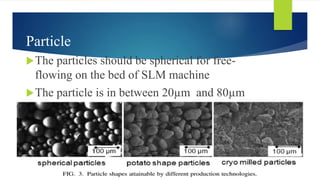
The document is a presentation on Selective Laser Melting (SLM) in additive manufacturing, covering its processes, methods, advantages, and parameters affecting quality. It highlights SLM's ability to create complex metal components layer by layer from CAD models without pre-production costs and with mechanical properties similar to traditional methods. The presentation also discusses applications in various industries, such as biomedical, automotive, and aerospace.